OpenAI details how they scaled PostgreSQL to handle millions of queries per second for ChatGPT's massive user base through connection pooling, read replicas, caching innovations, and strategic workload migration.
When ChatGPT exploded to 100 million users within weeks of launch, OpenAI's engineering team faced an unprecedented database scaling challenge. Their core transactional database – PostgreSQL – suddenly needed to handle exponential growth, with loads increasing over 10x in a year. This technical deep dive reveals how they scaled PostgreSQL to support 800 million users through rigorous optimization while maintaining five-nines availability.
The Scaling Dilemma
OpenAI's architecture relies on a single Azure PostgreSQL primary instance for writes and nearly 50 geo-distributed read replicas. While PostgreSQL handles read-heavy workloads efficiently, three critical pressure points emerged:
- Write amplification: PostgreSQL's MVCC implementation causes significant overhead, where updating a single field copies entire rows and creates dead tuples
- Single-writer bottleneck: All writes route through one primary instance
- Replication lag: Adding replicas increases primary's WAL shipping overhead
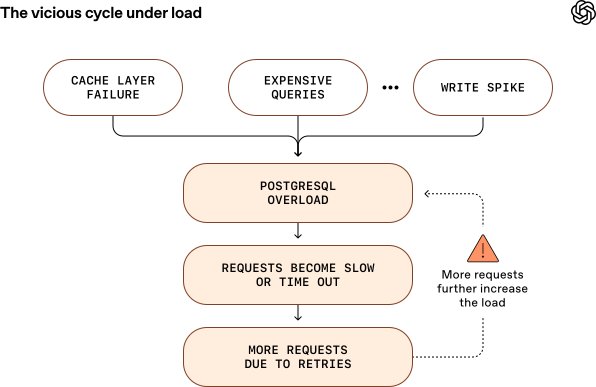 Caption: Scaling PostgreSQL under heavy load requires preventing vicious cycles of latency and retries
Caption: Scaling PostgreSQL under heavy load requires preventing vicious cycles of latency and retries
Architectural Solutions
Write Load Reduction
- Migrated shardable write-heavy workloads to Azure Cosmos DB
- Implemented lazy writes and write coalescing to smooth traffic spikes
- Enforced strict backfill rate limits (some operations take >1 week)
- Prohibited new tables in PostgreSQL, defaulting to sharded systems
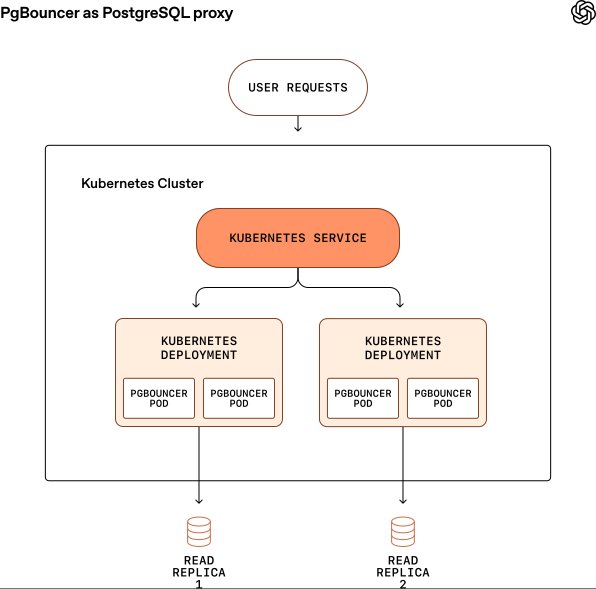
Connection Management Deploying PgBouncer in transaction pooling mode reduced connection setup latency from 50ms to 5ms and prevented connection storms:
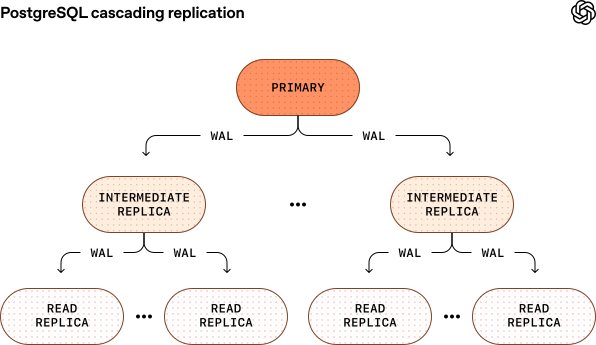
Replication Scaling With 50+ replicas, WAL shipping threatened to overwhelm the primary. OpenAI is testing cascading replication where intermediate replicas relay WAL downstream:
Cache Protection Implemented cache leasing:
- Only one request fetches data on cache miss
- Concurrent requests wait for populated cache
- Prevents cache-miss storms from overwhelming PostgreSQL
Critical Optimizations
- Query Tuning: Eliminated 12-table joins, moved complex joins to application layer
- Workload Isolation: Separated high/low-priority traffic to prevent "noisy neighbor" effects
- Schema Management: Restricted schema changes to lightweight operations avoiding full-table rewrites
- Rate Limiting: Implemented multi-layer throttling at application, proxy, and query levels
Performance Results
Despite scaling challenges, the team achieved:
- p99 latency in double-digit milliseconds
- 99.999% availability over 12 months
- Only one SEV-0 PostgreSQL incident during viral feature launch
- Capacity headroom for continued growth
Future Directions
- Complete migration of non-shardable write workloads
- Production rollout of cascading replication
- Evaluation of sharded PostgreSQL for future needs
This scaling journey demonstrates PostgreSQL's underappreciated capacity for massive read-heavy workloads. As OpenAI engineer Bohan Zhang notes: "With rigorous optimization, we've pushed PostgreSQL to handle millions of QPS while maintaining low latency and high reliability – something many considered impractical at our scale."

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion