Microsoft's new Infrastructure as Code templates streamline PostgreSQL deployments on Azure VMs with Azure NetApp Files, transforming multi-hour manual configurations into consistent, secure environments deployable in minutes.
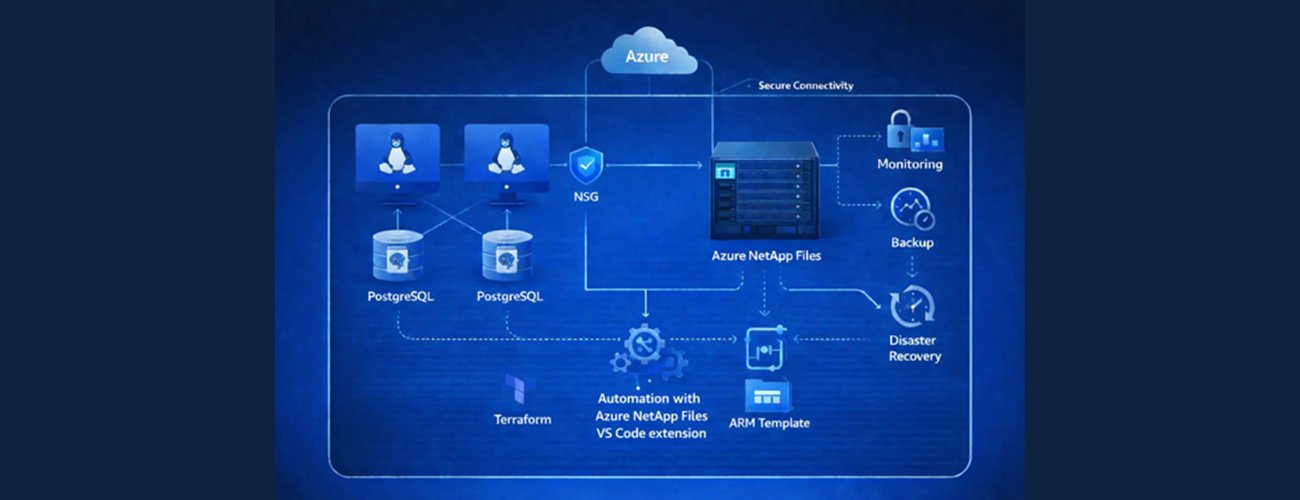
Deploying PostgreSQL on Azure virtual machines with high-performance storage traditionally required extensive manual configuration across networking, storage, and database layers. This complexity created significant bottlenecks for teams managing development, testing, and production environments. Microsoft's newly released Infrastructure as Code (IaC) templates fundamentally change this dynamic by automating the entire deployment process for PostgreSQL on Azure VMs using Azure NetApp Files storage.
Storage Performance Comparison: Azure NetApp Files vs Alternatives
Azure NetApp Files provides differentiated performance characteristics crucial for database workloads when compared to standard Azure storage options:
| Storage Solution | Latency | Scalability Approach | Database-Optimized Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Azure NetApp Files | Consistent sub-millisecond | Independent scaling of capacity/performance | Instant snapshots, built-in replication |
| Azure Managed Disks | Variable (shared infrastructure) | Coupled with VM size | Limited native snapshot capabilities |
| Azure Blob Storage | Higher latency | Scale independently but not performance-optimized | Cost-effective for backups only |
Azure NetApp Files offers three distinct service tiers:
- Standard: 16 MiB/s per TB (development/low I/O)
- Premium: 64 MiB/s per TB (production databases)
- Ultra: 128 MiB/s per TB (high-performance analytics)
The Flexible tier provides independent throughput/capacity scaling, enabling precise cost optimization. This tiered approach contrasts sharply with managed PostgreSQL services like Azure Database for PostgreSQL, which offer less storage customization but lower administrative overhead.
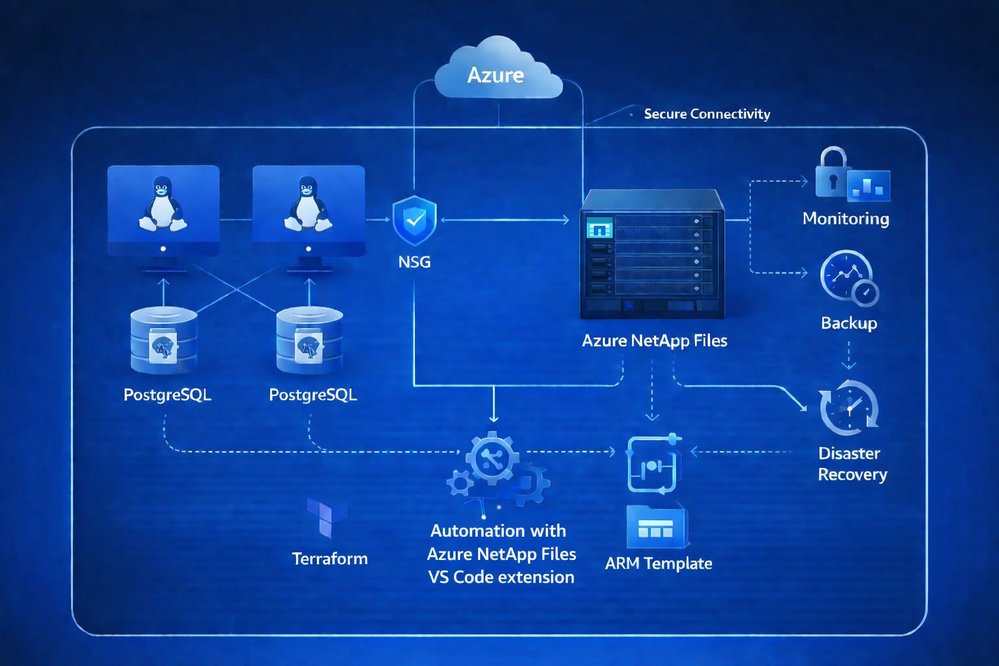
Deployment Transformation: Manual vs Automated
Traditional Deployment Process (6-10 hours per environment):
- Infrastructure provisioning: VMs, networking (2-3 hours)
- Storage configuration: Azure NetApp Files pools, volumes, NFS exports (1-2 hours)
- PostgreSQL installation and configuration (1-2 hours)
- Database initialization and security hardening (30-60 minutes)
Automated IaC Deployment (Under 1 hour): The templates encapsulate best practices across three deployment modalities:
- Terraform: For multi-cloud or complex infrastructure needs
- ARM Templates: Native Azure deployments via portal or DevOps pipelines
- PowerShell: Script-based automation for Windows-centric teams
The automation handles everything from subnet delegation to PostgreSQL initialization, eliminating manual SSH sessions and configuration drift.
Business and Operational Impact
Development Acceleration Teams can now provision production-equivalent PostgreSQL instances in minutes instead of days, with built-in security policies and performance optimization. This eliminates the "works in dev, fails in prod" syndrome through environment parity.
Economic Advantages
- Cost Control: Shut down non-production environments when inactive
- Reduced Defect Costs: Consistent configurations minimize production issues
- Optimized Storage: Right-size performance tiers using Flexible service levels
Migration Efficiency
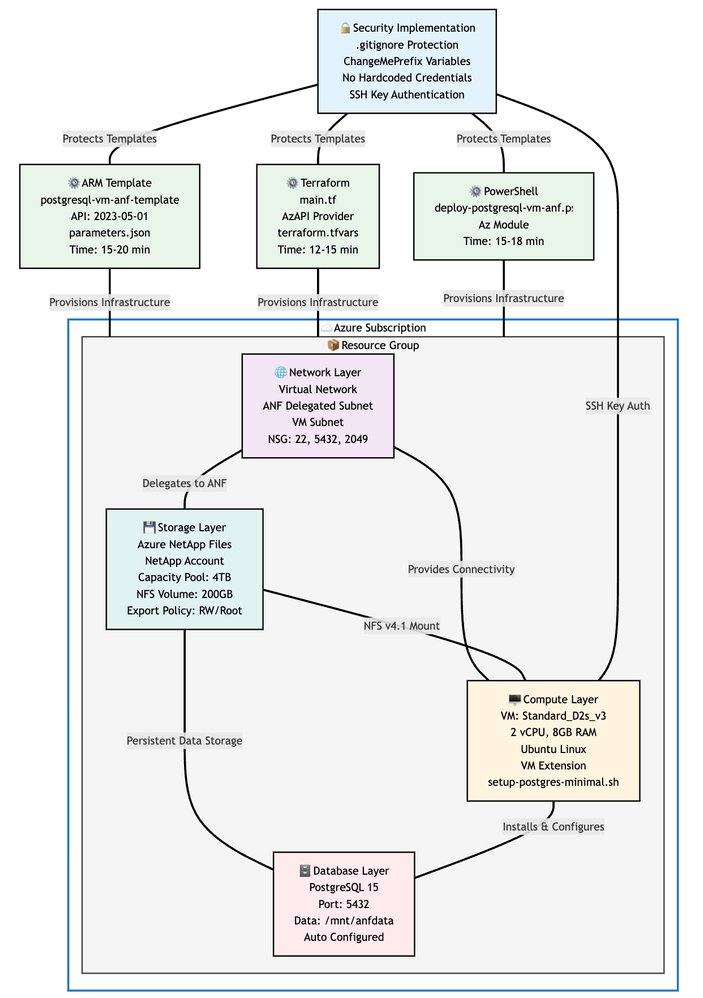
For database migrations, the solution enables:
- Accelerated data transfers via high-throughput NFS
- Snapshot-based rollback capabilities
- Phased cutovers with minimal downtime This reduces migration risks and business disruption costs compared to manual approaches.
Strategic Implementation Considerations
When to Choose This Approach Over Managed Services
- Required: Full control over PostgreSQL configuration and extensions
- Needed: Custom storage performance profiles
- Existing: Investment in VM-based infrastructure
Cost-Benefit Analysis While Azure Database for PostgreSQL offers simpler management, this VM-based approach provides:
- 30-50% storage cost savings for high-IOP workloads
- Custom tuning for specialized extensions like pgvector
- No restrictions on PostgreSQL version or configuration
Implementation Recommendations
- Start with development environments to validate throughput requirements
- Use Flexible service tier for variable workloads
- Integrate deployment pipelines with CI/CD systems
- Leverage Azure NetApp Files snapshots for point-in-time recovery
Future Evolution
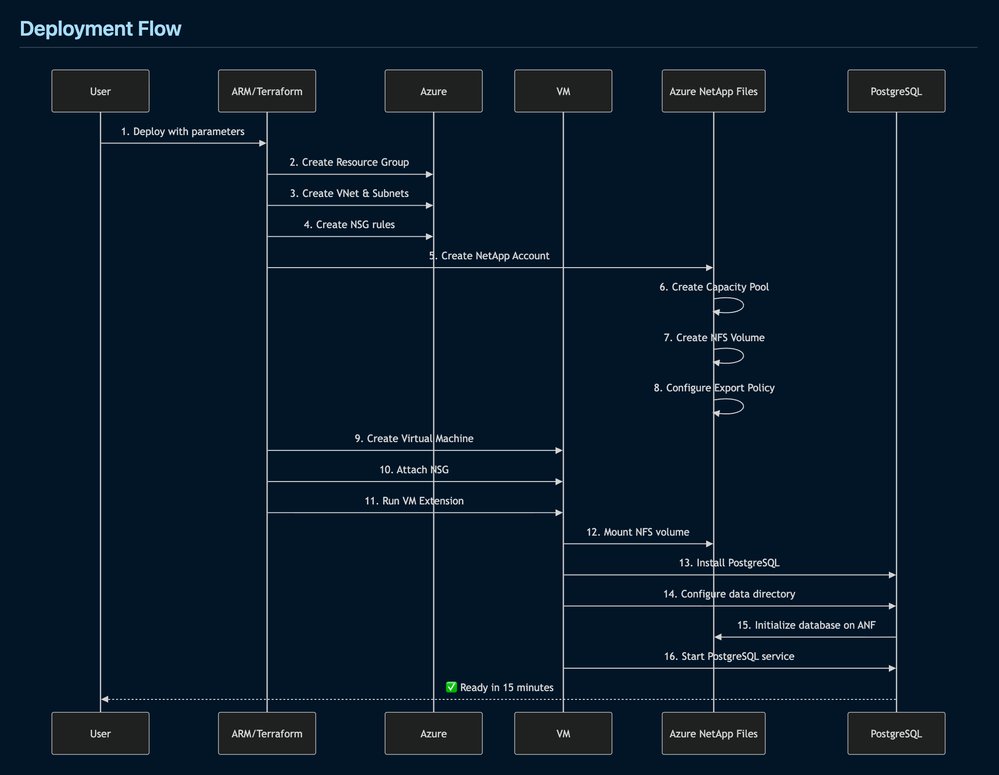
The templates currently support single-node deployments. For production critical systems, consider complementing with:
- PostgreSQL streaming replication between multiple VMs
- Azure NetApp Files cross-region replication
- Scheduled snapshot policies for backup Microsoft indicates future template versions may incorporate these high-availability patterns.
Conclusion
These IaC templates significantly reduce the operational burden of deploying PostgreSQL on Azure infrastructure while maintaining enterprise-grade performance through Azure NetApp Files. By automating what was previously a fragmented, error-prone process, organizations gain:
- Consistent environments across development-to-production pipelines
- 80-90% reduction in deployment time
- Built-in security and performance optimization
For teams requiring granular control over PostgreSQL configurations alongside high-performance storage, this solution presents a compelling alternative to managed database services. The templates are available in the azure-netapp-files-storage GitHub repository, with detailed documentation for Terraform, ARM, and PowerShell deployments. Azure NetApp Files capabilities are further documented in Microsoft's official storage documentation.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion