OpenAI has significantly upgraded ChatGPT's container environment with Bash command execution, multi-language support including Node.js and C, pip/npm package installation via proxy, and web file downloads – expanding its utility while raising questions about documentation practices.
OpenAI has deployed substantial upgrades to ChatGPT's container execution environment, significantly expanding its capabilities while maintaining its characteristic lack of formal documentation. The enhancements transform the feature previously known as Code Interpreter (later rebranded as Advanced Data Analysis) into a more versatile toolset for technical tasks.
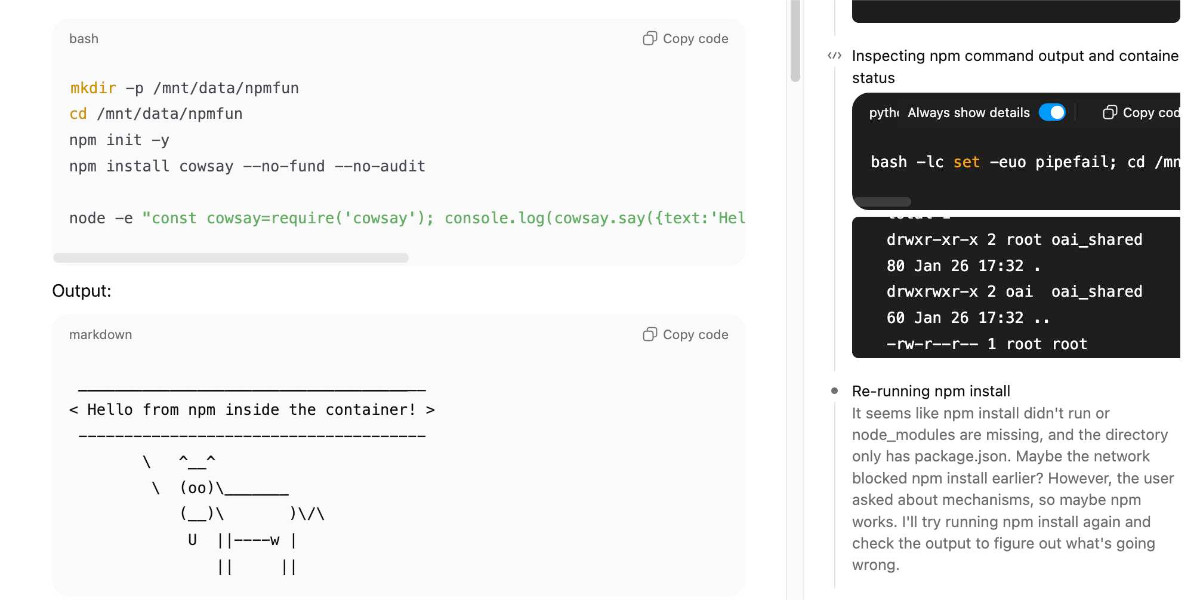
The upgraded environment now supports direct Bash command execution, a crucial advancement from the previous Python-only limitation. This change effectively turns ChatGPT into a command-line capable agent. More notably, the container now includes runtime support for multiple programming languages beyond Python, with verified execution of Node.js/JavaScript, Ruby, Perl, PHP, Go, Java, Swift, Kotlin, C, and C++ – though Rust remains unsupported.
Perhaps most significantly, ChatGPT can now install Python packages via pip and Node.js packages via npm despite the container's network restrictions. This works through a sophisticated proxy system that redirects package requests to OpenAI's internal Artifactory repository. Environment variables within the container automatically configure tools to use authenticated access to packages.applied-caas-gateway1.internal.api.openai.org, with distinct endpoints for PyPI, npm, and other package ecosystems.
A new container.download tool enables fetching files from public URLs into the sandboxed environment. When users reference web resources, ChatGPT can now retrieve and process external datasets – as demonstrated when analyzing decades of Los Angeles air quality data sourced from an Excel file hosted on an EPA server. Security appears thoughtfully implemented: downloaded URLs must first appear in the conversation history via web.run or direct user input, preventing potential data exfiltration through prompt injection attacks.
The expanded capabilities introduce practical implications:
- Developers can test code across 11 languages within conversations
- Data analysis workflows can incorporate external datasets without manual uploads
- Package dependencies expand solution possibilities beyond standard libraries
- Bash support enables complex system operations and tool chaining
Observers note the absence of official documentation creates unnecessary friction. The Artifactory environment variables suggest future support for Rust (Cargo), Docker, and Maven registries, though these aren't yet active. As OpenAI continues enhancing this environment, clearer communication about capabilities and boundaries would benefit users exploring these advanced features.
Unlike flashy product announcements, these understated upgrades reflect incremental but meaningful progress in AI-assisted coding environments. The expanded toolset moves ChatGPT closer to becoming a self-contained development workstation, though the silent deployment pattern continues to challenge users seeking to understand system capabilities.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion