Google Fiber’s rollout of a new 20 Gbps optical network terminal (ONT) shatters the long‑standing 10 Gbps barrier, delivering symmetrical speeds that meet the demands of next‑generation AI workloads and immersive media. The deployment, powered by a 25 Gbit/s passive optical network (PON), signals a strategic shift toward future‑proof infrastructure for both residential and enterprise customers.
A New Benchmark for Residential and Enterprise Connectivity
Google Fiber’s latest public update, released on December 3 2025, details the first commercial installation of its GFiber 20 Gbps ONT. The device, a three‑times smaller iteration of its predecessor, is built on a 25 Gbit/s PON foundation that allows the network to deliver up to 19.9 Gbps downstream and 19.6 Gbps upstream—symmetrical speeds that were previously unimaginable for a fiber‑to‑the‑home (FTTH) service.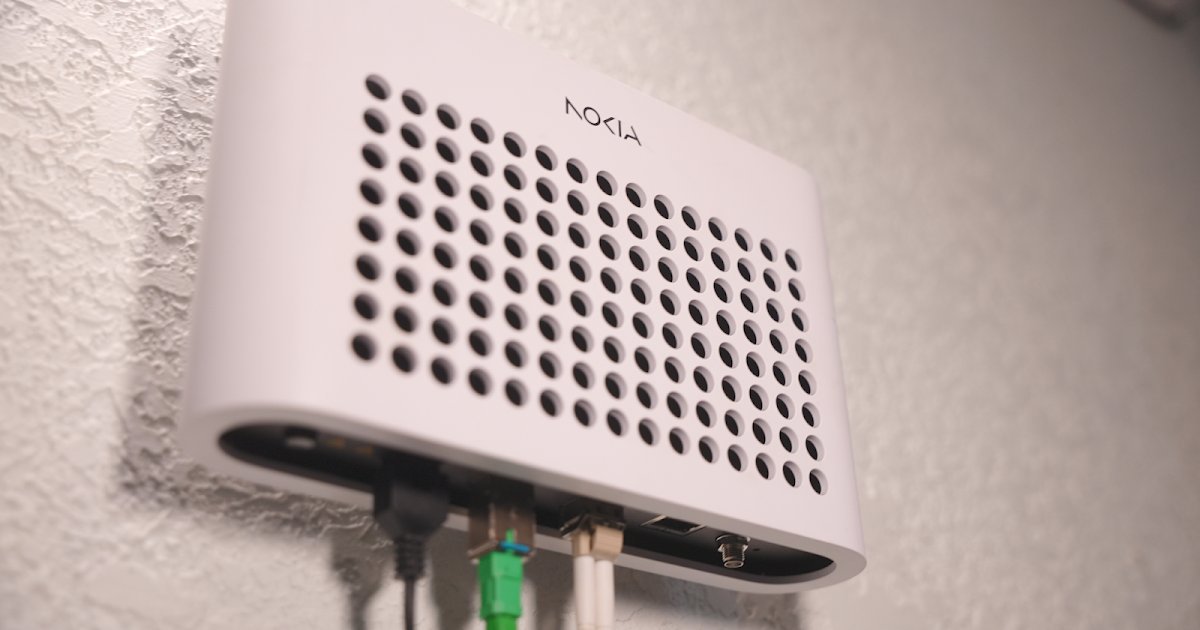 
The company’s early‑access program was launched with an audacious goal: to break the 10 Gbps ceiling that has long constrained broadband architectures. By investing in 25 G PON technology, Google Fiber has positioned roughly 90 % of its footprint as 20 Gbps‑capable, a figure that dwarfs the reach of current XGS (10 Gbps) or DOCSIS cable networks.
How 25 G PON Enables 20 Gbps Symmetry
Passive optical networks (PONs) rely on a shared fiber trunk that splits signals to multiple endpoints via optical splitters. Traditional XGS-PON (10 Gbit/s) can deliver 10 Gbps downstream and 10 Gbps upstream, but the bandwidth is shared among all users on the same split. In contrast, 25 G PON doubles the downstream capacity and quadruples the upstream bandwidth relative to XGS. By pairing this with a more efficient ONT that consumes less power and occupies less space, Google Fiber can push the entire 25 G bandwidth to a single customer.
"The 25 G PON is the foundation that will support the next wave of multimodal AI and immersive media," says Liz Hsu, Senior Director of Product & Billing at Google Fiber. "It’s not just about speed; it’s about delivering a future‑proof platform that can scale with the demands of our users."
Real‑World Performance and Customer Impact
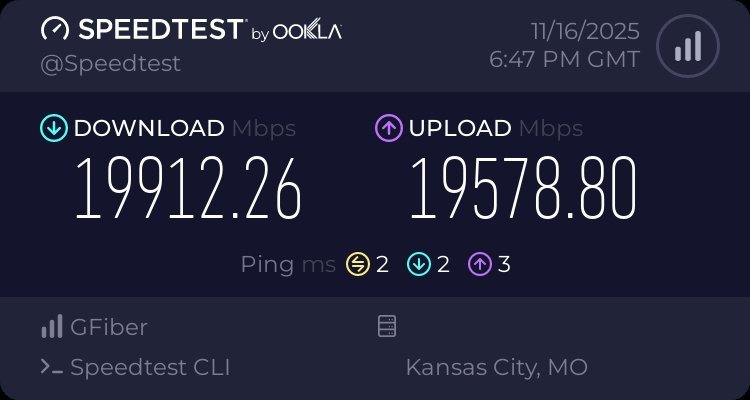
A November 16, 2025 speed test conducted by a GFiber customer yielded 19.9 Gbps download and 19.6 Gbps upload—figures that validate the company’s strategic investment. The test was repeated across multiple households, confirming consistency and reliability.
For residential power users, the leap to 20 Gbps means near‑instantaneous streaming of 8K video, real‑time collaboration on large datasets, and seamless participation in virtual reality environments. Enterprise customers—such as research institutions and data‑centric startups—benefit from reduced latency and higher throughput, enabling faster model training, real‑time analytics, and robust cloud connectivity.
The Bigger Picture: A Future‑Proof Foundation
Google Fiber’s 20 Gbps rollout is more than a marketing milestone; it represents a strategic shift toward densifying the network without laying new fiber lines. The 25 G PON architecture reduces the need for additional fiber deployments, lowering capital expenditure and accelerating time to market.
Industry analysts note that the move aligns with the broader trend of telecom operators adopting higher‑capacity PONs to meet the bandwidth demands of AI, edge computing, and the Internet of Things. By delivering a single, scalable foundation, Google Fiber sets a benchmark that competitors may soon need to match.
Closing Thoughts
Google Fiber’s 20 Gbps ONT demonstrates that ambitious speed goals can be achieved through thoughtful investment in optical network technology. As AI workloads continue to grow and consumers demand richer media experiences, the 25 G PON and its 20 Gbps endpoint will likely become the new baseline for high‑performance broadband.
{{IMAGE:5}}
For more details on the technical specifications and deployment roadmap, visit the official Google Fiber blog post.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion