A new open source project brings Mistral AI's Voxtral speech recognition model to low-level environments with a dependency-free C implementation and streaming API.
Developers now have a portable way to run Mistral AI's Voxtral Realtime 4B speech-to-text model thanks to a new pure C implementation from creator Salvatore Sanfilippo (antirez). The project eliminates Python and CUDA dependencies while maintaining real-time transcription capabilities through an efficient streaming architecture.
The implementation features two key components: a self-contained Python reference for understanding the model's mechanics, and a production-oriented C version optimized for Apple Silicon's Metal Performance Shaders. This dual approach addresses what Sanfilippo describes as unnecessary complexity in existing inference solutions, writing in the project's documentation: "Limiting the inference to a partnership with vLLM, without providing a self-contained reference implementation in Python, limits the model's actual reach."
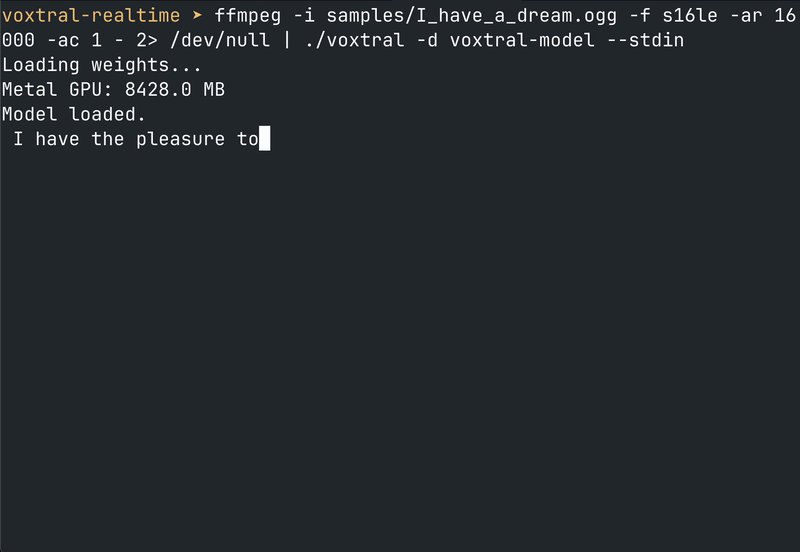
Technical highlights include:
- Zero-dependency operation: Only requires C standard library for basic functionality
- Metal GPU acceleration: Achieves 23.5ms per token generation on Apple M3 Max
- Memory-mapped weights: 8.9GB model loads instantly via mmap
- Circular KV cache: Enables unlimited audio length with fixed memory footprint
- Live microphone support: macOS users can transcribe directly from device input
Performance benchmarks show the Metal-accelerated version running 2.5x faster than real-time on modern Apple hardware, while the BLAS-compatible version remains viable for Intel and Linux systems. The project implements Mistral's sliding window attention with a 750-token context window, automatically compacting older states to maintain consistent memory usage.
Developers can integrate the transcription capabilities through:
- Command-line interface: Supports WAV files, stdin piping, and live mic input
- C streaming API: Enables incremental audio processing with callback-based token delivery
- Python reference: Provides educational implementation using PyTorch
The GitHub repository includes complete build instructions for macOS and Linux, along with a model download script that fetches the Apache-2.0 licensed weights. Early adopters should note the implementation remains experimental, with the creator cautioning that "more testing needed" against long-form audio samples.
This project demonstrates how core AI models can be made accessible beyond the Python ecosystem, potentially enabling integration into embedded systems, mobile applications, and other performance-sensitive environments where minimal dependencies are critical.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion