A sophisticated GoBruteforcer botnet campaign is targeting cryptocurrency platforms through FTP and database vulnerabilities, leveraging AI-generated defaults and legacy web stacks.
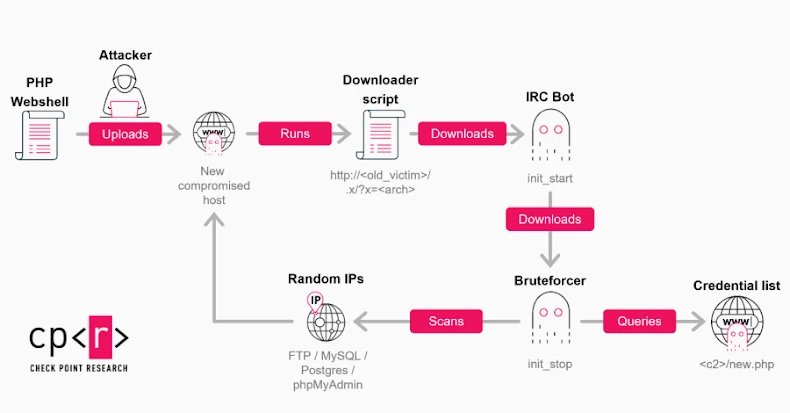
Security researchers have uncovered a new wave of attacks by the GoBruteforcer botnet specifically targeting cryptocurrency and blockchain infrastructure. This campaign exploits weak credentials in services like FTP, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and phpMyAdmin on Linux servers, converting compromised systems into attack nodes.
According to Check Point Research, attackers are capitalizing on two critical vulnerabilities: "The mass reuse of AI-generated server deployment examples that propagate common usernames and weak defaults, and the persistence of legacy web stacks such as XAMPP that expose FTP and admin interfaces with minimal hardening."
The malware, first documented in 2023, has evolved significantly. The latest variant analyzed in mid-2025 features:
- Heavily obfuscated IRC bot rewritten in Golang
- Enhanced persistence mechanisms
- Process-masking techniques
- Dynamic credential lists targeting crypto environments
Credentials being exploited include predictable combinations like cryptouser:Abcd@123 and root:admin123456 – defaults frequently appearing in database tutorials and vendor documentation. These patterns have been reinforced by large language models (LLMs) reproducing the same vulnerable configurations in code snippets.
Attack Methodology:
- Initial Access: Exploits exposed FTP services on XAMPP servers
- Web Shell Deployment: Uploads PHP-based backdoor
- Bot Installation: Downloads architecture-specific IRC bot via shell script
- Brute-Force Operations: Scans internet for vulnerable FTP/DB services
Compromised hosts serve triple purposes: password brute-forcing, payload hosting for other infected systems, and acting as backup command-and-control nodes. Evidence shows attackers have developed specialized modules to scan TRON blockchain addresses for accounts with non-zero balances using tronscanapi[.]com.
Practical Protection Measures:
- Credential Hygiene: Replace all default credentials with complex, unique passwords
- Service Hardening: Disable unused services (especially FTP/admin panels) and implement network segmentation
- LLM Safeguards: Audit AI-generated deployment scripts for embedded credentials
- Monitoring: Deploy intrusion detection for repeated authentication attempts
- Patch Management: Immediately update legacy stacks like XAMPP
Check Point emphasizes that while "the botnet itself is technically straightforward, its operators benefit from the vast number of misconfigured services that remain online." This campaign coincides with GreyNoise findings of systematic scanning for exposed LLM endpoints, highlighting the expanding attack surface in decentralized infrastructure.
Blockchain projects face elevated risks due to the combination of valuable assets and frequently overlooked administrative interfaces. Regular credential rotation and strict access controls for database services are non-negotiable for crypto-focused organizations.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion