Augment Code faced critical performance issues in its VS Code extension as conversations grew complex, leading to crashes and UI freezes. By replacing their reactive state management with Redux and Redux-Saga—and building a custom Svelte-Redux bridge—they achieved 2x faster inference, eliminated memory leaks, and made previously impossible features feasible. This deep dive reveals their architectural overhaul and lessons for complex extension development.
The State Management Overhaul That Rescued a Failing VS Code Extension
When Augment Code's VS Code extension began crashing during long conversations, the team confronted a pivotal choice: apply quick fixes or rebuild their state management foundation. They chose the latter—a decision that resulted in 2x faster chat inference, crash-free long threads, and debugging cycles reduced from days to minutes. This is the story of how they transformed their extension's architecture.
The Breaking Point
Early symptoms seemed manageable—occasional UI freezes, slowdowns during lengthy chats. But as features grew (parallel tool calls, agent workflows), the cracks widened into systemic failures:
- Implicit state ownership: Multiple components claimed responsibility for the same data, causing unpredictable update sequences
- Hidden side effects: State changes triggered cascading reactions buried in component lifecycles
- Inconsistent async handling: Mix of promises, callbacks, and event emitters bred race conditions
An analysis of three months of bug fixes revealed 70% traced back to state management flaws. Complex features like true parallel tool orchestration were architecturally impossible.
Redux: The Architectural Reset
The team rebuilt using Redux with strict principles:
// Core architecture pillars
1. Single source of truth: Centralized store with typed schema
2. Transactional updates: State changes via explicit, logged actions
3. Normalized storage: Flat data relationships to prevent duplication
4. Selector-based derived state: Memoized pure functions for computed data
5. Explicit lifecycle management: Clear persistence/hydration paths
This brought unprecedented observability—every state change became traceable through action logs.
Bridging Redux and Svelte
Existing Svelte solutions lacked Redux's control. Their answer: createSelector(), a custom bridge returning Svelte-readable selectors:
const selectActiveConversation = createSelector(
(state) => state.conversations.active
);
// Usage in Svelte 5 component
const conversation = selectActiveConversation(store);
Key innovations:
- Lazy evaluation: Selectors only run when actively used
- Surgical tracking: Updates only affect selectors dependent on changed state slices
- Advanced caching: Results cached until inputs change
Conquering Async Chaos with Sagas
Complex workflows (e.g., processing user messages) required robust async orchestration. Redux-Saga provided the solution:
function* handleUserMessage(action) {
const { message, conversationId } = action.payload;
const exchange = yield call(createExchange, message);
yield put(exchangeCreated({ conversationId, exchange }));
const stream = yield call(api.streamCompletion, message);
yield fork(handleStream, stream, exchange.id);
// ...
}
Sagas enabled previously impossible features—parallel tool execution, multi-threaded conversations, and reliable cancellation—by making async workflows explicit and testable.
Agent-Assisted Refactoring at Scale
Migrating the entire extension required meticulous strategy:
- Agent-optimized docs: Scoped
_docs/directories with navigable architecture guides - Pattern-driven porting: AI identified state dependencies and rewrote logic using predefined patterns
- The "Big Bang" PR: A single massive refactor validated by AI-generated test cases comparing action logs
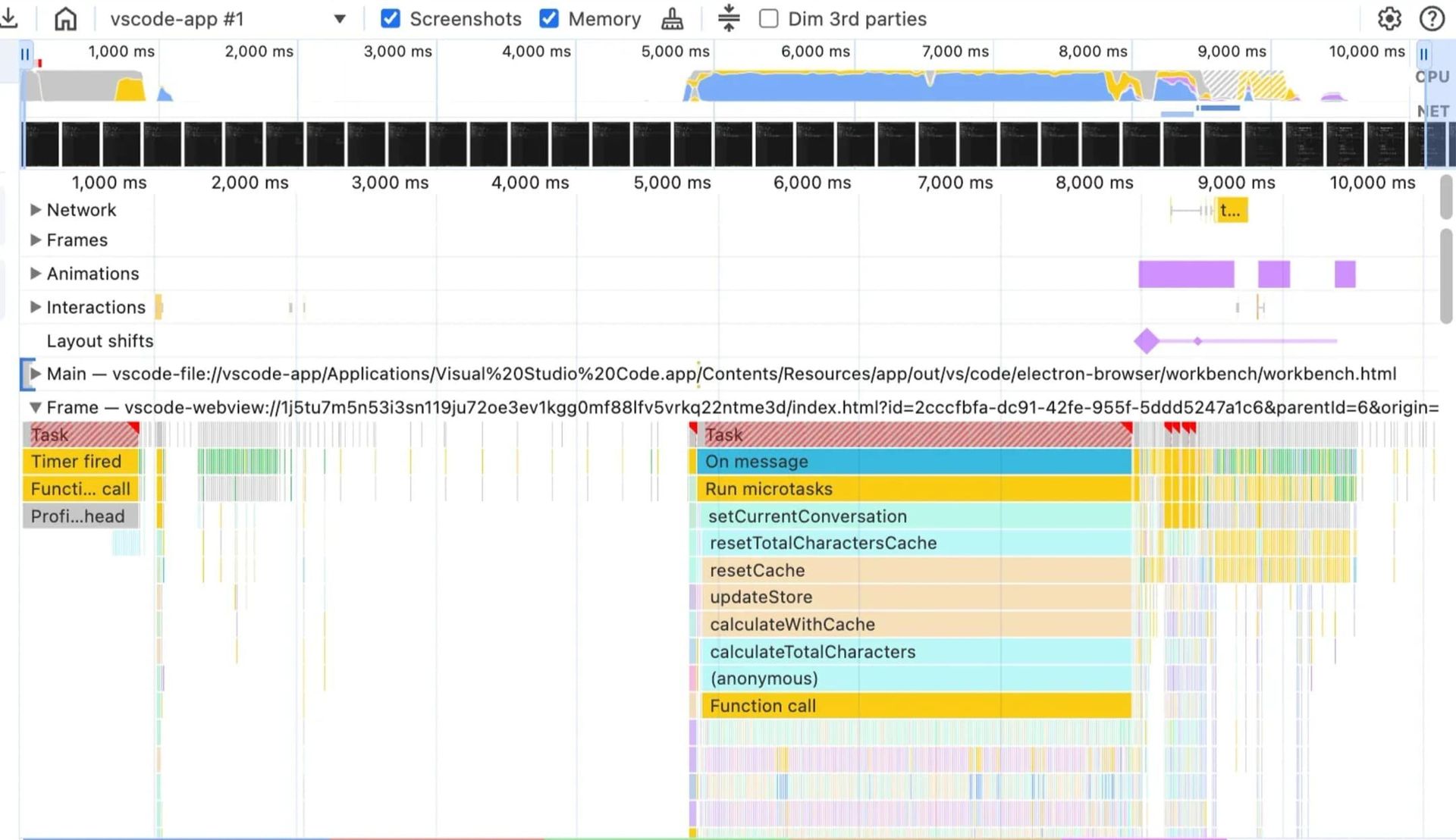 Flame chart showing UI blocking during JSON import pre-refactor
Flame chart showing UI blocking during JSON import pre-refactor
{{IMAGE:3}} Post-refactor: Same operation with minimal UI impact
Tangible Results
- Performance: 1.2–2× faster tool-heavy workflows; long threads load instantly
- Stability: UI freezes and memory leaks eliminated
- Debugging: Race conditions diagnosed in minutes via action logs instead of weeks
- Capability: Enabled parallel conversations and multi-agent workflows
Critical Lessons for Extension Developers
- Warning signs: Long sessions degrading performance? "Impossible" bugs? Architecture likely has implicit coupling.
- Redux pays off: Boilerplate is an investment—the action log alone justifies it.
- Observability is non-negotiable: Log every state change explicitly.
- Agent refactoring requires structure: Contextual documentation is essential for reliable AI assistance.
- Build bridges: Don't compromise—create integrations between ecosystems when needed (like their Svelte-Redux connector).
The overhaul unlocked ambitious next steps: richer UIs, multi-agent collaboration, and Redux DevTools-like debugging for VS Code. For teams building complex extensions, Augment's journey proves that foundational architecture isn't overhead—it's the bedrock of innovation.
Source: Augment Code Blog
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion