Roblox introduces OpenGameEval, an open-source evaluation framework and benchmark specifically designed to assess AI assistants in game development workflows. Unlike traditional coding benchmarks, it measures contextual reasoning in stateful 3D environments, revealing critical gaps in current models' capabilities.
Evaluating AI assistants in game development presents unique challenges. While coding benchmarks traditionally focus on isolated programming tasks, Roblox Studio workflows demand understanding of 3D hierarchies, multiplayer interactions, and persistent world states. This gap prompted Roblox engineers to develop OpenGameEval—a native evaluation framework and benchmark that simulates real development environments to properly assess AI assistants.
Why Standard Benchmarks Fall Short
"Creators leverage Roblox Studio’s AI Assistant to accelerate development, but evaluating performance on interactive development tasks remains a challenge," explain Roblox engineers Tiantian Zhang, Kartik Ayyar, Mengsha Sun, and Lynn Gong. Traditional benchmarks can't capture the multistep reasoning required when modifying live game states or coordinating client-server interactions—core aspects of Roblox development.
Inside OpenGameEval's Architecture
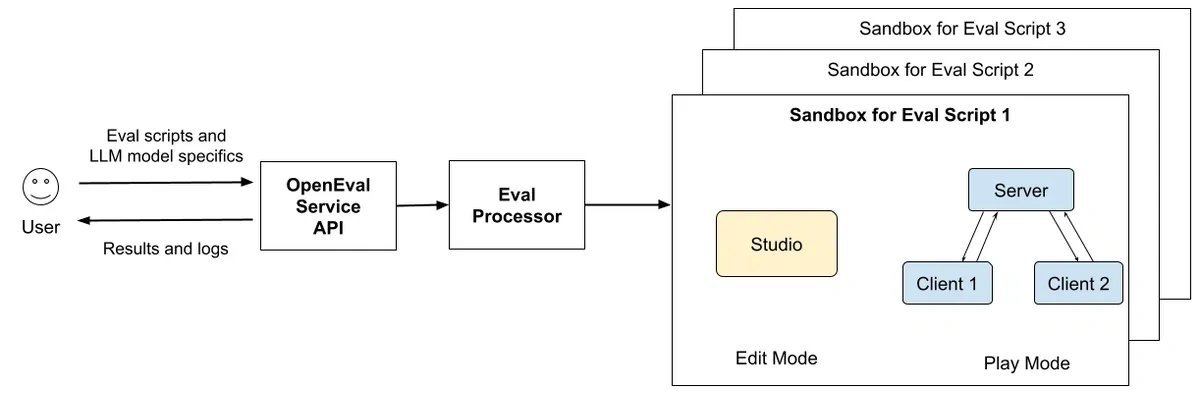
The framework replicates Roblox Studio's edit/play environment, simulating physics, networking, and multiplayer behavior. Its input system programmatically mimics player actions like button clicks and camera manipulation. Crucially, it exposes these capabilities through a unified API, letting researchers benchmark diverse LLM-based agents without environment modifications.
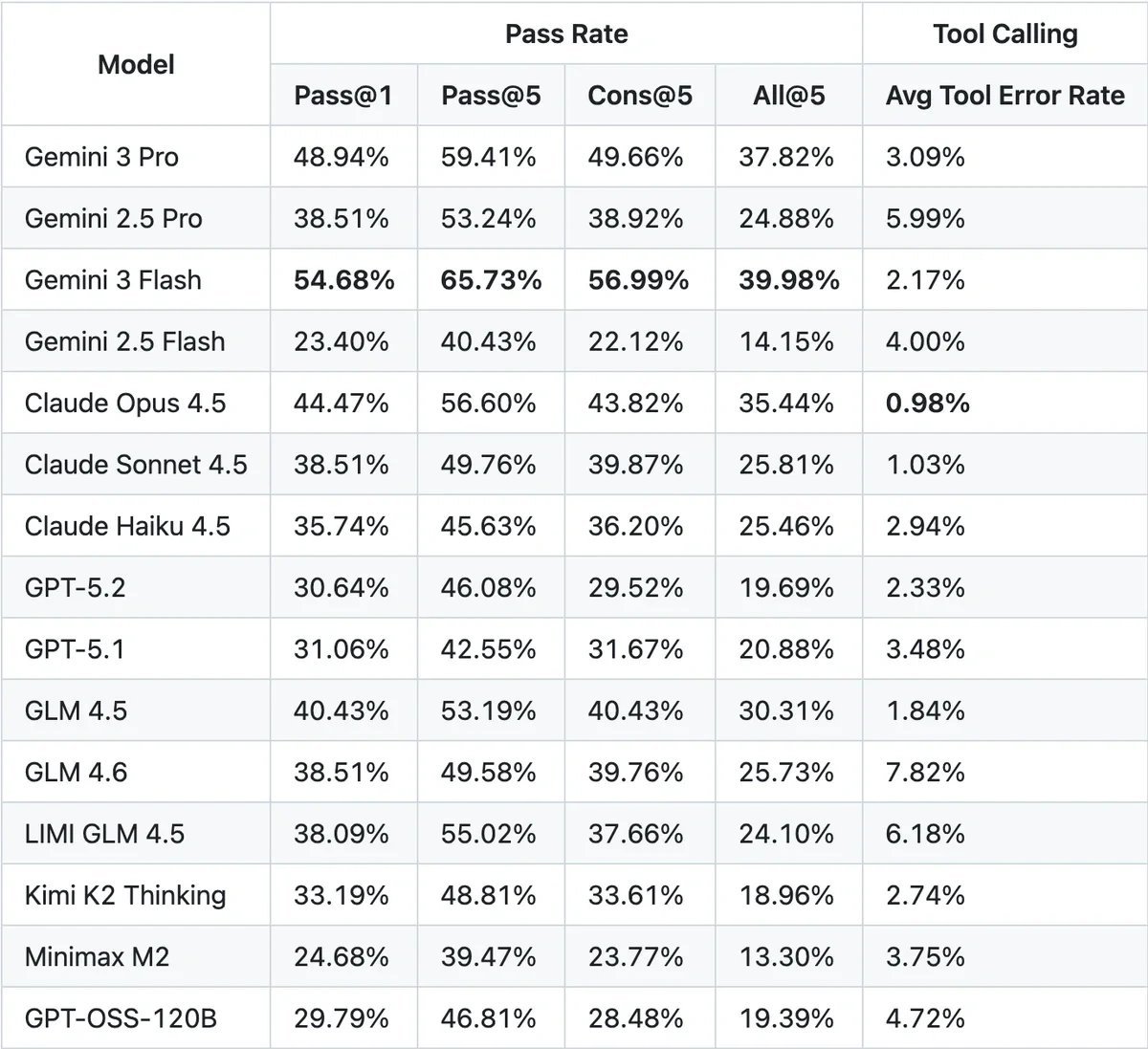 OpenGameEval's leaderboard tracks model effectiveness for Roblox development tasks
OpenGameEval's leaderboard tracks model effectiveness for Roblox development tasks
The accompanying benchmark dataset features 47 rigorously curated test cases across domains like game mechanics, animation, and UI design. Each scenario undergoes human verification for comprehensiveness and stability. Scoring uses industry-standard metrics (pass@k, cons@k, all@k) to quantify performance on executable unit tests.
Testing Contextual Intelligence
Unlike function-level coding challenges, OpenGameEval demands end-to-end mastery:
- Navigating 3D instance hierarchies
- Analyzing object states
- Inferring user intent from environmental context
Consider a health regeneration task: An AI must implement a system that activates 2 seconds post-damage and heals 10 HP/second. Success requires:
-- Pseudo-code for expected logic
local function onDamageTaken(player)
debounceRegen(player)
wait(2)
startRegeneration(player, 10)
end
The test validates server-client synchronization, delay accuracy, and regeneration rate—all within a sandboxed game instance.
The Context Variation Challenge
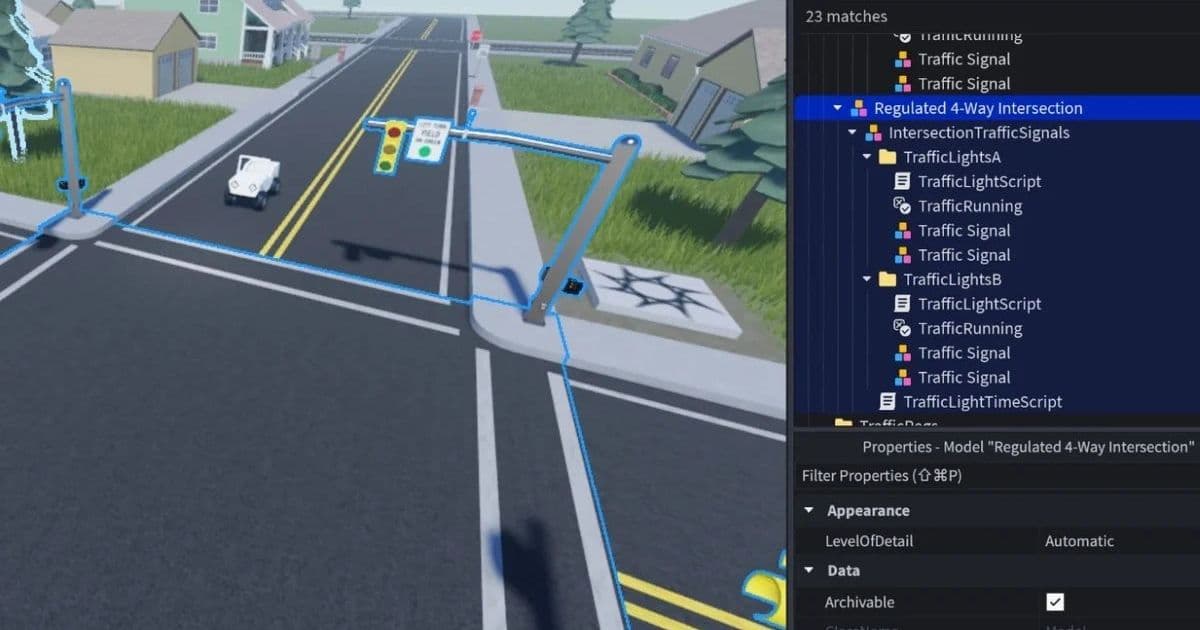
Roblox highlights how identical tasks demand different solutions based on environmental context. Their traffic light scripting example includes three variations:
- Baseplate Environment: Empty scene with single traffic light model
- Suburban Setup: Multiple traffic lights among complex assets
- Mixed Signals: Traffic lights alongside functional pedestrian signals
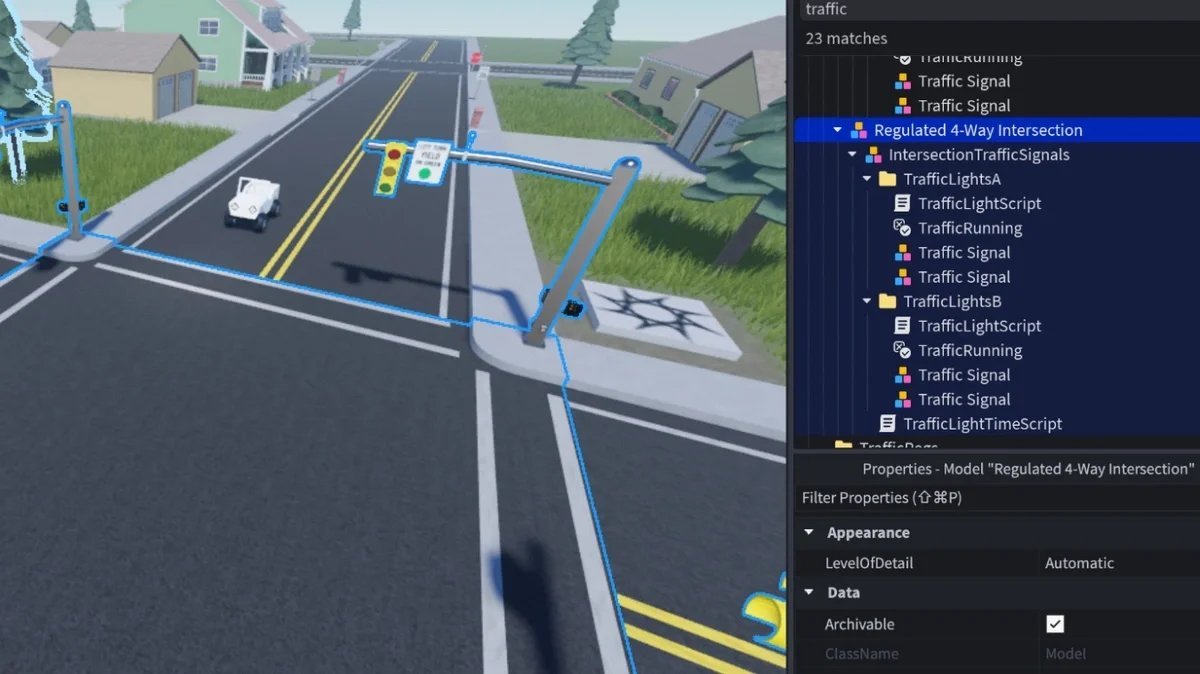
 Traffic light in minimal baseplate environment
Traffic light in minimal baseplate environment
 Traffic light in asset-rich suburban environment
Traffic light in asset-rich suburban environment
Models must adapt solutions to each context—identifying correct objects despite naming inconsistencies or structural differences.
Early Findings: Atomic Skills vs. Contextual Reasoning
Initial results reveal stark contrasts:
- Atomic Operations: Near-perfect success in direct tasks (e.g., modifying jump power)
- Contextual Reasoning: Severe struggles in coordinated tasks like health systems or traffic lights
Yet rapid evolution is evident. Where models once universally failed to locate a "Roblox logo" cube (due to absent keyword matches), newer versions succeed via structural reasoning—inspecting properties rather than relying solely on names.
Future Directions
Roblox plans to:
- Expand transparency through regular leaderboard updates
- Broaden API support for frictionless benchmarking
- Incorporate community-driven scenarios
This initiative creates a much-needed testing ground for agentic AI—pushing beyond syntax generation toward genuine contextual problem solving in immersive creation environments. As gaming and metaverse platforms evolve, such frameworks will become essential for measuring true assistant capability.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion