Meta will deploy Nvidia's Arm-based Grace CPUs as standalone processors across its AI data centers, reporting up to 2x performance-per-watt improvements, with next-gen Vera CPUs entering production in 2027 alongside Spectrum-X networking upgrades.
Meta is accelerating its AI infrastructure strategy through a multi-year partnership with Nvidia that includes deploying standalone Grace CPUs across production data centers. This marks the industry's first large-scale implementation of Nvidia's Arm-based server processors without paired GPUs. The hyperscaler confirmed plans to integrate "millions" of Nvidia Blackwell and Rubin GPUs alongside these CPU deployments as part of its broader $135 billion AI infrastructure investment targeting 2026.
Technical Specifications: Grace to Vera Transition
Nvidia's Grace CPU leverages 72 Arm Neoverse V2 cores with configurations supporting up to 480GB of LPDDR5X memory in single-chip packages or 144 cores with 960GB memory in dual-chip Superchip designs connected via NVLink-C2C. Meta reports these configurations deliver up to twice the performance per watt for specific CPU-bound workloads compared to previous solutions.
The next-generation Vera CPU, already in testing with Meta, scales to 88 custom Arm cores (176 threads) with 1.5TB LPDDR5X memory capacity and 1.2TB/s bandwidth. Scheduled for production deployment in 2027, Vera introduces PCIe Gen6 and CXL 3.1 connectivity while becoming Nvidia's first CPU supporting confidential computing across entire rack-scale systems. Early benchmarks indicate "very promising" efficiency gains according to Nvidia executives.
Infrastructure and Market Implications
Beyond processors, Meta will implement Nvidia's Spectrum-X Ethernet switches featuring co-packaged optics. This architecture eliminates separate optical transceivers, reducing networking power consumption by up to 10% per rack—critical when scaling to GPU-dense AI clusters where power constraints increasingly dictate compute density.
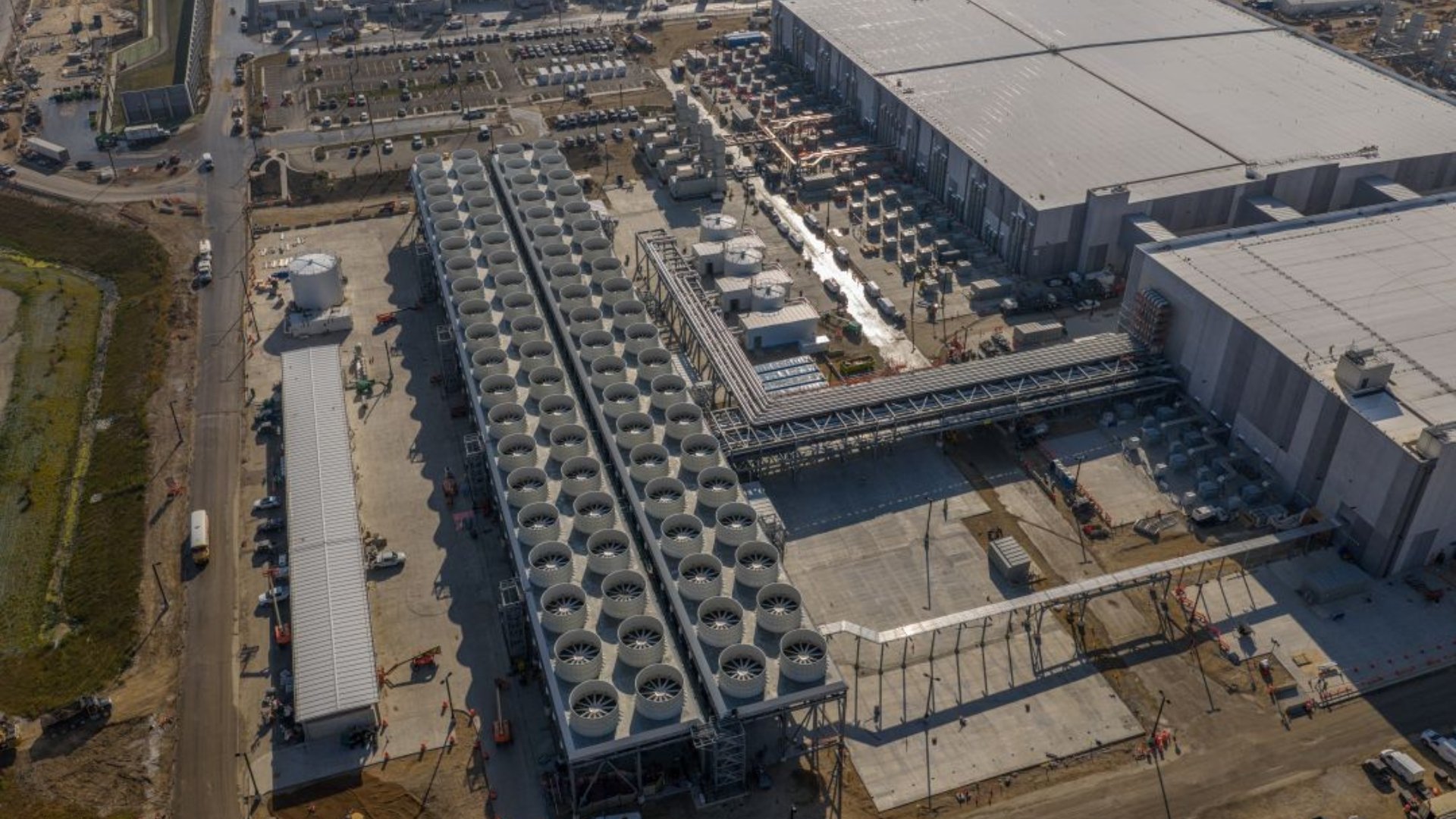

The partnership extends to software optimization, with Nvidia providing AI model tuning expertise to enhance Meta's inference and training workloads. This collaboration signals Nvidia's successful expansion into standalone data center CPUs, challenging established x86 vendors. With Meta's infrastructure serving billions of users daily, the architectural shift underscores how processor efficiency improvements translate directly to reduced operational costs at hyperscale. As AI model complexity grows, specialized CPU architectures optimized for memory bandwidth and power efficiency become increasingly vital for balancing system-level performance in trillion-parameter training environments.
Meta's commitment positions Grace and Vera as viable alternatives for memory-intensive workloads beyond traditional GPU-accelerated AI, potentially reshaping data center procurement strategies across the industry. The hyperscaler's deployment scale provides crucial validation for Arm-based server processors in performance-critical environments previously dominated by x86 architectures.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion