Microsoft Education unveiled 18 major updates at Bett 2026, focusing on AI-driven content creation, personalized learning platforms, and deeper LMS integrations. The announcement highlights a strategic shift toward making Copilot and AI tools central to the educator workflow, from unit planning in Microsoft 365 to dedicated Minecraft Education servers for cross-school collaboration.
Microsoft Education's presence at Bett 2026 in London was marked by a significant wave of updates, totaling 18 new features and capabilities. The announcements signal a clear strategic direction: embedding AI deeply into the educator's daily workflow while expanding the reach of its learning platforms across different operating systems and learning management systems (LMS). The updates span from foundational tools like the Teach Module in Microsoft 365 to new standalone applications like Microsoft Learning Zone, and extend into student-facing tools and gaming environments.
What Changed: A Unified AI and Learning Platform
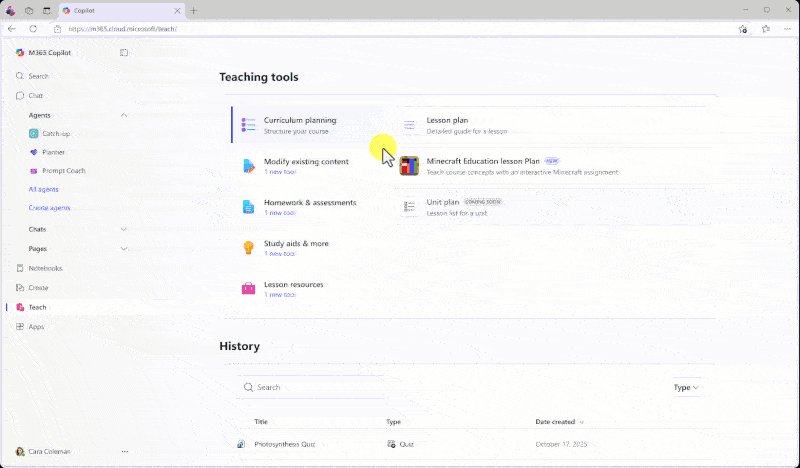
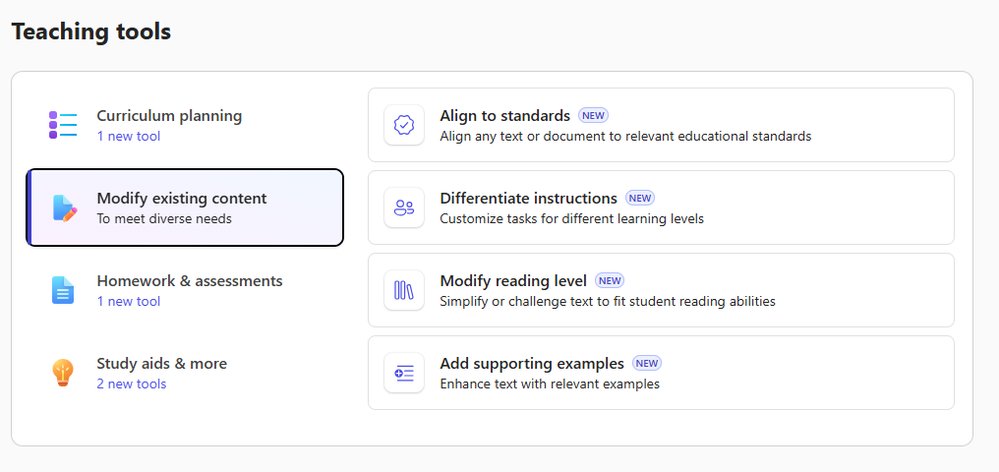
The core of the updates revolves around making AI assistance more accessible and context-aware for educators and students. For educators, the Teach Module in Microsoft 365 is receiving a suite of AI-powered tools designed to modify existing content. This includes the ability to Align to Standards, Differentiate Instructions, Modify Reading Level, and Add Supporting Examples. These tools are currently in private preview and are designed to save time by adapting existing lesson materials rather than requiring educators to create everything from scratch.
For students, the Study and Learn Agent is entering preview in January 2026. This conversational agent, available within the Microsoft 365 Copilot App, aims to help learners understand concepts, practice skills with activities like flashcards, and prepare for tests. It's important to note that this agent does not require an additional Copilot license for Microsoft Education customers.
A major new standalone application, Microsoft Learning Zone, is now available for download on Windows. This app is positioned as a classroom-ready solution that uses AI on Copilot+ PCs to transform any idea or resource into an interactive, personalized lesson. It includes a library of ready-to-learn lessons developed in partnership with organizations like NASA, the World Wildlife Fund, and OpenStax. The app has also earned the ISTE Seal of Alignment, signaling its adherence to educational technology standards.
In the gaming and computational thinking space, Minecraft Education is introducing dedicated servers. This feature, currently in beta and targeting general availability in February, will allow IT administrators and educators to host persistent worlds. This enables cross-tenant gameplay, a key development for running Minecraft esports programs or collaborative projects between different schools.
Integration is a key theme. Updates are coming to Teams EDU and OneNote EDU to better incorporate these new AI and learning activities. For example, educators will soon be able to set AI guidelines directly within Teams Assignments, providing clear expectations for student use of AI tools. Learning Activities, such as Flashcards and Fill-in-the-Blanks, are being integrated into Teams Assignments and will soon be embeddable directly into OneNote pages.
Furthermore, Microsoft is deepening its connection with the broader LMS ecosystem through Microsoft 365 LTI. New "Create with Copilot" options will allow educators to draft lesson materials directly within their LMS (like Canvas, Blackboard, or Moodle) and publish them seamlessly. Learning Zone lessons will also be assignable within LMS platforms via this integration.

Provider Comparison: Microsoft's Ecosystem Play
Microsoft's strategy with these updates is distinct from competitors like Google Workspace for Education and Apple's educational offerings. While Google focuses on seamless collaboration and simplicity within its ecosystem, and Apple emphasizes creativity and design tools, Microsoft is building a deeply integrated, AI-centric platform that bridges its own services (Office 365, Teams, Minecraft) with external systems (LMS, third-party content providers).
Google Workspace for Education: Google's strength lies in its lightweight, collaborative apps like Docs, Sheets, and Classroom. Its recent AI push with "Duet AI" focuses on enhancing these core apps. However, Google lacks a dedicated, AI-driven lesson creation platform like Learning Zone and doesn't have a gaming ecosystem comparable to Minecraft Education. Google's approach is more about enhancing existing workflows, whereas Microsoft is introducing new, dedicated AI-powered applications.
Apple Education: Apple's ecosystem is built around creativity tools (iMovie, GarageBand, Keynote) and its Classroom app for device management. It excels in hands-on, creative projects but has a less pronounced focus on AI-driven content modification or large-scale, cross-school multiplayer gaming environments. Apple's updates are often tied to hardware cycles and specific creative applications, not the broad, AI-infused platform updates Microsoft is announcing.
Specialized EdTech Platforms: Companies like Kahoot! (for gamified quizzes) or Nearpod (for interactive lessons) focus on specific niches. Microsoft's approach is to either build similar capabilities in-house (like the new Learning Activities) or integrate with them (e.g., creating Kahoot! quizzes within Learning Zone). The advantage for Microsoft is the unified identity and data flow across its entire suite, reducing the need for multiple logins and disparate data silos.
Pricing and Licensing: A key strategic move is making many of these tools available within existing licenses. Microsoft Learning Zone is included at no additional cost with all Microsoft Education licenses. The Study and Learn Agent does not require an extra Copilot license. This contrasts with some competitors where advanced AI features may be part of premium tiers. Minecraft Education is included in Microsoft A3 and A5 subscriptions, bundling a powerful engagement tool with core productivity software.
Business Impact: Efficiency, Personalization, and Ecosystem Lock-in
For educational institutions, these updates present both opportunities and considerations. The primary business impact is in operational efficiency and personalized learning at scale.
Time Savings for Educators: Tools like Modify Content and Learning Zone's AI lesson generation directly address the chronic issue of educator workload. By automating the adaptation of materials and the creation of interactive lessons, Microsoft aims to free up teacher time for direct student interaction and instructional planning. The integration with LMS platforms via Microsoft 365 LTI further reduces context switching and manual data entry.
Personalized Learning Pathways: The combination of the Study and Learn Agent for students and the insights provided by Learning Zone for educators creates a feedback loop for personalization. Students can get adaptive help, and teachers can see where class-wide or individual gaps exist, allowing for targeted intervention. This moves beyond one-size-fits-all instruction.
Enhanced Engagement and Skill Building: The dedicated Minecraft Education servers and the new Learning Activities (Fill in the Blanks, Matching, Quizzes) are designed to increase student engagement through gamification and interactive practice. These tools aim to build not just subject knowledge but also collaboration, problem-solving, and computational thinking skills.
Migration and Integration Considerations: For schools already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, these updates strengthen the value proposition. The deepening LMS integrations make it easier to stay within the Microsoft suite for content creation and assignment management, even if the primary LMS is a third-party platform. However, for institutions using other productivity suites (like Google Workspace), adopting these new AI-powered tools would require a more significant platform shift. The cost of migration, retraining staff, and ensuring device compatibility (especially for AI-heavy features like Learning Zone on Copilot+ PCs) would be major considerations.
Data and Privacy: With AI playing a larger role in content creation and student interaction, data privacy and security remain paramount. Microsoft emphasizes that its education tools are built with privacy in mind, but institutions will need to review how student data is used to train or power these AI models and ensure compliance with local regulations like FERPA or GDPR.
The Strategic Direction: An AI-First, Integrated Learning Ecosystem
Microsoft's Bett 2026 announcements paint a picture of a company moving beyond providing individual productivity tools to offering a holistic, AI-powered learning ecosystem. The strategy is to make Copilot and AI the central nervous system of the educational experience, from planning and content creation to delivery and assessment.
The introduction of a standalone app like Learning Zone, which runs on Windows and is included in existing licenses, is a direct play to capture more classroom time and reduce reliance on web-based tools that may not offer the same level of integration or offline capability. The partnership with diverse content providers (Nobel Peace Center, PBS NewsHour, etc.) for the Learning Zone library shows an understanding that content is king, and schools need trusted, high-quality resources.
The focus on cross-platform and cross-tenant capabilities, especially with Minecraft Education's dedicated servers, is also strategic. It encourages collaboration beyond the walls of a single school or district, fostering a larger community and potentially opening up new avenues for esports and project-based learning.
For IT administrators, the updates present both a streamlined management opportunity and a new set of requirements. The ability to deploy Microsoft 365 LTI to a wide range of LMS platforms simplifies integration. However, the growing reliance on AI features may necessitate ensuring that school networks and devices (particularly for AI workloads) are adequately equipped.
Conclusion
Microsoft Education's Bett 2026 updates represent a significant evolution in its educational technology strategy. By deeply integrating AI into content creation tools, launching a dedicated AI-powered lesson platform, and expanding the reach of its gaming and collaboration tools, Microsoft is positioning itself as a comprehensive, AI-first partner for modern education. The focus on reducing educator workload, personalizing student learning, and fostering engagement through interactive and gamified experiences addresses key pain points in the education sector. While the move requires institutions to consider platform integration and device capabilities, the promise of a more efficient, personalized, and engaging learning environment is a compelling value proposition in an increasingly competitive EdTech landscape.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion