The AI revolution is fueling an unprecedented boom in data center construction, with spending projected to hit $50 billion by 2025, but it brings crippling energy demands that could consume 9% of the U.S. grid. Innovations in liquid cooling, efficient algorithms, and renewable integration are emerging as critical solutions to prevent blackouts and slash emissions. This deep dive explores the tech breakthroughs turning data centers from power hogs into sustainable engines of growth.
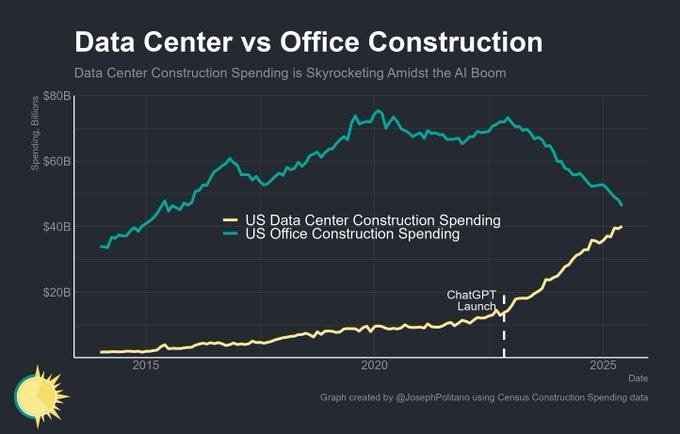
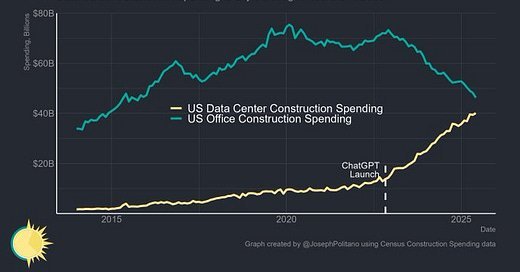
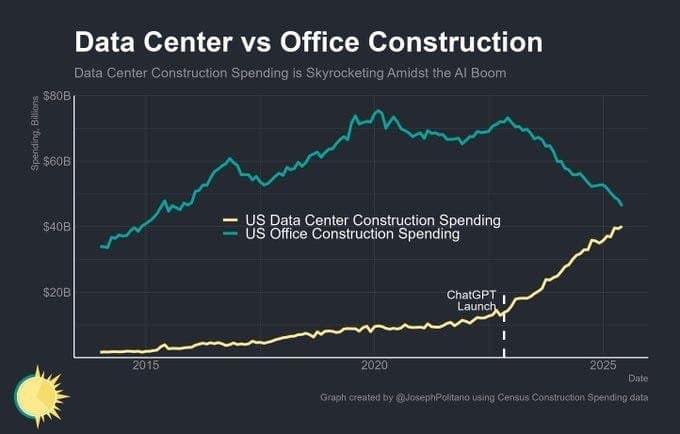
The U.S. construction sector is witnessing a seismic shift: while office building investments flatline, data center projects are exploding, driven by the AI gold rush ignited by ChatGPT's 2022 debut. Census data reveals a stark contrast—office spending stagnates at $60-80 billion annually, but data center construction is rocketing from under $10 billion in the early 2020s to a projected $50+ billion by 2025. This isn't just growth; it's a redefinition of infrastructure priorities, with data centers becoming the new powerhouses of economic and technological advancement. Yet, this boom has unleashed an energy crisis, as AI's voracious appetite for electricity strains grids and threatens sustainability. How is the industry responding? Through a wave of innovations that could reshape computing's future.
The AI Energy Crisis: Why Power Consumption Is Spiraling
AI workloads, particularly inference for real-time applications like chatbots, demand specialized hardware such as NVIDIA GPUs, each drawing up to 700W. Scale this to clusters of thousands, and power needs hit gigawatt levels—equivalent to small cities. Training models like GPT-4 emits CO2 comparable to driving a car 5-20 miles per million tokens processed. By 2030, global data center electricity use could double to 945TWh (matching Japan's annual consumption), with U.S. AI facilities alone accounting for 9% of grid power. Cooling is a major culprit, consuming 40% of site energy due to inefficient Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) ratings above 1.5, where half the power is lost to overhead. This volatility risks blackouts, especially in AI hubs like Virginia and Texas, where demand could surge 81%. Without intervention, data centers might emit as much CO2 as the airline industry by 2030.
Innovations Cooling the Fire: Liquid Tech and AI-Driven Efficiency
Traditional air cooling is obsolete for AI's heat-intensive servers, paving the way for liquid-based solutions that slash energy use by 30-50%. Direct-to-chip (D2C) cooling, deployed by Microsoft in zero-waste systems, channels coolant directly to hotspots, while immersion cooling submerges servers in dielectric fluids—allowing waste heat to be repurposed for heating or agriculture. Hybrid systems, like Shumate Engineering’s model, cut water usage by 97% and energy costs by half. AI optimizes this further: Ecolab’s 3D TRASAR platform uses real-time monitoring to reduce cooling energy by 10%, boosting efficiency up to 50%. NVIDIA’s latest clusters integrate onboard capacitors and liquid cooling, trimming peak power by 30%. Though retrofits are costly, operational savings of up to 40% make these upgrades essential for supporting higher power densities.
Smarter Hardware, Leaner Algorithms: Cutting Waste at the Source
Beyond cooling, hardware and software innovations are crucial for efficiency. Power capping limits GPU draw to 60-80% of maximum, with tools like MIT’s Clover dynamically adjusting settings to save 20-40% energy. Integer-based computations (e.g., BitEnergy’s L-Mul) replace floating-point methods, reducing usage by up to 95% for specific tasks. Compact AI models and modular server designs from Cisco, Lenovo, and AMD prevent overprovisioning, while AI-driven workload management redistributes tasks in real-time, cutting cloud energy by 20%. Geographic load balancing—siting data centers in cooler regions—adds another 30% savings. These advances help hyperscalers achieve near-optimal PUEs of 1.1, proving that smarter code and silicon are as vital as physical upgrades.
Renewable Revolution: Powering AI Without the Carbon Cost
To decouple from fossil fuels, data centers are rapidly adopting renewables and novel energy sources. Solar-battery hybrids, managed by AI platforms like Trinasolar, cut costs by 38% and emissions by nearly half. Some facilities already operate on 100% wind or solar, while others pilot small modular nuclear reactors (SMRs) and hydrogen fuel cells—ECL’s systems achieve PUEs of 1.1 with zero grid reliance. Companies like Oklo and NuScale are advancing nuclear-powered AI hubs, and xAI’s Colossus cluster is transitioning from gas to 150MW of renewables. Regulatory pushes, like the EU’s mandate for 100% renewable data centers by 2032, accelerate this shift, with AI forecasting mitigating intermittency issues. This isn't just compliance; it's a reimagining of energy resilience.
With $300 billion earmarked for AI infrastructure in 2025 alone, these innovations aren't optional—they're the blueprint for sustainable scale. Developers and engineers must now prioritize efficiency in system design, as tools like liquid cooling and integer computing become mainstream. The data center boom, once an environmental threat, is evolving into a showcase for how tech can harmonize growth with planetary limits. As one expert noted, 'The future isn't just powered by AI—it's powered responsibly.' What energy-saving trends are you implementing in your projects?
Source: Analysis based on data from Pragmatic AI.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion