Notepad++ has implemented a 'double-lock' security mechanism for its update system after a six-month supply-chain compromise by Chinese state hackers.
Notepad++ has adopted a “double-lock” design for its update mechanism to address recently exploited security gaps that resulted in a supply-chain compromise. The new mechanism landed in Notepad++ version 8.9.2, announced yesterday, although work on it began in version 8.8.9 with implementing the verification of the signed installer from GitHub.
The second part of the double-lock system is checking the signed XML from the notepad-plus-plus.org domain. In practice, this means that the XML file returned from the update service is digitally signed (XMLDSig). The combination of the two verification mechanisms adds to a more robust "and effectively unexploitable" update process, says the team behind the massively popular open-source text and source code editor.
Additional security-oriented changes applied to the auto-updater include:
- Removal of libcurl.dll to eliminate DLL side-loading risk
- Removal of two unsecured cURL SSL options: CURLSSLOPT_ALLOW_BEAST and CURLSSLOPT_NO_REVOKE
- Restriction of plugin management execution to programs signed with the same certificate as WinGUp
The new announcement also notes that users can exclude the auto-updater during UI installation or deploy the MSI package with: msiexec /i npp.8.9.2.Installer.x64.msi NOUPDATER=1
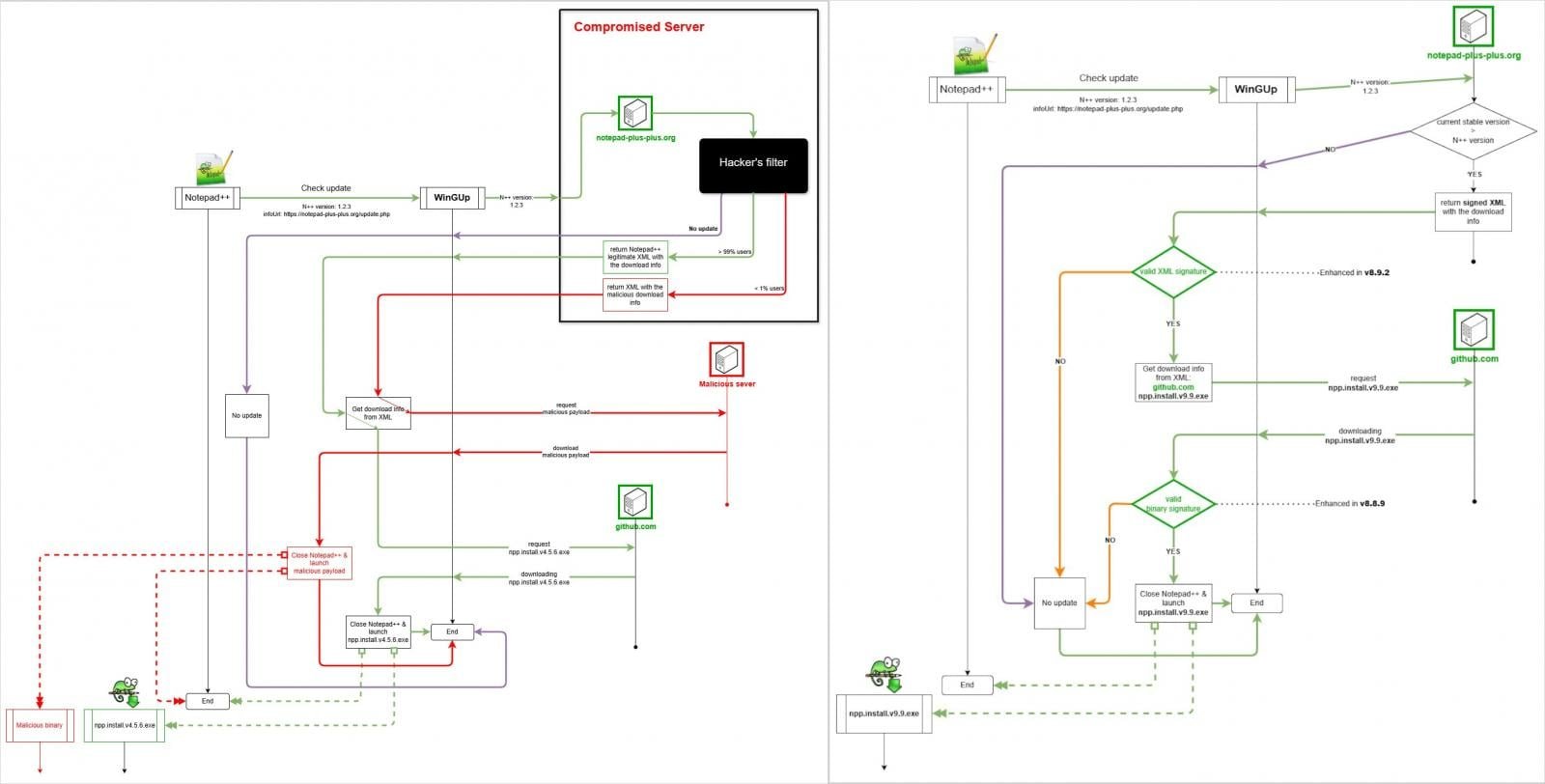
Vulnerable update model (left) and new, secure model (right) Source: Notepad++
Earlier this month, Notepad++ and Rapid7 researchers disclosed that the update infrastructure was compromised in a six-month-long campaign attributed to Lotus Blossom, a threat group linked to China. Starting in June 2025, the bad actor compromised the hosting provider that ran the Notepad++ updater and selectively redirected update requests from specific users to malicious servers.
The attacks exploited weak update verification controls used in older versions of the software, and continued until their discovery on December 2, 2025. Rapid7’s analysis revealed that the Chinese hackers used a custom backdoor called “Chrysalis” as part of the attack chain.
Apart from the newly introduced security measures, the project immediately switched to a different hosting provider, rotated credentials, and fixed flaws exploited in the discovered attacks. The recommended action for all Notepad++ users is to upgrade to version 8.9.2, and ensure that installers are always downloaded from the official domain, notepad-plus-plus.org.
This incident highlights the critical importance of secure update mechanisms in software supply chains. As Don Smith, Senior Director of Threat Intelligence at Secureworks, notes: "Supply chain attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, targeting the trust relationships between software vendors and their users. The Notepad++ compromise demonstrates how even widely-used, reputable software can become a vector for targeted attacks when update mechanisms aren't properly secured."
The double-lock mechanism represents a significant improvement in security posture. By requiring both GitHub-signed installers and XMLDSig verification from the official domain, Notepad++ has created a defense-in-depth approach that makes it substantially harder for attackers to compromise the update process. This layered security approach means that even if one verification mechanism is bypassed, the second layer provides protection.
For organizations using Notepad++, the upgrade to version 8.9.2 should be prioritized. The ability to disable the auto-updater during installation provides additional flexibility for enterprise environments that prefer centralized update management. The removal of libcurl.dll and the unsecured SSL options addresses specific technical vulnerabilities that could have been exploited through various attack vectors, including man-in-the-middle attacks and DLL side-loading techniques.
This incident serves as a reminder that software update mechanisms are high-value targets for threat actors. Organizations should regularly review their software update policies, ensure they're using the latest versions of applications, and consider implementing additional controls such as application whitelisting and network-level blocking of known malicious domains.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion