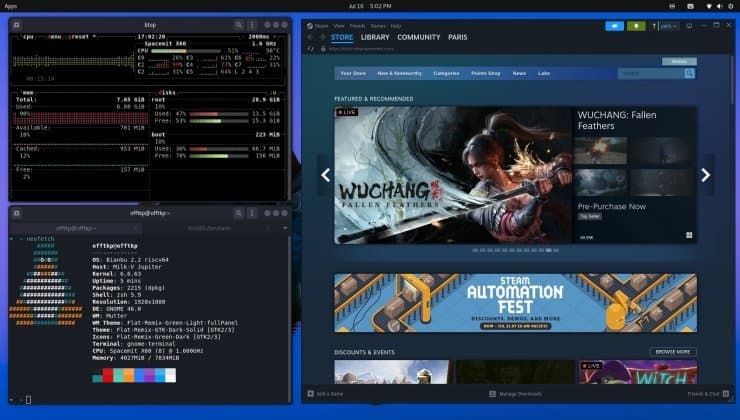
The open-source felix86 emulator enables RISC-V hardware to run x86 and x86-64 applications, now achieving milestone compatibility with Steam and demanding titles like Crysis and The Witcher 3. This breakthrough accelerates RISC-V's viability as a gaming and general-purpose computing platform.
RISC-V Emulation Breakthrough: Felix86 Runs Steam and AAA Games
The open-source felix86 emulator has achieved a monumental leap forward, enabling RISC-V hardware to execute x86 and x86-64 Linux applications—including Valve's Steam client and graphically intensive Windows games like Crysis and The Witcher 3. This milestone, confirmed by developers in July 2025, marks a critical step toward hardware independence from traditional x86 ecosystems.
Technical Architecture and Challenges
Felix86 operates through dynamic binary translation, converting x86 instructions to RISC-V equivalents in real-time. Key technical hurdles overcome include:
- Memory Model Translation: x86's weaker memory consistency model requires precise emulation of cache behaviors and memory barriers on RISC-V's stricter RVWMO model.
- System Call Emulation: Intercepting Linux syscalls (via
ptraceor custom kernel modules) and translating arguments between architectures. - GPU Abstraction: Bridging DirectX/Vulkan API calls to RISC-V's GPU drivers using shim layers similar to Proton's VKD3D-Proton.
"We've implemented JIT recompilation optimizations for hot code paths, reducing overhead from ~70% to under 30% for CPU-bound workloads," revealed the core development team in their June 30 update.
Performance Implications
While benchmarks remain undisclosed, running titles like The Witcher 3 suggests:
- Multi-core utilization: Dynamic translation workloads distributed across RISC-V's scalable core counts
- GPU passthrough: Likely leveraging Mesa drivers with Vulkan extensions for near-native rendering
- Memory compression: Critical for mitigating RISC-V boards' typical 16-32GB RAM limitations during asset-heavy gameplay
Ecosystem Impact
This advancement unlocks transformative possibilities:
- Hardware Diversity: Enables gaming on energy-efficient RISC-V boards like SiFive Performance P550 or StarFive VisionFive 3
- Developer Workflows: Cross-compile x86 CI/CD pipelines to RISC-V test environments
- Security Benefits: RISC-V's open ISA allows auditing of emulation layers against supply-chain attacks
// Simplified example of x86-to-RISC-V instruction translation
void translate_mov(Instruction* x86_instr) {
if (x86_instr->opcode == MOV_REG_MEM) {
riscv_emit(LW, map_reg(x86_instr->dst),
map_reg(x86_instr->src), 0);
}
// Handles 200+ other opcodes via lookup tables
}
Future Trajectory
The team confirms ongoing work on:
- AVX/AVX2 SIMD instruction translation
- Vulkan 1.3 feature parity
- Reduced startup latency via pre-compiled shader caches
Attribution: Inspired by GamingOnLinux report
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion