A cybercrime group has compromised university HR systems across the U.S., redirecting payroll payments through meticulously crafted phishing campaigns that exploit weak authentication. Microsoft reveals how Storm-2657 evaded detection by deleting security alerts and enrolling attacker-controlled MFA devices.
The 'Payroll Pirate' Plunder: Inside the University HR Heist

Microsoft Threat Intelligence has exposed an ongoing cybercrime campaign targeting higher education institutions, where attackers dubbed Storm-2657 have successfully hijacked payroll systems at three U.S. universities since March 2025. By compromising Workday accounts through sophisticated social engineering, the threat actors redirected faculty salaries to attacker-controlled accounts while systematically evading detection.
Anatomy of an Academic Heist
The operation begins with hyper-targeted phishing emails tailored to academic environments, including fabricated alerts about campus illness outbreaks, faculty misconduct reports, and even messages impersonating university presidents. These lures contain adversary-in-the-middle (AITM) links designed to intercept multi-factor authentication (MFA) credentials.
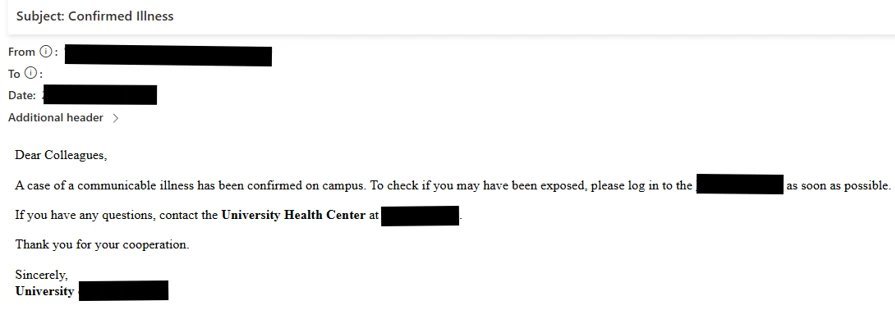 Sample phishing email used in attacks (Microsoft)
Sample phishing email used in attacks (Microsoft)
Once inside victims' Exchange Online accounts, attackers deploy a calculated evasion strategy:
- Inbox rule sabotage: Automatic deletion of Workday security notifications
- Payroll diversion: Modification of direct deposit information in HR systems
- Persistence mechanisms: Enrollment of attacker-owned devices in Duo MFA or Workday profiles
- Attack proliferation: Use of compromised accounts to launch new phishing waves across 25 universities
Why Traditional MFA Failed
Microsoft emphasizes this isn't a Workday vulnerability but an exploitation of authentication gaps:
"These attacks... represent threat actors taking advantage of the complete lack of multifactor authentication (MFA) or lack of phishing-resistant MFA to compromise accounts."
The attackers specifically targeted institutions without FIDO2 security keys or Windows Hello for Business implementations—proving that conventional SMS or push-notification MFA can be bypassed with AITM techniques.
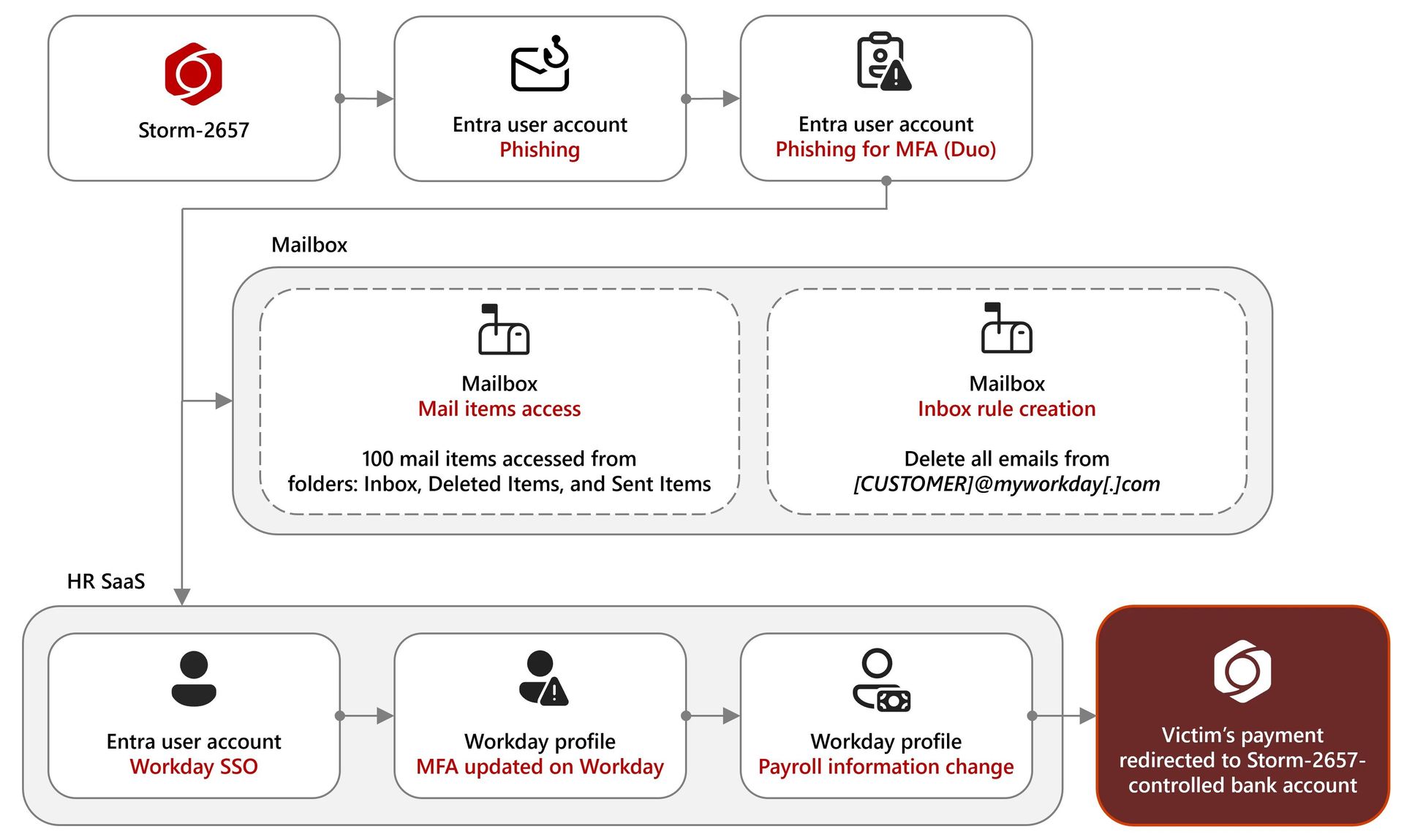 Attack workflow showing payment diversion (Microsoft)
Attack workflow showing payment diversion (Microsoft)
The $2.7 Billion Context
This "payroll pirate" strategy is a sophisticated evolution of Business Email Compromise (BEC) scams, which the FBI reports caused $2.7 billion in losses in 2024 alone. The academic targeting reveals new trends:
- Third-party SaaS platforms as attack vectors
- Internal-to-internal phishing for lateral movement
- Payment fraud automation through compromised HR systems
Mitigation Imperatives
Microsoft recommends immediate actions for organizations:
1. Implement phishing-resistant MFA (FIDO2/Windows Hello)
2. Audit inbox rules for suspicious activity patterns
3. Monitor HR systems for payment detail changes
4. Restrict MFA enrollment to trusted endpoints
The Storm-2657 campaign demonstrates that payroll systems have become critical infrastructure—and that securing them requires moving beyond authentication theater to verifiable, phishing-resistant safeguards. As educational institutions manage increasingly complex digital ecosystems, this attack serves as a stark reminder that human resources departments now sit squarely on cybersecurity's front lines.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion