A critical path traversal vulnerability in Fortinet FortiWeb is being actively exploited in the wild, allowing unauthenticated attackers to create administrative accounts on vulnerable devices. Organizations using FortiWeb versions 8.0.1 and earlier must patch immediately and review their systems for signs of compromise.
A critical zero-day vulnerability in Fortinet's FortiWeb web application firewall is being actively exploited by threat actors to create administrative accounts without authentication, creating a significant security risk for organizations worldwide.

The vulnerability, identified as a path traversal issue, affects the following endpoint:
/api/v2.0/cmdb/system/admin%3f/../../../../../cgi-bin/fwbcgi
Threat actors are sending HTTP POST requests to this path with crafted payloads that create local admin-level accounts on targeted devices. Researchers have observed multiple sets of created credentials, including usernames like "Testpoint", "trader1", and "trader", with passwords such as "3eMIXX43", "AFT3$tH4ck", and "AFT3$tH4ckmet0d4yaga!n".
Exploitation Timeline and Global Spread
The exploitation was first detected by threat intelligence company Defused on October 6, 2025, when they reported an "Unknown Fortinet exploit" being used against exposed devices. Since that initial discovery, attacks have increased dramatically, with threat actors now spraying the exploit globally across a wide range of IP addresses.
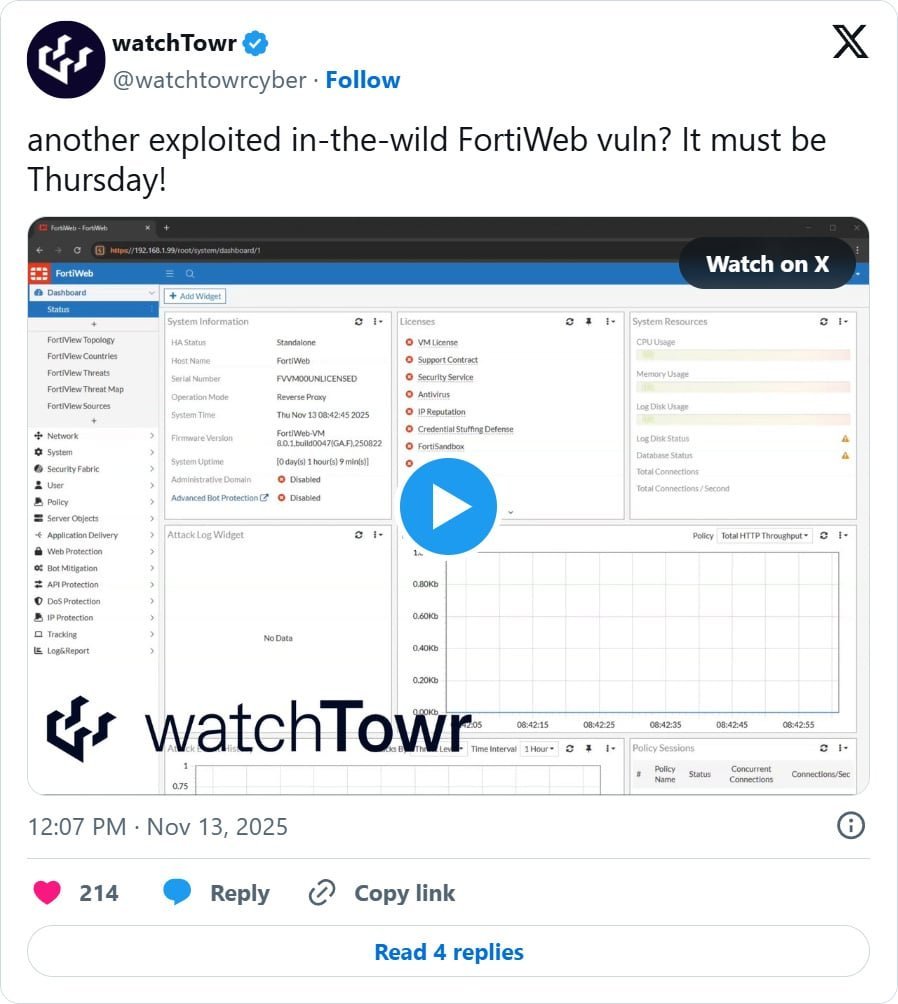
Security researchers at watchTowr Labs have confirmed the exploit, posting a video demonstration showing a failed FortiWeb login attempt, the execution of the exploit, and a subsequent successful login as the newly created admin user.
"This vulnerability represents a critical failure in access controls that could allow attackers to completely compromise security perimeters."
Technical Details and Impact
According to research published by Daniel Card of PwnDefend and Defused, the flaw affects FortiWeb versions 8.0.1 and earlier. The vulnerability was fixed in version 8.0.2, which was released at the end of October 2025. However, Fortinet has not yet published a formal disclosure on their PSIRT site matching the exploited vulnerability.
watchTowr Labs has released a tool called "FortiWeb Authentication Bypass Artifact Generator" to help defenders identify vulnerable devices. The tool attempts to exploit the flaw by creating an admin user with an 8-character random username derived from a UUID.
Rapid7 has tested the exploit across multiple versions, confirming that versions 8.0.1 and earlier are vulnerable to this path traversal attack.
Mitigation Steps for Administrators
Given the active exploitation of this vulnerability in the wild, Fortinet administrators should take immediate action:
- Update immediately: Apply the FortiWeb 8.0.2 patch or later version
- Review accounts: Check for unusual administrative accounts that may have been created
- Examine logs: Look for requests to the
fwbcgipath in access logs - Investigate traffic: Monitor activity from the identified suspicious IP ranges:
- 107.152.41.19
- 144.31.1.63
- 185.192.70.0/24
- 64.95.13.8
- Network segmentation: Ensure management interfaces are not reachable from the internet and are restricted to trusted networks or VPN-only access
Broader Security Implications
This active exploitation highlights the increasing sophistication of attacks targeting network security appliances. When devices designed to protect applications become vulnerable themselves, they can create significant blind spots in an organization's defense strategy.
The widespread nature of this exploitation, with attacks originating from diverse IP addresses, suggests a coordinated campaign rather than isolated incidents. This pattern indicates that threat actors are actively scanning the internet for vulnerable FortiWeb instances and exploiting them at scale.
As organizations continue to rely on security appliances as part of their defense-in-depth strategy, the importance of timely patching and proper network segmentation becomes even more critical. This incident serves as a reminder that security perimeters are only as strong as their weakest link, and that unpatched management interfaces can provide attackers with a direct path to compromise entire networks.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion