As organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies, automated privilege enforcement becomes critical. We analyze how Azure Functions compare with AWS Lambda and Google Cloud Functions in implementing least-privilege access controls, examining architectural patterns, cost implications, and migration considerations.

The Shift Toward Automated Privilege Enforcement
Recent incidents involving overprivileged accounts have accelerated cloud providers' investments in automated privilege management solutions. Where manual processes once dominated, we now see:
- Azure's Functions-based approach (as demonstrated in our technical implementation) using timer-triggered automation with Databricks SDK integration
- AWS Lambda with IAM Access Analyzer combining event-driven triggers with policy validation
- Google Cloud Functions paired with Privileged Access Manager using AI-driven anomaly detection
This evolution reflects growing enterprise demand for continuous compliance rather than periodic audits.
Provider Comparison: Implementation Patterns
| Capability | Azure | AWS | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execution Model | Timer/Event-triggered Functions | EventBridge-triggered Lambdas | Cloud Scheduler-triggered Functions |
| Privilege Validation | Databricks SDK + Managed Identity | IAM Access Analyzer APIs | Cloud Asset Inventory + Policy Troubleshooter |
| Native Integration | Azure PIM | AWS Organizations SCPs | GCP Policy Intelligence |
| Pricing Model | Per-second execution + app plan costs | Per-request + compute duration | per-second execution + memory allocation |
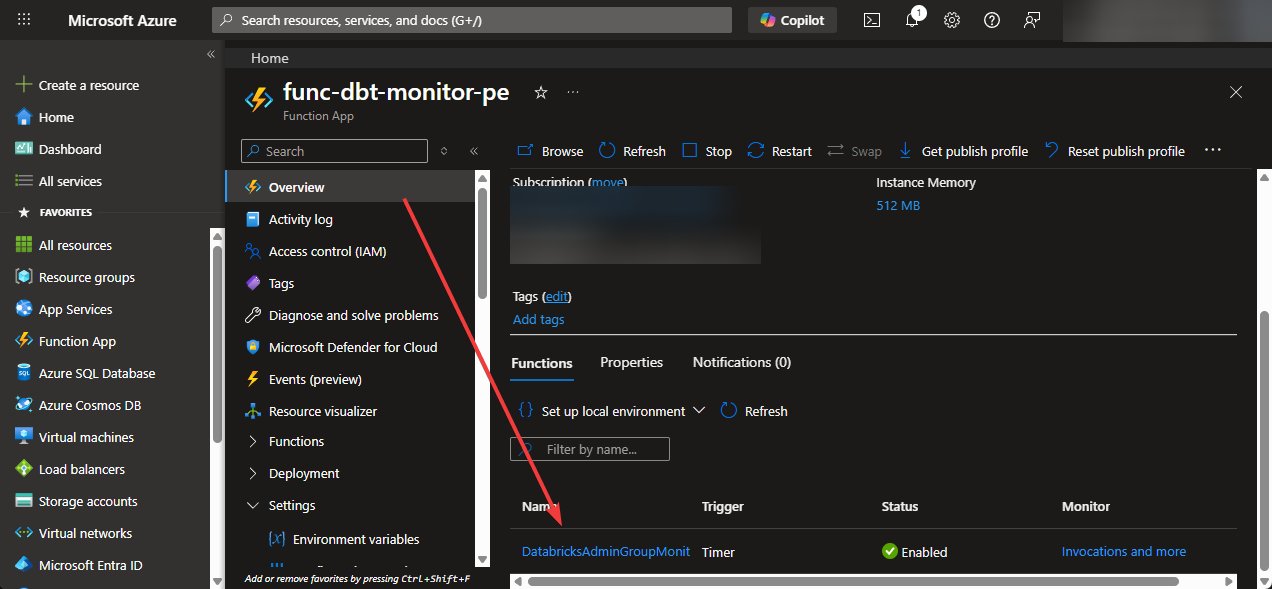 Figure 1: Architectural comparison of privilege management workflows
Figure 1: Architectural comparison of privilege management workflows
Key Technical Differences:
- Azure leverages tight integration with Entra ID and resource manager APIs, enabling deep subscription-level visibility
- AWS emphasizes event-driven architectures through CloudTrail integration
- GCP prioritizes policy-as-code implementations using Deployment Manager
Business Impact Analysis
Cost Considerations:
- Azure's Flex Consumption model proves cost-effective for frequent (5-15 minute) checks
- AWS's per-request pricing benefits irregular monitoring patterns
- GCP's sustained use discounts favor 24/7 monitoring implementations
Migration Challenges:
- Databricks-specific implementations (like our example) require significant rework when moving to AWS SageMaker or GCP Vertex AI
- Identity mapping between Azure Managed Identities and AWS IAM Roles creates integration complexity
- Policy translation between Azure RBAC and AWS IAM introduces governance gaps
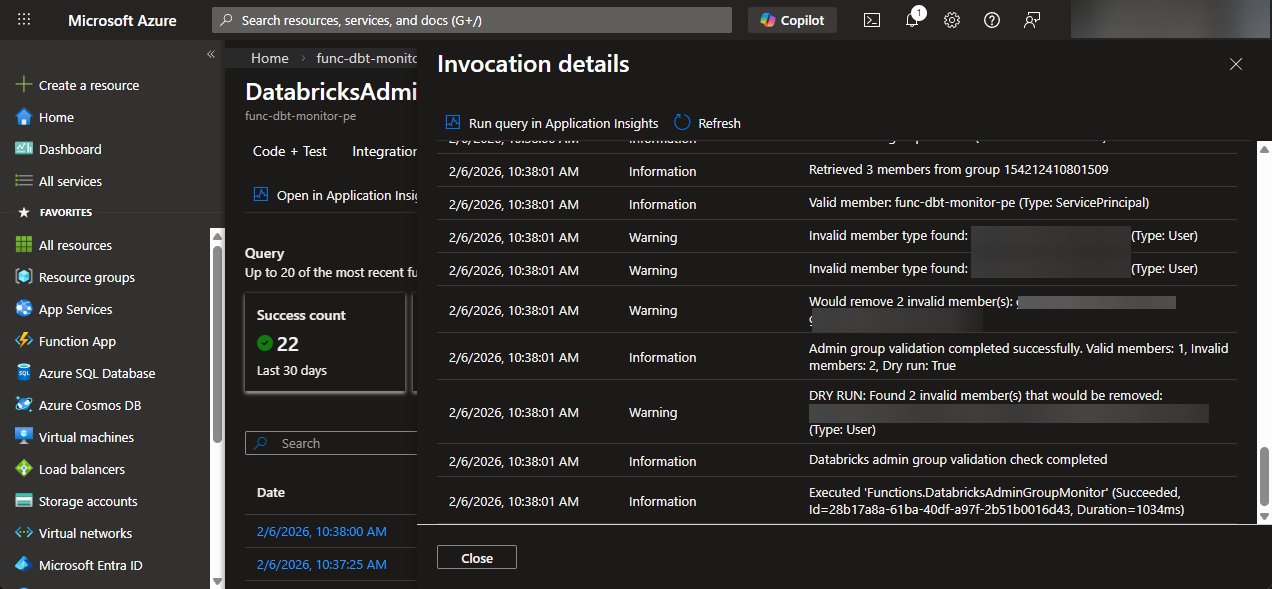 Figure 2: Cross-provider privilege management maturity assessment
Figure 2: Cross-provider privilege management maturity assessment
Strategic Recommendations
- Hybrid Approaches: Use Azure Functions for Microsoft ecosystem tools while employing AWS Lambda for Amazon-native services
- Cost Optimization: Implement provider-specific monitoring intervals based on pricing models (e.g., frequent checks in Azure vs. event-driven in AWS)
- Migration Pathway:
- Establish central identity provider (e.g., Okta) before cross-cloud migrations
- Use intermediary tools like HashiCorp Boundary for consistent access controls
- Leverage CloudHealth by VMware for unified policy monitoring
Emerging Patterns
Leading organizations now combine these approaches:
- Azure Functions for Active Directory-integrated systems
- AWS Lambda for infrastructure-centric controls
- GCP Cloud Functions for data-centric governance with centralized reporting through tools like SailPoint.
As cloud environments grow in complexity, the strategic selection and implementation of privilege management automation becomes a critical competitive differentiator. Enterprises must weigh provider-specific capabilities against their existing investments and future roadmap when designing these systems.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion