MongoDB's new Embedding and Reranking API brings Voyage AI models directly into Atlas, eliminating the operational complexity of stitching together separate vector search and embedding services.
MongoDB has announced the public preview of its Embedding and Reranking API on MongoDB Atlas, marking a significant step toward simplifying AI retrieval systems. The new API integrates Voyage AI's search models directly into the managed cloud database, enabling developers to build semantic search and AI-powered assistants within a single environment with consolidated monitoring and billing.
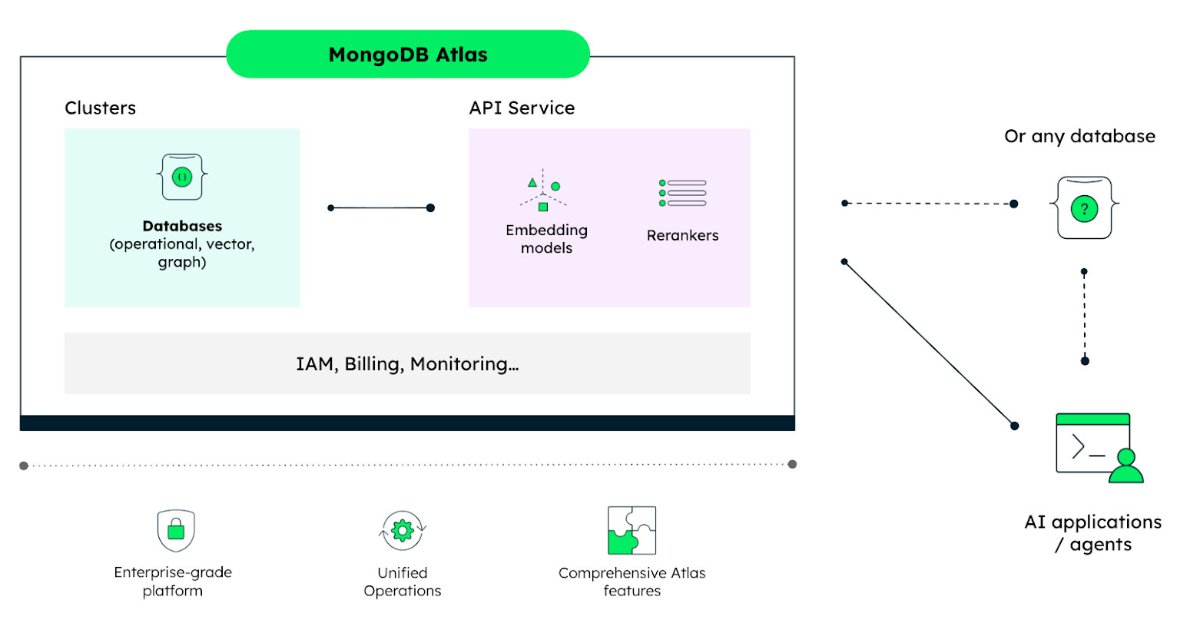
The Problem: Operational Complexity in AI Retrieval
Building AI retrieval systems today typically involves piecing together multiple services: a database, vector search capabilities, and separate embedding model providers. Each component introduces its own operational overhead, from managing API keys to handling different billing models and monitoring systems.
Deepak Goyal, an AI engineer, highlighted this pain point on LinkedIn: "I spent 3 hours yesterday debugging a 12-hour sync lag in our vector store. It's a 'Sync Tax' that almost every AI team is paying right now. (...) If your data is 24 hours old, your RAG isn't 'intelligent'—it's just a well-indexed archive."
This fragmentation creates what Goyal calls a "Sync Tax"—the hidden cost of keeping data synchronized across multiple systems. The result is that many RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) implementations end up being "well-indexed archives" rather than truly intelligent systems.
The Solution: Integrated Embedding and Reranking
MongoDB's approach consolidates the components needed for AI retrieval into a single platform. Thibaut Gourdel, senior technical product marketing manager at MongoDB, and Wen Phan, staff product manager at MongoDB, explain: "Building AI retrieval today means stitching together databases, vector search, and retrieval model providers—each introducing operational complexity. To address this, we're introducing the Embedding and Reranking API on MongoDB Atlas."
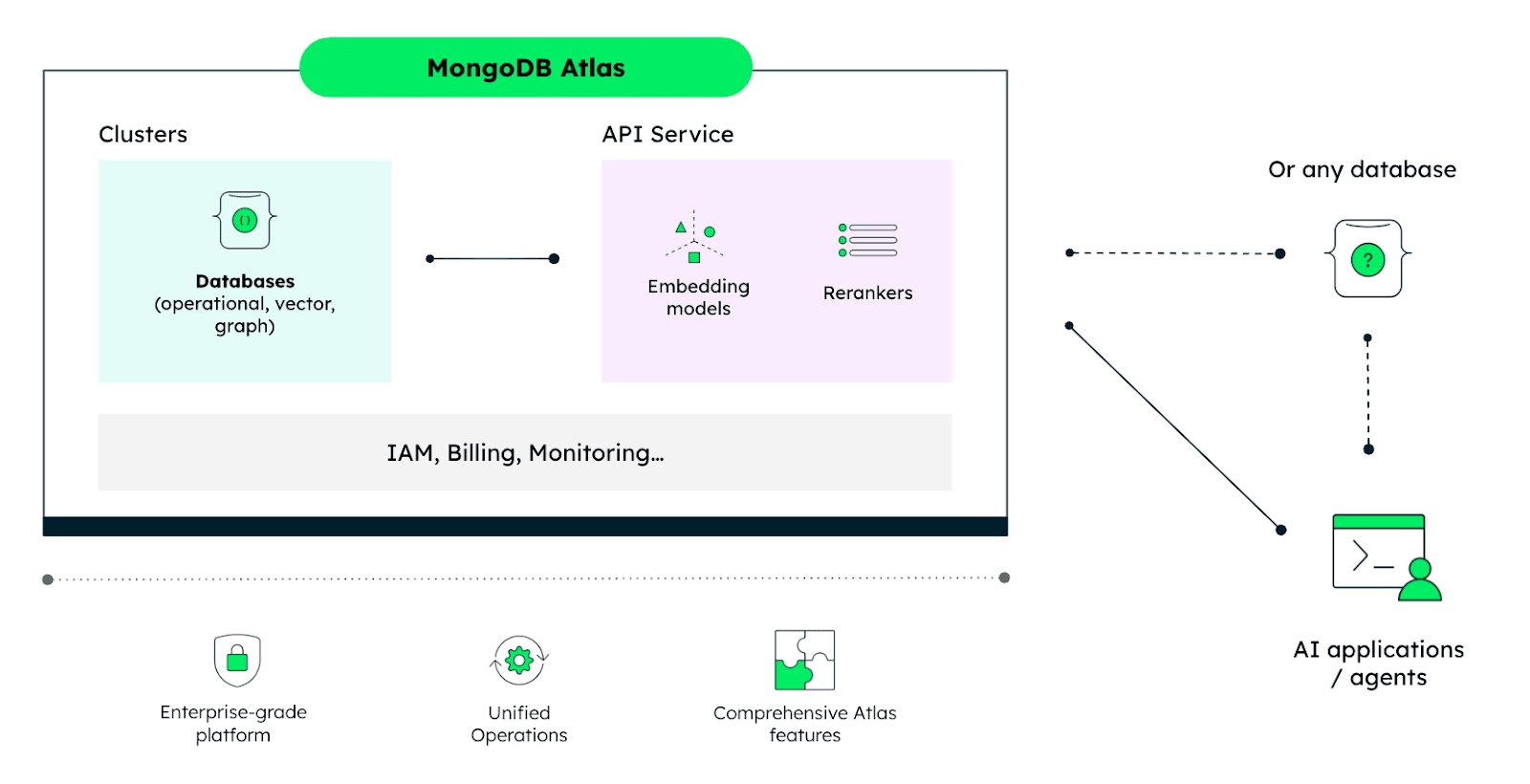
The API is database-agnostic, meaning it can be integrated into any tech stack or database, but it's designed specifically for teams building retrieval-powered AI systems. This includes semantic search, RAG applications, and AI agents.
Voyage 4 Models: A New Generation of Embedding
The Voyage 4 series, announced at the .local San Francisco event, represents a significant advancement in embedding technology. The series includes four models:
- voyage-4-large
- voyage-4
- voyage-4-lite
- voyage-4-nano (open-weights)
Unlike previous generations where identical models were required for both query and document embedding, Voyage 4 models work in the same embedding space. This means teams can store data using voyage-4-large and run queries with any Voyage 4 model, providing flexibility in balancing accuracy, cost, and speed.
The models support dimensions from 256 to 2048 and include quantization options. Beyond general-purpose models, Voyage provides specialized options for specific fields, whole-document analysis, multimodal data, and reranking in multi-step search systems.
Production Benefits: Speed and Simplicity
Goyal's observation about the shift toward integrated solutions resonates with many AI teams: "By unifying the flow, we're seeing a shift. Specialized vector stores are starting to feel like the external GPUs of the AI world—powerful, but for 90% of production use cases, 'integrated' is winning on speed and simplicity."
This consolidation addresses several production challenges:
Reduced Latency: By eliminating network hops between separate services, the integrated approach can significantly reduce retrieval times.
Simplified Operations: Teams no longer need to manage multiple service accounts, billing systems, and monitoring dashboards. Consistent Performance: With all components on the same platform, performance characteristics are more predictable and easier to optimize.
Enhanced Vector Search Capabilities
Alongside the Embedding and Reranking API, MongoDB has also introduced additional vector search features:
Automated Embedding in Vector Search: Available in preview in the community edition, this feature automatically generates embeddings for documents as they're inserted into the database.
Lexical Prefilters for MongoDB Vector Search: Now in public preview, this feature provides text and geo analysis filters alongside vector search, enabling more precise retrieval through hybrid search approaches.
The MongoDB-Voyage AI Acquisition Context
The integration of Voyage AI's capabilities into MongoDB Atlas has been anticipated since MongoDB announced its acquisition of Voyage AI almost a year ago. This move represents MongoDB's strategy to provide a comprehensive platform for AI applications, rather than just a database with vector search capabilities.
Gourdel and Phan emphasize that while MongoDB Atlas already supports built-in vector search, the new API brings additional simplicity: "This matters for building production AI systems. Scaling LLM applications requires delivering the right context at the right time, which means tightly integrating operational data with high-performance search."
Getting Started with the API
The Embedding and Reranking API is currently in preview. MongoDB has provided a "Voyage AI Quick Start" tutorial as a Python notebook on GitHub, making it straightforward for developers to experiment with the new capabilities.
For teams building AI applications, this integration represents a significant reduction in complexity. Rather than managing separate embedding services, vector databases, and monitoring systems, developers can now work within a unified environment that handles all aspects of AI retrieval.
As AI applications move from prototypes to production, the operational challenges of managing multiple services become increasingly burdensome. MongoDB's integrated approach addresses these challenges head-on, potentially accelerating the adoption of sophisticated AI retrieval systems across industries.
The question for many teams will be whether the convenience of integration outweighs the benefits of using specialized, best-of-breed components. However, for the majority of production use cases, MongoDB's bet on integration over fragmentation appears to be resonating with developers who are tired of paying the "Sync Tax" and managing operational complexity.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion