Apple warns Q2 2026 revenue will be constrained by TSMC's advanced chip capacity shortages, as AI accelerator demand competes with iPhone production needs.
Apple this week signaled that its second-quarter fiscal 2026 performance will be constrained by limited availability of processors manufactured on TSMC's leading-edge production nodes, marking a rare supply warning from the company in recent years.
During its earnings call, Apple CEO Tim Cook acknowledged that the company's Q2 guidance reflects constraints in advanced node capacity, particularly affecting iPhone production. The company expects revenue growth of 13-16% year-over-year to approximately $107.75-110.62 billion for the quarter, down from the 23% growth achieved in Q1.
TSMC's N3 Supply Reaches Critical Limits
The supply constraints appear to stem from multiple factors converging at TSMC's 3nm-class manufacturing facilities. Apple's latest iPhone 17 and iPhone 17 Pro models utilize the A19 and A19 Pro chips produced using TSMC's N3P fabrication technology. While Apple has historically enjoyed priority access as TSMC's alpha customer for new nodes, the company now faces competition from surging AI accelerator demand.
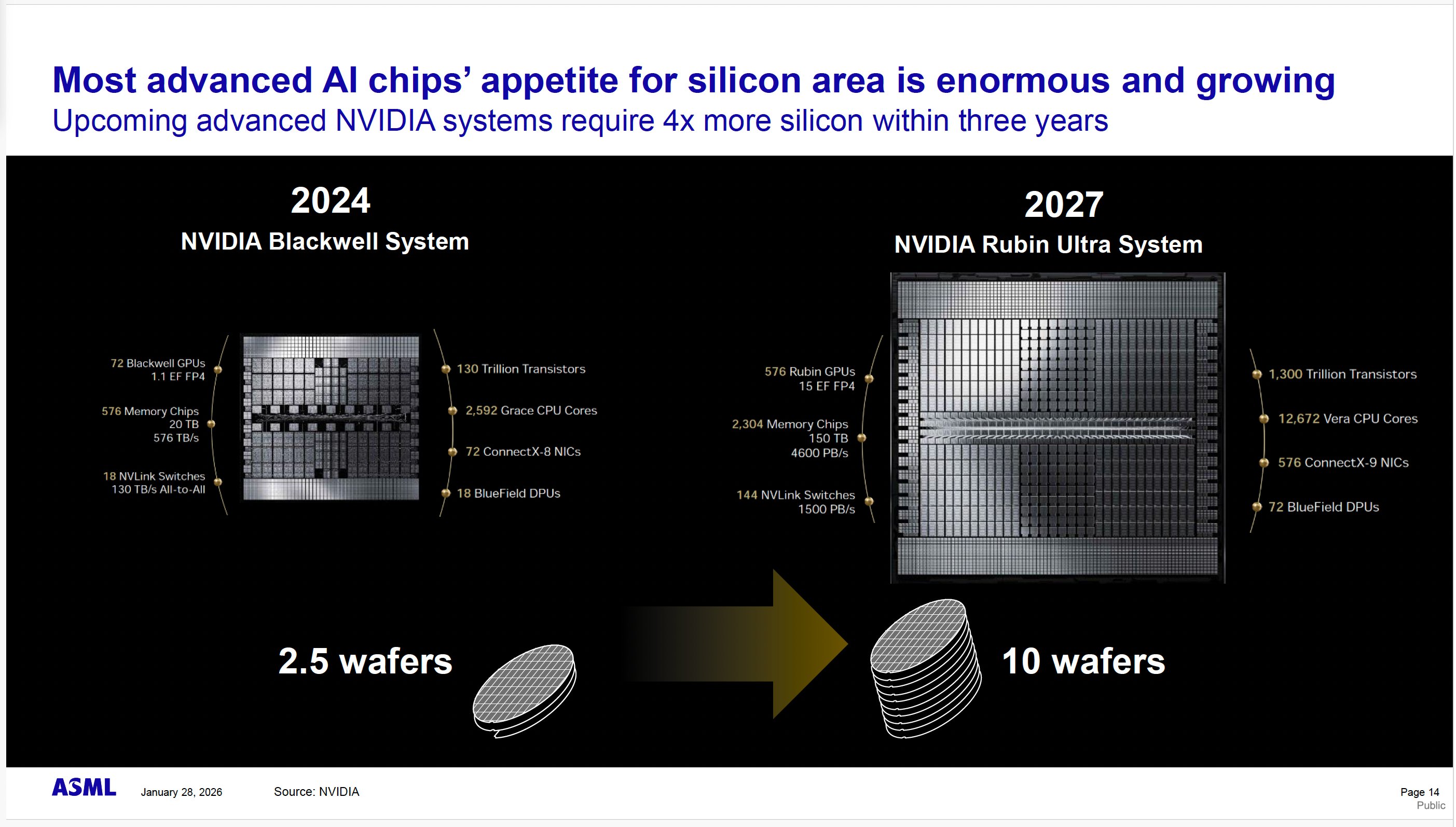
Nvidia's upcoming Rubin Ultra platform represents a significant capacity consumer. ASML estimates that Nvidia's next-generation VR300 NVL576 Rubin Ultra rack-scale solution will require ten 300mm silicon wafers per system, compared to 2.5 wafers for the current GB200 NVL72 configuration. While exact TSMC silicon allocation percentages are difficult to determine, industry analysts estimate that between 25-50% of this wafer demand flows through TSMC's 3nm capacity.
TSMC has been working to expand N3 production through multiple initiatives. The company is converting existing N5 capacity to N3 where possible, pulling forward fab schedules in Taiwan and Arizona, and focusing on capacity optimization across nodes. However, these efforts represent mid-term projects rather than immediate solutions.
Memory and Storage Concerns Add Complexity
Beyond logic chip constraints, Apple also expressed concerns about memory and storage supply chains. The company finds itself in "a supply chase mode to meet very high levels of customer demand," an unusual position for a firm known for its sophisticated supply chain management.
Memory supply dynamics differ fundamentally from logic chip manufacturing. DRAM vendors can redirect capacity across customers, die densities, and memory types (HBM, LPDDR, GDDR) with fewer process changes and shorter qualification cycles. Large OEMs like Apple must qualify memory devices before production, but once qualified, these components can be sourced more flexibly than custom logic chips.
Apple has reportedly qualified Yangtze Memory Technologies Co.'s (YMTC) 3D NAND memory for iPhones sold in China, demonstrating the company's efforts to diversify its memory supply chain.
Market Impact and Future Outlook
Despite supply concerns, Apple reported record quarterly performance with total sales of $143.756 billion, up 15.6% year-over-year. iPhone sales reached $85.269 billion, up 23% from the previous year, while services revenue hit $30.013 billion, up 13.9%.
However, the company's CFO Kevan Parekh emphasized that Q2 guidance is based on "best estimates of constrained supply," acknowledging the dynamic nature of current market conditions. When asked about supply projections beyond Q2, Cook declined to comment, noting that "supply is a function of a lot of things in the industry that move around a lot."
TSMC's challenge reflects broader industry dynamics as AI accelerator demand competes with traditional consumer electronics for advanced manufacturing capacity. The foundry's widely used 3nm-class nodes (N3E and N3P) employ up to 19 EUV lithography layers, down from 25-28 layers in the original N3B, allowing for improved output when EUV scanner availability is limited.
As the semiconductor industry continues to grapple with capacity constraints, Apple's experience highlights the increasing complexity of balancing AI infrastructure demands with consumer device production in an era of intense competition for advanced manufacturing resources.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion