.NET's polyglot development platform receives a focused update aimed at streamlining AI-assisted workflows, improving daily CLI operations, and clarifying Azure deployments, with the new Model Context Protocol integration serving as the headline feature.
The .NET team has released Aspire 13.1, an incremental update to its polyglot, observability-first development platform. While building on the foundational architecture introduced with Aspire 13, this release is less about sweeping architectural changes and more about refining the developer experience for daily tasks, particularly in the context of AI-assisted coding and cloud-native deployments. The update focuses on three primary areas: enhanced integration with AI coding agents via the Model Context Protocol (MCP), meaningful improvements to the command-line interface (CLI), and clearer, more predictable behavior for Azure deployments.
MCP Integration: Formalizing AI Agent Collaboration
A central addition in Aspire 13.1 is its expanded support for AI coding agents through integration with the Model Context Protocol. MCP is a protocol designed to allow AI tools to discover and interact with external resources and services in a standardized way. Aspire now provides a dedicated command, aspire mcp init, to initialize a project with MCP support. This enables compatible AI tools (like GitHub Copilot, Cursor, or future agents) to automatically discover Aspire integrations, inspect the application's structure, and interact with its running resources.
When an MCP-compatible AI agent connects to an Aspire project, it can query the application state, view logs, and inspect distributed traces through exposed endpoints. This integration is designed to eliminate the need for custom setup or manual context provision for each AI tool, allowing developers to stay in their flow while leveraging AI assistance for tasks like debugging, code generation, or understanding complex service dependencies. For example, an AI agent could be asked to "explain the current error in the catalog-service logs" or "generate a new API endpoint that integrates with the existing payment-service"—all by leveraging the standardized context provided by Aspire's MCP implementation.
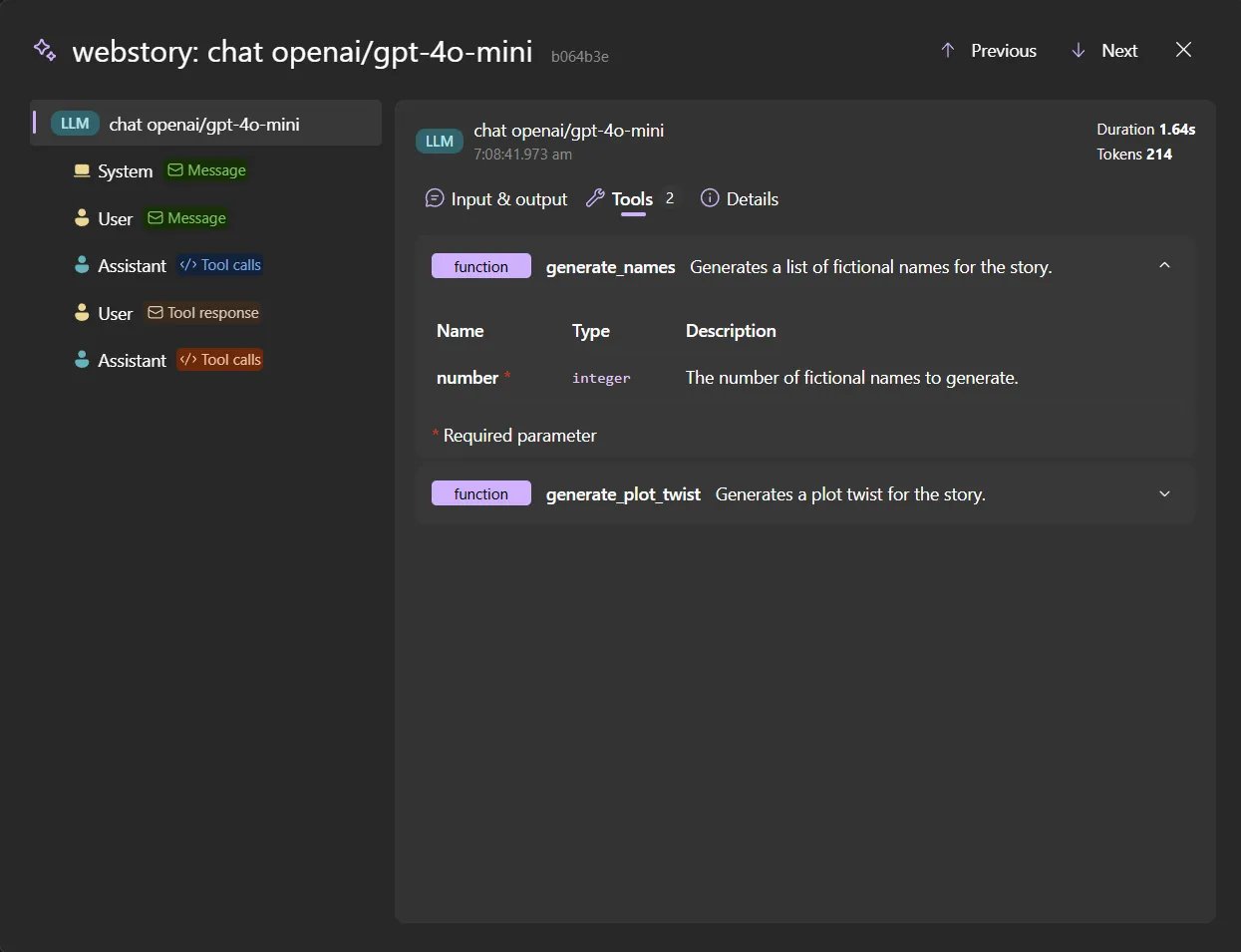
CLI Enhancements: Reducing Friction in Daily Workflows
The Aspire CLI has received several targeted updates designed to reduce friction when creating, running, and maintaining projects. One notable improvement is the introduction of channel selection during project creation. Developers can now specify a channel (e.g., for .NET 10 SDK compatibility) when creating a new project, and this preference is persisted globally. This ensures consistent behavior across new projects and simplifies the setup process for teams working with specific SDK versions.
The CLI now also detects already running project instances and automatically stops them before starting a new run. This prevents common conflicts that arise from port collisions or resource contention, which are frequent pain points in local development. Additionally, the installation scripts now offer an option to skip modifying the system PATH. This is particularly useful in controlled or enterprise environments where system-wide changes require administrative approval or where developers prefer to manage their PATH manually.
Dashboard and Observability Refinements
The Aspire dashboard, a key component for visualizing distributed applications, has been updated for better clarity and visibility. A new Parameters tab allows developers to view and manage configuration values directly from resource details, streamlining the process of inspecting and modifying app settings without leaving the dashboard interface.
For AI-centric workflows, the GenAI visualizer has been enhanced. It now provides better displays for tool definitions, evaluations, and related logs. Furthermore, it supports previewing audio and video content generated by AI models or application services, which is crucial for developers working with multimodal AI applications. Several stability issues in the dashboard have also been addressed, improving the overall reliability of the tooling.
Azure Deployment: Clarity and Validation
On the Azure deployment side, Aspire 13.1 introduces clearer naming and stronger validation to prevent deployment failures. The Azure Redis integration has been renamed to better match the underlying Azure Cache for Redis service, reducing confusion. More importantly, additional checks are performed earlier in the deployment process to surface configuration issues sooner, helping developers catch problems before they reach production.
Azure resources now expose standardized connection properties that work across supported languages. This makes it easier for non-.NET applications (e.g., Python or Node.js services) to connect to Azure resources using consistent settings, aligning with Aspire's polyglot philosophy. The release also adds support for deployment slots in Azure App Service and provides finer control over default role assignments, giving teams more granular security management.
Container and Frontend Workflow Improvements
Container and deployment workflows have been refined with the introduction of a general container registry resource. This allows developers to target registries beyond Azure Container Registry (ACR), such as Docker Hub or other private registries, increasing flexibility. Container image pushes are now more explicit and predictable, especially when deploying to Azure Container Apps, reducing ambiguity in the deployment pipeline.
Docker Compose support has been improved to enhance portability and reduce race conditions during parallel builds. For JavaScript and frontend development, a new starter template combines an ASP.NET Core backend with a Vite-based frontend, offering a modern, full-stack starting point. Improved HTTPS handling for development and fixes for package manager-related issues further streamline the frontend development experience. Certificate handling has been simplified with new APIs for configuring HTTPS and terminating TLS in supported containers.
Stabilization and Breaking Changes
Aspire 13.1 stabilizes several integrations that were previously in preview, including Dev Tunnels, endpoint proxy support, and Azure Functions. Templates have been updated to reflect consistent patterns, and a broad set of bug fixes improves reliability across platforms.
Developers upgrading from earlier versions should note that Aspire 13.1 requires the .NET 10 SDK or later. The release includes breaking changes, particularly around Azure Redis APIs and renamed connection properties. Reviewing the official release notes is essential for a smooth upgrade.
For those interested in exploring the new features, the official Aspire documentation provides detailed setup guides and usage examples. The integration with MCP and the enhanced CLI capabilities represent a significant step toward making Aspire a more cohesive environment for modern, AI-assisted software development.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion