Veracode's 2025 study of 100+ AI models reveals nearly half of generated code contains critical vulnerabilities, with Java samples failing security tests at 72%. Despite advances in functionality, security performance remains stagnant across model generations. The findings expose hidden risks in AI-assisted development pipelines.
AI Code Generation's Dirty Secret: 45% of Output Fails Security Tests

Analysis of 100+ AI models reveals systemic security gaps in generated code, with Java vulnerabilities hitting 72%
When developers prompt AI assistants to generate code, they expect efficiency—not hidden vulnerabilities. Yet Veracode's comprehensive 2025 GenAI Code Security Report delivers a sobering reality check: 45% of AI-generated code samples contained OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities across Java, Python, C#, and JavaScript. The study tested over 100 large language models, revealing that functional correctness doesn't equate to security.
The Vulnerability Breakdown
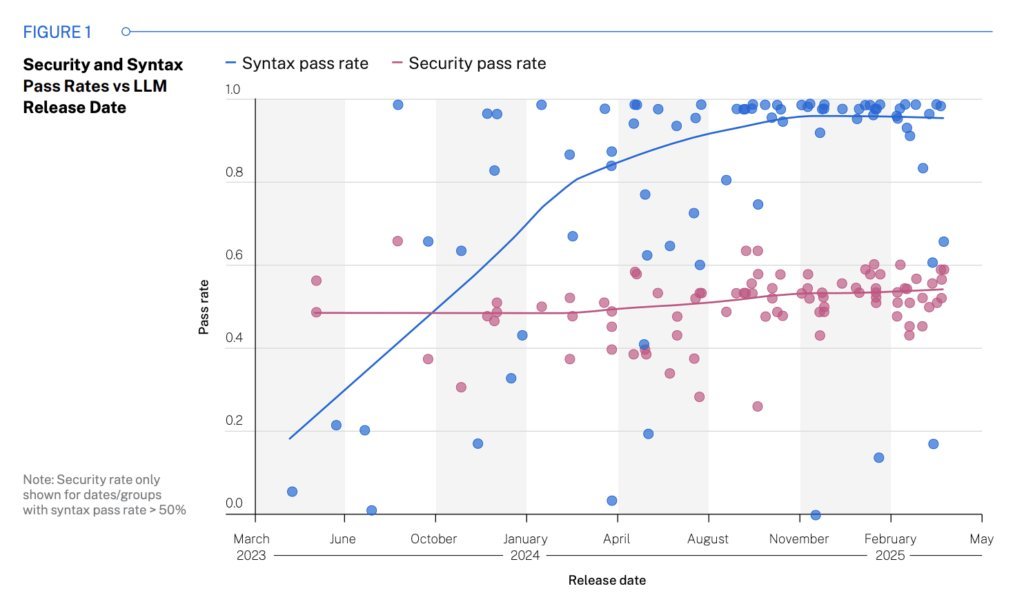 Figure 1: Security vs. syntax pass rates show stagnant security performance despite model advancements (Source: Veracode)
Figure 1: Security vs. syntax pass rates show stagnant security performance despite model advancements (Source: Veracode)
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) emerged as the most prevalent flaw, with AI tools failing to prevent it in 86% of relevant cases. Language-specific risks varied dramatically:
- Java: 72% security failure rate
- C#: 45%
- JavaScript: 43%
- Python: 38%
"These weren't edge-case vulnerabilities," notes the report. "They were fundamental security failures in common scenarios."
The Model Maturity Myth
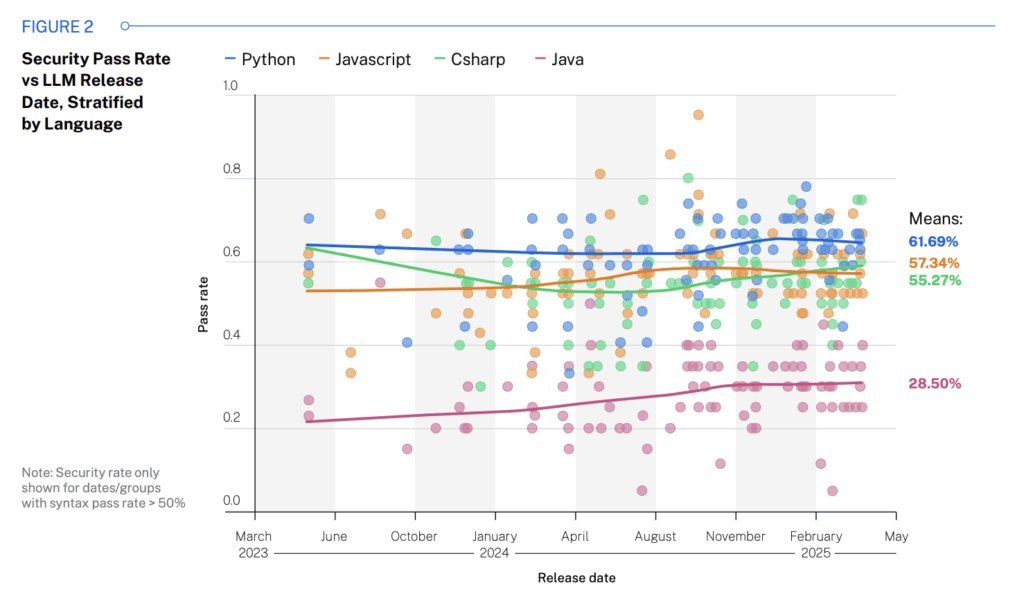 Figure 2: Security pass rates show no improvement across language-specific model generations (Source: Veracode)
Figure 2: Security pass rates show no improvement across language-specific model generations (Source: Veracode)
Contrary to expectations, newer and larger models showed negligible security improvements despite better syntax accuracy. Security performance plateaued regardless of:
- Model size parameters
- Training data sophistication
- Release timeline
"Security isn't a natural byproduct of scale. Without explicit security training, models repeat the same mistakes," the report concludes.
The Silent Supply Chain Threat
Vulnerable AI code isn't limited to direct usage. It's proliferating through:
- Open-source dependencies
- Third-party vendor tools
- Low-code/no-code platforms
- Outsourced development
This creates invisible supply chain risks where organizations deploy vulnerable code without awareness. The consequences: data breaches, compliance violations, and remediation costs multiplying across software ecosystems.
Mitigation Strategies
- Scan All Generated Code: Treat AI output like human code with SAST/SCA scans
- Implement Guardrails: Require security validation before AI code merges
- Targeted Training: Educate developers on AI-specific vulnerabilities (e.g., prompt injection risks)
"Speed without security is technical debt waiting to explode," warns the report. As AI code generation becomes ubiquitous, these findings underscore the urgent need for security-first AI development practices.
Source: 2025 GenAI Code Security Report by Jens Wessling, Veracode CTO
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion