Coder's engineering team has uncovered a severe security flaw in Go's standard database/sql package that lingered undetected since at least Go 1.10. The vulnerability (CVE-2025-47907) enables attackers to corrupt SQL query results during context cancellation, potentially leading to full application compromise. Immediate updates to Go 1.24.6 are critical for all affected systems.

A subtle yet dangerous vulnerability has been hiding in Go's core database/sql package for years, allowing attackers to manipulate SQL query results under specific conditions. Discovered by Coder's engineering team, this flaw—officially designated CVE-2025-47907—exploits a data race during query cancellation that could corrupt memory buffers and alter database responses. The implications range from data integrity breaches to full application takeover, demanding immediate attention from the Go ecosystem.
The Mechanics of the Flaw
When a database query is canceled in vulnerable Go versions (prior to 1.24.6), the underlying SQL driver connection may be prematurely returned to the connection pool while results are still being decoded ("scanned"). If a second query reuses this connection before decoding completes, it can overwrite the memory buffers of the initial query—corrupting its results.
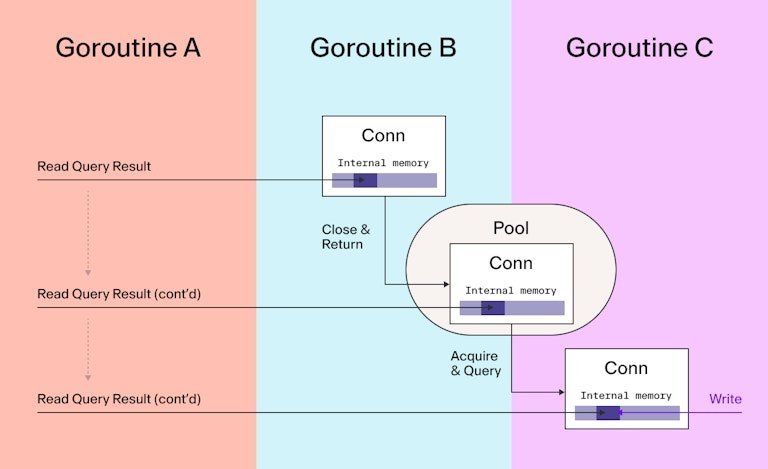
"It's analogous to a 'use-after-free' bug," explains Coder's technical analysis. "Instead of raw memory, we're dealing with a shared resource—a database connection—being recycled too early."
Exploit Complexity vs. Impact
While exploitation is challenging—requiring precise timing, driver-specific memory layouts, and continued use of canceled query results—the stakes are alarmingly high:
- Authentication bypasses if password verification queries are corrupted
- Financial system manipulation through altered transaction amounts
- Privilege escalation via tampered role-checking logic
Notably, no public exploits exist yet, but the potential for targeted attacks against high-value systems remains.
Discovery: From CI Anomaly to Security Breakthrough
Coder's team initially detected the issue through Go's race detector during routine CI runs, observing unexplained data corruption during API key decoding. Early dismissals attributed it to driver bugs (like lib/pq), but deeper investigation revealed the root cause lay in database/sql's handling of canceled contexts:
// Simplified vulnerability trigger scenario
rows, err := db.QueryContext(cancelCtx, "SELECT...")
// If canceled mid-scan:
rows.Close() // Returns connection to pool prematurely
// New query reuses connection, overwriting buffer
rows.Scan(&data) // Now reads corrupted data
The vulnerability evaded detection since at least 2021, with prior reports misdiagnosing symptoms as driver-specific glitches.
Mitigation and Response
- Go 1.24.6 contains the official patch. All teams using
database/sqlmust upgrade immediately. - Coder has released patched application versions (2.25.1, 2.24.3, 2.23.5).
- Drivers retaining internal buffers (common for performance) are highest risk.
Coder acknowledges the Go team's swift collaboration in resolving the flaw. This discovery underscores how subtle concurrency bugs in foundational libraries can morph into critical security threats—reinforcing why vigilance in dependency management and static analysis isn't optional, but existential.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion