A innovative technique swaps learned lookup tables for binned Gaussian splats in vision transformers, enabling the generation of 8x8 image patches that render at arbitrary resolutions without fixed constraints. By leveraging differentiable splatting and custom kernels, this approach reduces blur and boundary seams in AI-generated imagery, as demonstrated through cat synthesis experiments. The method's flexibility could transform high-res workflows in generative AI, balancing visual fidelity with
Gaussian Splats Replace Lookup Tables in Vision Transformers for Scalable Image Patch Generation
Vision transformers have redefined image processing by treating patches as tokens, but generating high-fidelity visuals at scale remains a hurdle. In a compelling follow-up to prior work on patch-based synthesis, a technical exploration introduces binned Gaussian splats as a dynamic alternative to static learned lookup tables. This shift allows for flexible, resolution-agnostic rendering of 8x8 patches, opening new avenues for efficient generative modeling in AI-driven applications.
Decoding the Splat Mechanism
The foundation lies in a specialized splat kernel: a cosine-modulated function that mimics a Gaussian but incorporates sinc-like oscillations, dipping below zero to sharpen edges and curb blur—much like wavelet transforms. Within each patch, the transformer outputs parameters for 16 splats, specifying mean positions, RGB values, precision matrices for elliptical shapes, and depth for alpha blending. Rendering sums these functions pixel-by-pixel, ensuring differentiability for seamless backpropagation.
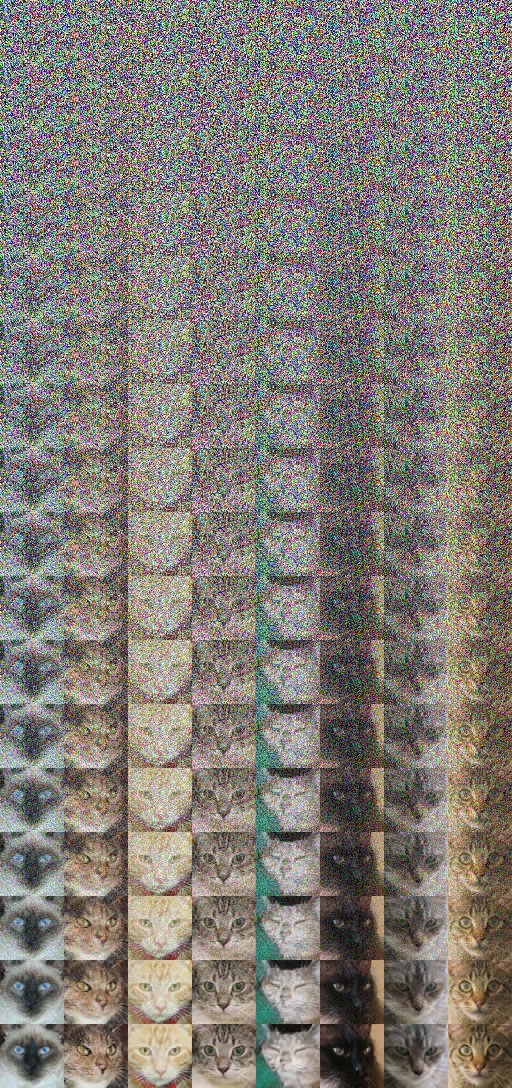
Training mirrors denoising diffusion paradigms, using a lerp-to-noise objective where the model refines noisy inputs into clean patches. The setup retains a familiar architecture: 16 self-attention layers processing 64 tokens per image. Remarkably, rollouts produce coherent cat generations with limited artifacts, highlighting the splats' capacity to model complex textures from probabilistic mixtures.

Scalability Gains and Boundary Challenges
The splat approach shines in its adaptability—unlike rigid lookup tables, patches render on expanded grids for higher resolutions, sidestepping the need for upsampling hacks. This could streamline workflows for developers in animation or augmented reality, where dynamic scaling enhances usability. Yet, patch independence breeds issues: seams emerge at edges during upscaling, as the model optimizes splats in isolation.
Normalized splats, visualized as uniform blobs, reveal the model's strategy—central splats dominate while peripherals align boundaries for continuity.  zooms into these interactions, exposing how positional tuning fosters subtle overlaps. Experiments suggest remedies like more splats per patch or broader training contexts, though these inflate complexity.
zooms into these interactions, exposing how positional tuning fosters subtle overlaps. Experiments suggest remedies like more splats per patch or broader training contexts, though these inflate complexity.
Kernel Tweaks for Sharper, Artistic Outputs
To amplify detail, the kernel evolves into sharper variants—a piecewise function sans negative lobes for stable blending. This curbs diffusion-induced softness, making features like whiskers or fur patterns stand out vividly. Applied to cat synthesis, the results impress: generations gain a polished, almost hand-crafted aesthetic, proving splats' versatility beyond technical utility.


Global splat optimization for full images falters on convergence speed, prompting a hybrid fix: extend evaluation to 3x3 patch neighborhoods, sharing splats across borders. This 10x computational hit yields near-seamless coherence, with light retraining restoring equilibrium. Such refinements underscore the technique's potential, albeit at a resource cost that invites optimization innovations.
Reshaping Generative Frontiers
By fusing transformer efficiency with splat rendering's fluidity, this method enriches the generative AI toolkit, particularly for vision tasks demanding spatial precision. Developers stand to benefit from its resolution independence, potentially accelerating tools in creative pipelines or scientific visualization. As seam mitigation evolves—perhaps via distributed computing or advanced priors—the balance of quality and speed could propel patch-based models into mainstream adoption, reimagining how AI crafts the visual world pixel by pixel.
Source: Generating Cats with Gaussian Splats by Alex Schr"odinger, November 30, 2025.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion