Discover why traditional text-to-SQL approaches fail for real business analytics and how semantic layers, multi-agent systems, and instruction-tuned retrieval transform raw data into actionable insights. Learn battle-tested patterns from Findly's journey building an AI analyst that handles complex workflows.
For years, text-to-SQL promised to democratize data access by translating natural language into database queries. Yet in production, teams at companies like Findly discovered a harsh truth: real business questions rarely map to single SQL statements. Questions like "Compare these cohorts over the last four releases and explain the variance" or "Create a trading strategy" demand multi-step workflows combining data retrieval, transformation, validation, and narrative explanation—far beyond what vanilla text-to-SQL delivers.
Why Text-to-SQL Alone Fails
Real-world analytics requires orchestration:
- Planning: Decomposing problems into steps
- Execution: Targeted SQL + Python for transformations
- Validation: Sanity checks and data quality guards
- Narrative: Explaining results with drill-down paths
Without this scaffolding, systems generate brittle queries that crumble on ambiguous joins, complex logic, or missing context. The solution? Treat text-to-SQL as one tool in an AI analyst’s toolbox—not the entire product.
The Semantic Layer: Your Business Logic Compiler
Findly’s breakthrough came from encoding business meaning explicitly via a semantic layer. Using Malloy—an open-source modeling language—they defined:
- Dimensions (e.g.,
region,order_date) - Measures (e.g.,
total_revenue is sum(price * quantity)) - Relationships (e.g.,
orders→customers) - Metadata (descriptions, units, constraints)
# Malloy model snippet
source: orders extend {
measure: total_revenue is sum(price * quantity)
dimension: order_date is cast(order_timestamp as date)
join_one: customers with customer_id
}
This acts as a "business logic compiler" that:
- Shrinks hallucination risk by restricting LLMs to validated concepts
- Enables pre-execution checks (e.g., catching invalid field references)
- Grounds code generation in single-source-of-truth definitions
Multi-Agent Workflows: The Orchestration Engine
Complex questions trigger a squad of specialized AI agents:
- Planner: Breaks down the problem
- Retriever: Fetches context via precision RAG
- Coder: Generates SQL/Python
- Validator: Runs sanity tests
- Narrator: Explains results
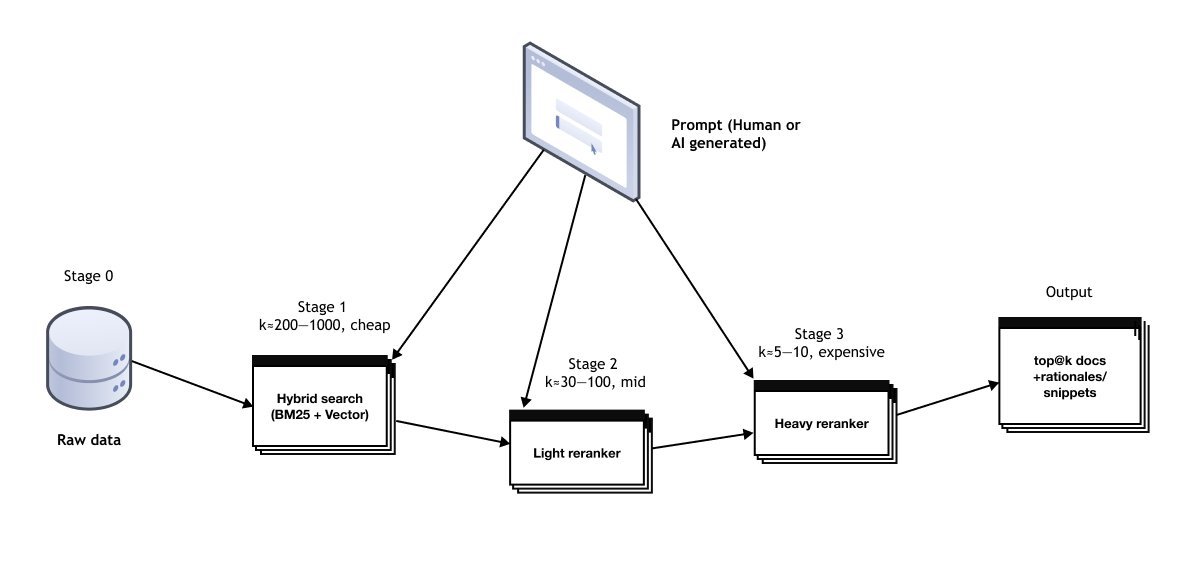
Multi-agent planning isolates failures and maintains accountability across steps.
Retrieval: Recommendation Systems for LLMs
Treating retrieval as a recommendation pipeline was pivotal. Findly uses:
- Keyword search: For exact acronyms/terms
- Embeddings: For semantic matches
- Fine-tuned rerankers: Instruction-optimized models (e.g., Voyage AI’s rerank-2.5) that boost relevance by 8%+
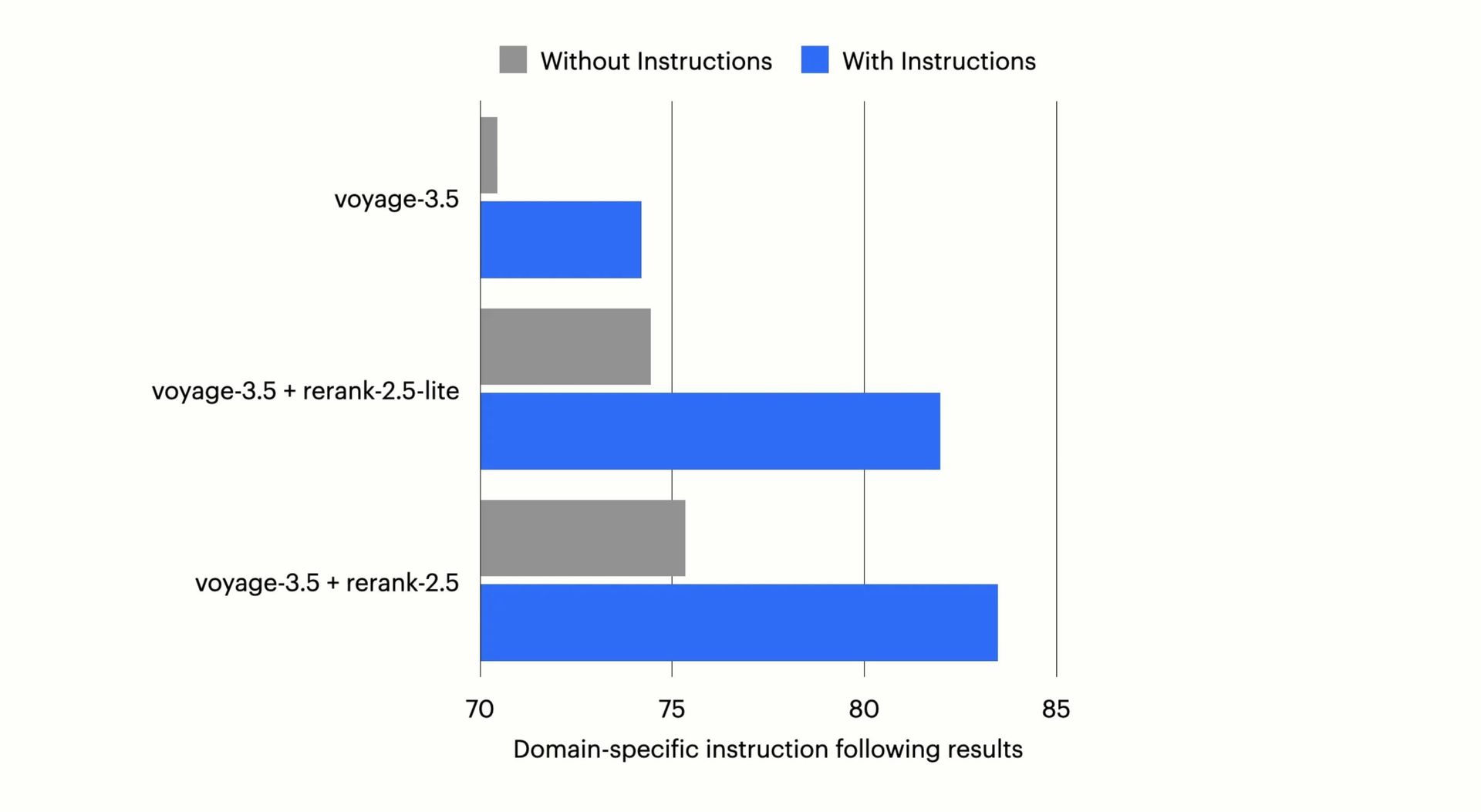
Instruction-following rerankers understand task-specific context like "filter to Q3 metrics"—critical for precision.
Python’s Strategic Role
SQL alone can’t handle:
- Statistical tests
- Time-series transforms
- Custom calculations
Sandboxed Python execution enables:
# Example: Currency conversion using semantic layer tags
df['revenue_eur'] = df['total_revenue_usd'] * get_exchange_rate('USD','EUR')
By composing pre-built functions (e.g., convert_currency()), LLMs generate concise, maintainable code.
Failure Modes & Fixes
Key production lessons:
- Ambiguous joins? Enforce grain/joins in semantic layer
- Slow responses? Route simple queries to faster models (e.g., o4-mini), complex ones to Gemini 2.5 Pro
- Silent errors? Add validation hooks and citation requirements
The Road to Adaptive Analytics
The future lies in systems that:
- Dynamically switch between fast/reasoning LLMs
- Autonomously critique and refine outputs
- Continuously harvest business logic from user interactions
As Pedro Nascimento notes: "Context isn’t just data—it’s the product." By architectural design, not prompt engineering, AI analysts move from demos to daily drivers.
Source: Lessons on building an AI data analyst by Pedro Nascimento (ex-Google/Twitter ML lead, Findly co-founder).
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion