Benedict Evans analyzes OpenAI's core challenges: despite massive adoption, user engagement remains shallow, while tech giants rapidly match its capabilities.
OpenAI's ChatGPT became the fastest-growing consumer application in history, amassing over 100 million weekly active users within months of launch. Yet according to analyst Benedict Evans, this impressive scale masks fundamental vulnerabilities. The core issue lies in what Evans describes as "very large user base but very narrow engagement" – most interactions remain brief, transactional queries rather than deep workflow integration.
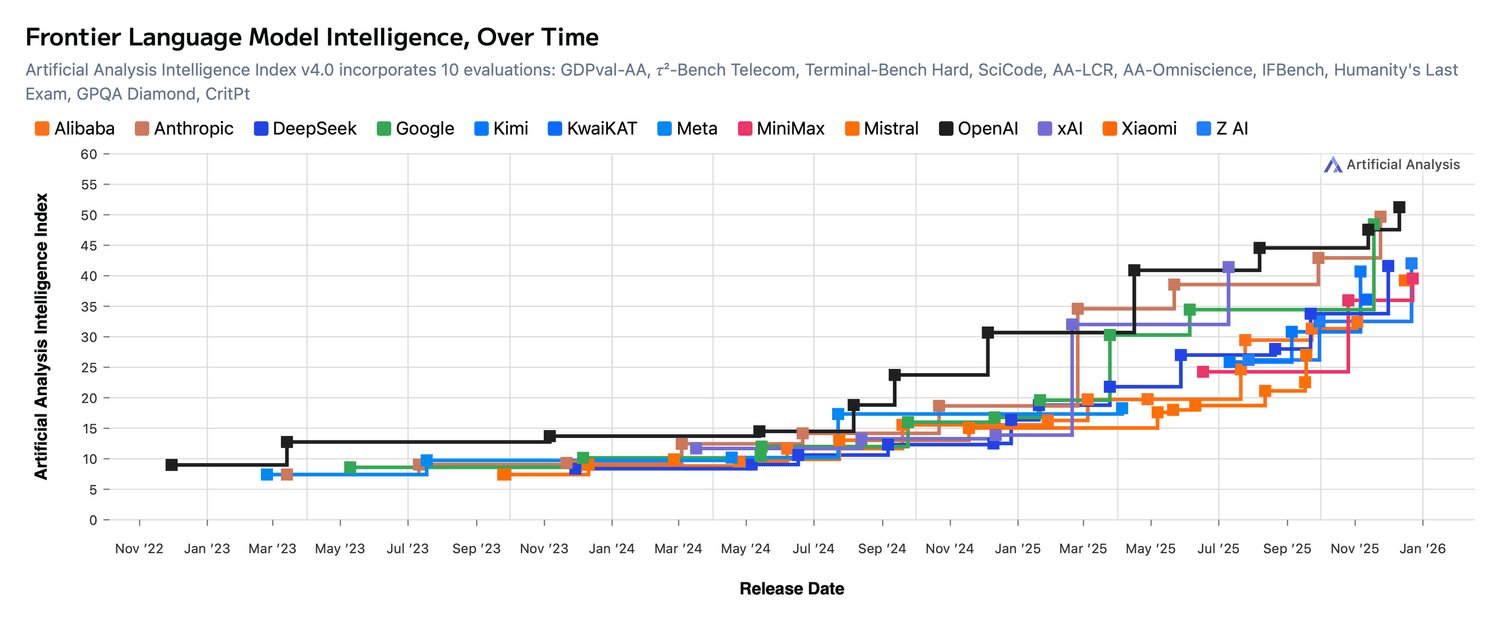 Frontier language model capabilities over time show competitive convergence (Source: Benedict Evans)
Frontier language model capabilities over time show competitive convergence (Source: Benedict Evans)
This engagement gap coincides with another critical challenge: rapid competitive convergence. When OpenAI released GPT-4 in 2023, its capabilities significantly outpaced offerings from Google, Meta, and Anthropic. By early 2026, that gap has substantially narrowed. Anthropic's Claude 3 series matches GPT-4 Turbo on most academic benchmarks while offering longer context windows. Google's Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves comparable reasoning performance with lower latency. Microsoft's Copilot ecosystem leverages OpenAI's own technology while layering enterprise integrations unavailable in ChatGPT.
Evans highlights OpenAI's research-driven culture as both strength and vulnerability: "Jakub and Mark set the research direction for the long run. Then after months of work, something incredible emerges." This approach yielded transformative models like GPT-3 and GPT-4. However, the iterative nature of AI advancement means competitors quickly replicate breakthroughs. Meta's open-source Llama models demonstrated how architectural innovations quickly disseminate across the industry.
Three structural limitations compound these challenges:
- Monetization-pressure mismatch: OpenAI projects $280B revenue by 2030 against $600B compute investments. Yet shallow user engagement makes premium subscription conversion difficult outside professional niches.
- Commoditization of base capabilities: As reasoning benchmarks plateau, differentiation shifts to specialized datasets, real-time data integration, and workflow design – areas where Salesforce, Adobe, and Microsoft hold advantages.
- Distribution dependency: Despite ChatGPT's brand recognition, over 60% of generative AI interactions occur within other platforms (Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, GitHub Copilot), limiting OpenAI's direct user relationships.
Recent industry developments underscore these dynamics. Anthropic's Claude Code Security demonstrates how competitors rapidly build specialized offerings atop foundational models. Meanwhile, OpenAI's rumored pursuit of $7 trillion for AI infrastructure suggests recognition that hardware scale may become its defensible moat as software advantages diminish.
The path forward likely requires reinvention beyond pure model development. As Evans implies, winning requires transforming ChatGPT from a curiosity into an indispensable daily tool – something neither engagement patterns nor competitive pressure currently support. For OpenAI, the post-scale era demands solving the engagement paradox before incumbents fully absorb its innovations.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion