Microsoft's takedown of criminal VDS provider RedVDS exposes critical security gaps exploited by threat actors across cloud environments, forcing organizations to reevaluate multi-cloud risk management.
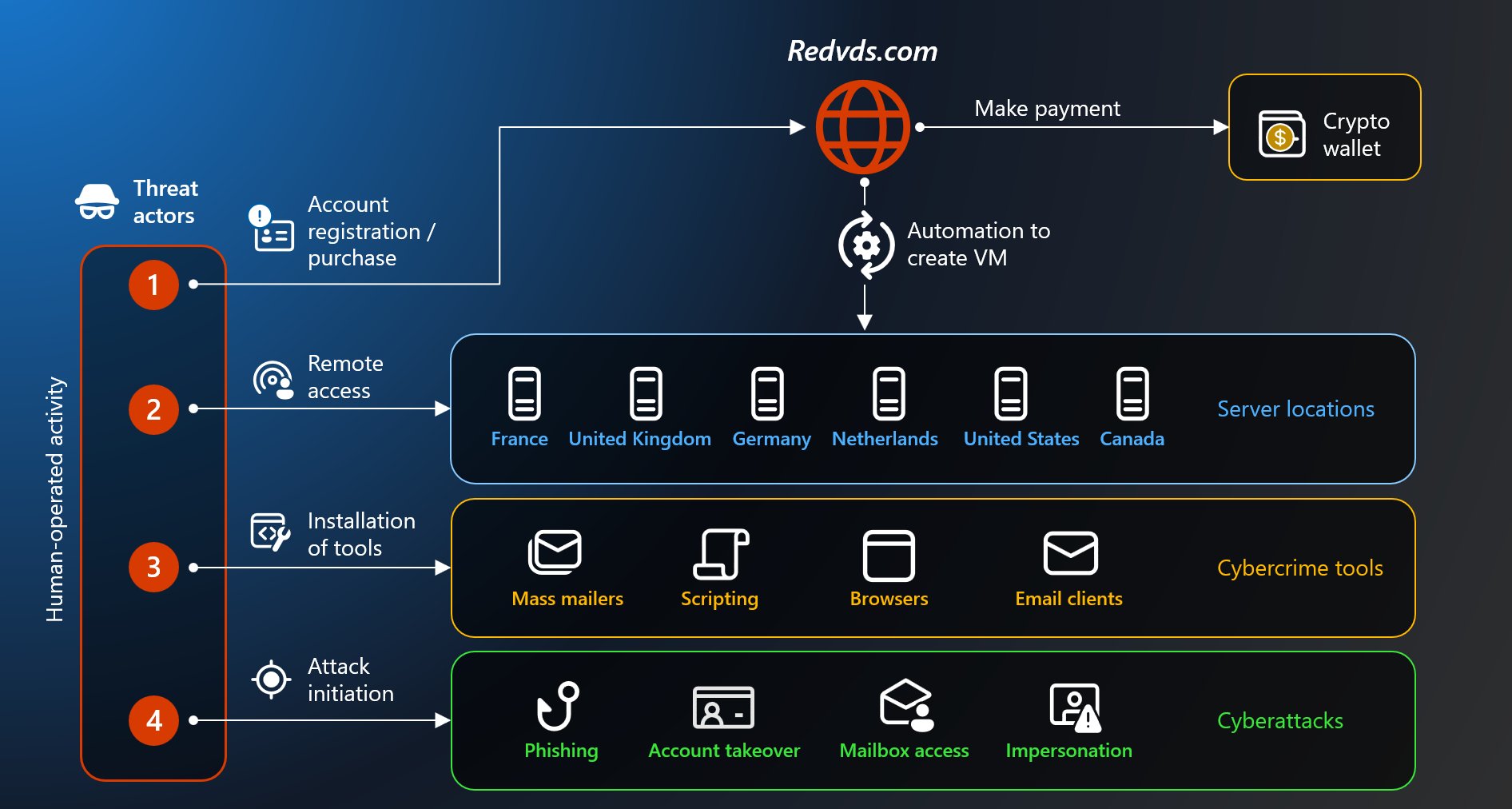
Microsoft's coordinated disruption of RedVDS infrastructure reveals fundamental security weaknesses criminals exploit across multi-cloud environments. This criminal virtual desktop provider enabled over $40 million in U.S. fraud losses alone by offering cloned Windows servers with identical forensic fingerprints – a stark contrast to commercial cloud providers' security practices.
What Changed: Criminal Infrastructure-as-a-Service Model
RedVDS operated as a criminal counterpart to legitimate cloud providers, offering Windows Server 2022 instances via RDP for cryptocurrency payments. Its operational model bypassed standard security controls:
- Cloned Infrastructure: All servers originated from a single Windows VM image (WIN-BUNS25TD77J) replicated via QEMU virtualization
- Anonymized Operations: Bitcoin/Litecoin payments with no usage logging or identity verification
- Geographic Evasion: Servers hosted across five providers in strategic locations (US/UK/Canada/France/Netherlands) to bypass geo-filters {{IMAGE:3}} Figure: RedVDS infrastructure cloning process enabled rapid deployment of identical malicious servers
Provider Comparison: Security Divergence
RedVDS exploited critical differences from enterprise cloud providers:
| Security Dimension | Legitimate Providers (Azure/AWS/GCP) | RedVDS Criminal Model |
|---|---|---|
| Provisioning | Randomized hostnames, unique IDs | Identical hostnames/hardware fingerprints |
| Authentication | Identity verification, compliance checks | Anonymous cryptocurrency payments |
| Monitoring | Activity logging, threat detection | No usage logs per terms of service |
| Software Licensing | Validated licenses | Stolen Windows Eval 2022 licenses |
| Geographic Control | Region-specific compliance | IPs strategically positioned near targets |
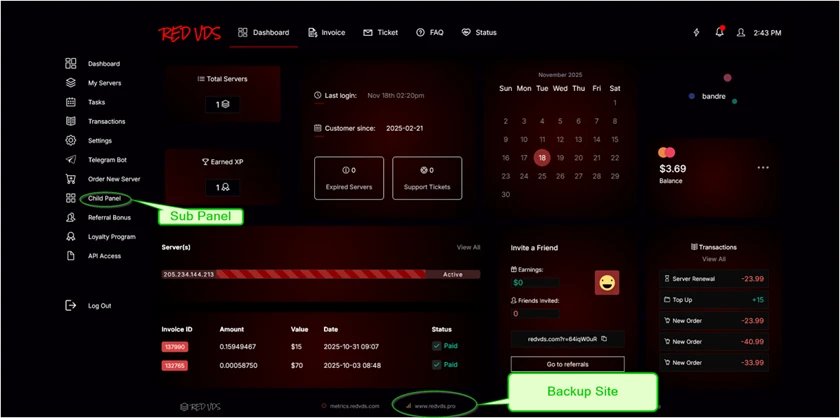 Figure: RedVDS user interface showing payment options and server configuration
Figure: RedVDS user interface showing payment options and server configuration
Business Impact: Multi-Cloud Threat Amplification
RedVDS enabled attacks against legal, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors by providing:
- Operational Scale: Automated phishing pipelines using tools like SuperMailer and AI-generated lures
- Attack Sophistication: Homoglyph domain hosting (3,700+ domains) for credible BEC attacks
- Evasion Advantage: Geographic distribution mimicking legitimate data center traffic patterns
 Figure: Global heatmap of RedVDS-enabled attacks showing concentration in banking centers
Figure: Global heatmap of RedVDS-enabled attacks showing concentration in banking centers
Financial implications extend beyond direct fraud losses. Recovery costs for credential compromises, mailbox takeovers, and system remediation create cascading operational impacts – particularly in industries with high transaction volumes.
Strategic Defense Recommendations
Organizations must adapt multi-cloud strategies with these security imperatives:
Infrastructure Hardening
- Implement host fingerprint detection for cloned system identifiers
- Enforce conditional access policies requiring phishing-resistant MFA
- Block RDP connections with self-signed certificates
Email Security Overhaul
- Configure Exchange Online Protection with DMARC enforcement
- Apply Safe Links policies to internal communications
- Conduct attack simulation training across Teams/email vectors
Cloud Workflow Controls
- Segment financial approval workflows from standard communications
- Implement payment verification protocols for vendor changes
- Restrict admin rights using Privileged Identity Management
Microsoft Defender XDR provides integrated detection for RedVDS-related activity including suspicious AnyDesk installations, inbox rule manipulation, and password spraying patterns. Security teams should prioritize these detection rules:
Compromised user account in recognized attack patternRisky sign-in following phishing email accessSuspicious mass-mailer tool execution

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion