OpenAI and Cerebras unveil GPT-5.3-Codex-Spark, a coding assistant running at 1,000 tokens per second on wafer-scale chips, delivering 4.8x faster inference than standard models.
OpenAI has unveiled GPT-5.3-Codex-Spark, a research preview coding assistant that achieves unprecedented inference speeds of 1,000 tokens per second when running on Cerebras' wafer-scale chips. This marks the first public collaboration between the two AI giants and represents a significant leap in coding assistant performance.
Side-by-Side Performance Comparison
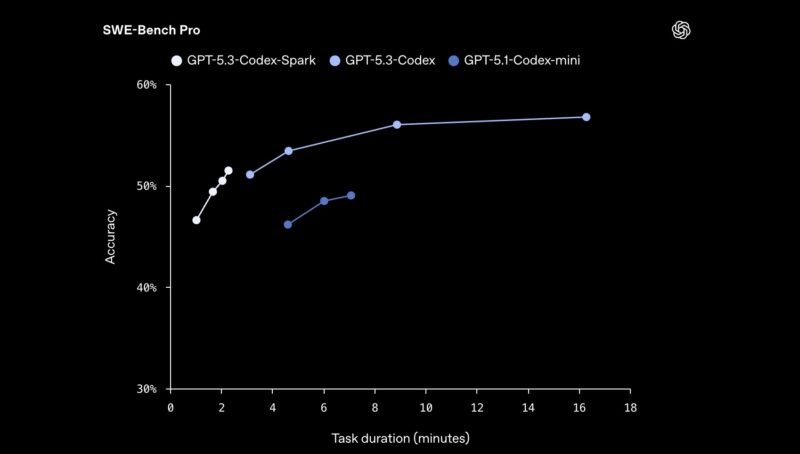
In a demonstration that highlights the stark performance difference, OpenAI showed GPT-5.3-Codex-Spark completing a "build a snake game" task in just 9 seconds. The same task on the standard GPT-5.3-Codex model at medium quality took nearly 43 seconds. That's a 4.8x speedup for the Spark variant.
The Cerebras Wafer-Scale Engine Advantage
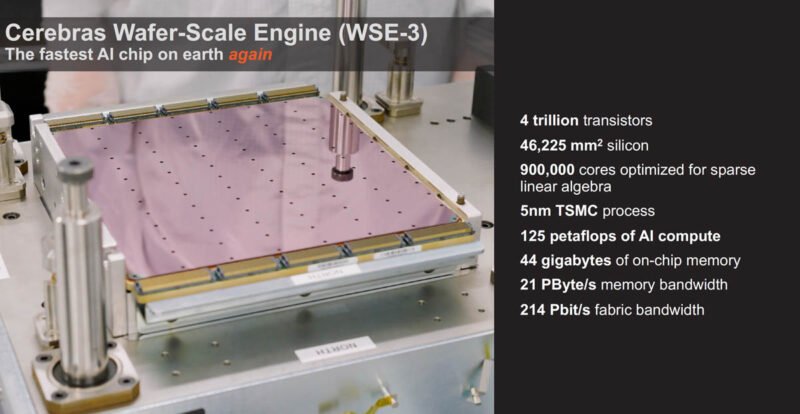
The breakthrough comes from running these models on the Cerebras Wafer-Scale Engine 3 (WSE-3), a monolithic chip that spans an entire silicon wafer. Unlike traditional AI accelerators that cut wafers into dozens or hundreds of smaller chips, Cerebras keeps the wafer intact and solves the engineering challenges of powering and cooling this massive single chip.
Technical Architecture
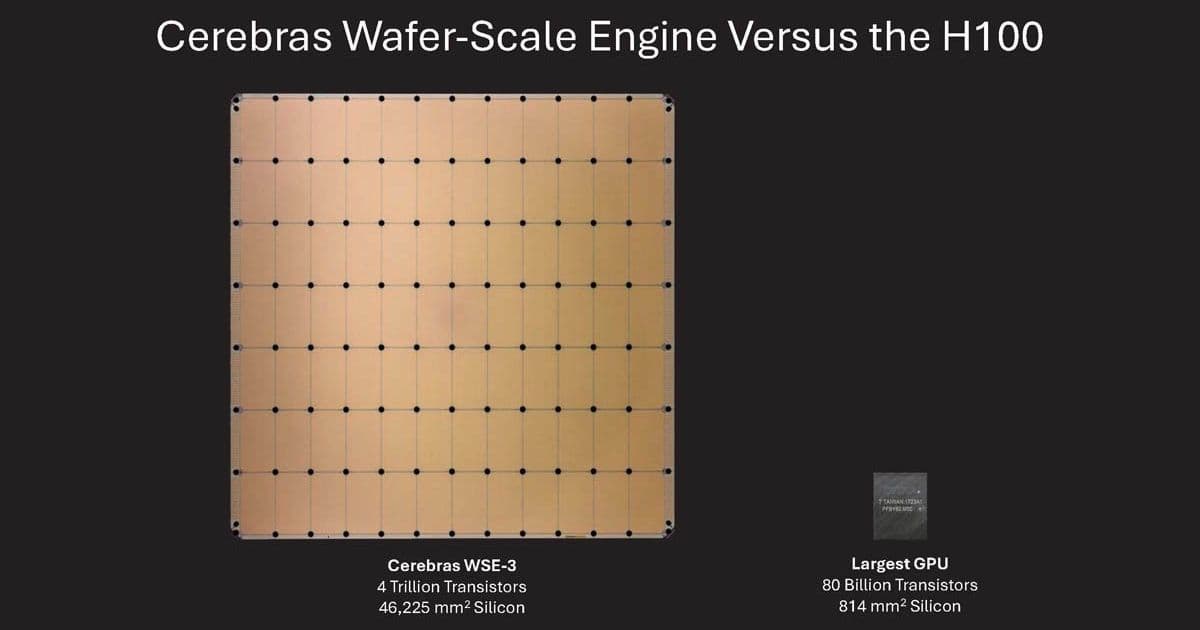
The WSE-3 contains 4 trillion transistors across 900,000 AI cores, with 44GB of on-chip SRAM. This massive memory bandwidth eliminates the need for external memory systems that typically bottleneck inference performance. The chip's architecture is specifically optimized for large language model inference, with each core capable of handling multiple simultaneous threads.
Why Speed Matters for Coding Assistants
For coding workflows, inference speed directly translates to productivity. When developers use AI coding assistants, they're often in a flow state, iteratively refining code. Waiting 43 seconds versus 9 seconds for each code generation cycle fundamentally changes the development experience.
This becomes even more critical for agentic AI systems that chain together multiple reasoning steps. Faster individual inferences mean entire workflows complete more quickly, enabling real-time code generation and debugging.
Quality Improvements Beyond Speed
OpenAI claims the Spark model isn't just faster—it's also higher quality than the previous GPT-5.1-Codex. The combination of the WSE-3's architecture and model optimizations results in both improved accuracy and reduced latency.
Industry Implications
The partnership between OpenAI and Cerebras signals a maturing AI hardware ecosystem where specialized chip architectures are becoming essential for pushing the boundaries of what's possible. While NVIDIA dominates the training market, Cerebras is carving out a niche in ultra-fast inference for specific use cases.
For developers using workflow automation tools like n8n or OpenClaw, this speed improvement means AI agents can complete complex tasks in seconds rather than minutes. The "build a snake game" example—going from concept to working browser game in 9 seconds—demonstrates how quickly ideas can become reality with this technology.
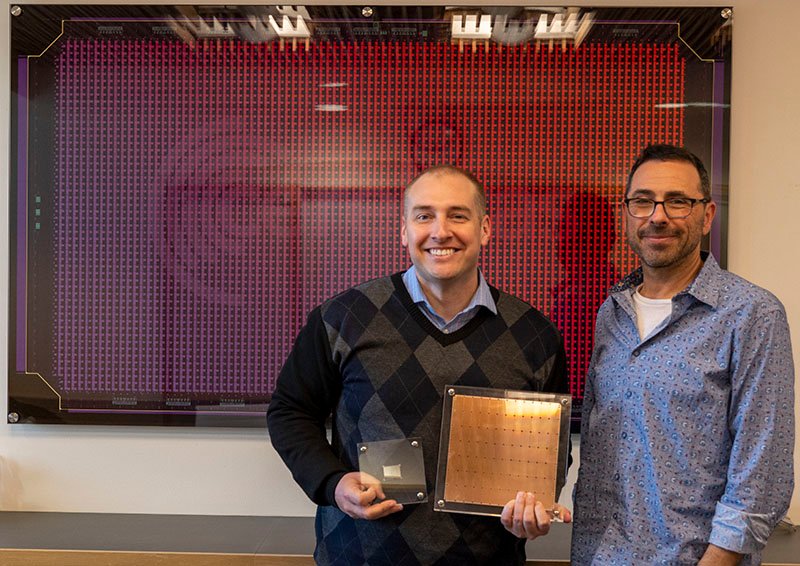

Looking Forward
The success of GPT-5.3-Codex-Spark on Cerebras hardware suggests we'll see more specialized AI hardware partnerships in the future. As models grow larger and inference demands increase, the performance gap between general-purpose GPUs and purpose-built AI accelerators will likely widen.
For now, developers lucky enough to access this research preview will experience coding assistance at speeds that were science fiction just a few years ago. The question isn't whether this technology will become mainstream, but how quickly the rest of the industry can catch up to 1,000 tokens per second.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion