Modern enterprises need seamless integration between SAP S/4HANA and cloud applications to avoid data silos and enable real-time business processes. This article explores common integration patterns, key challenges, and proven best practices for building scalable, secure SAP cloud integrations.
Modern enterprises rely on a mix of core ERP systems and cloud-based applications to run their operations efficiently. SAP S/4HANA, as a next-generation ERP, plays a central role in finance, supply chain, and manufacturing. To unlock its full value, seamless integration with cloud applications is essential.
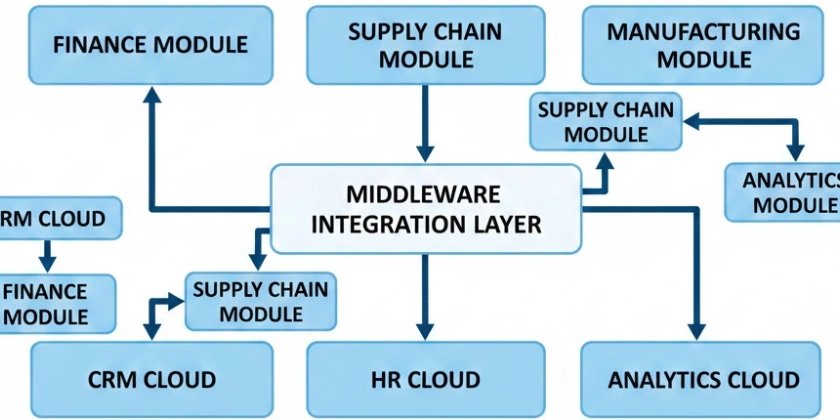
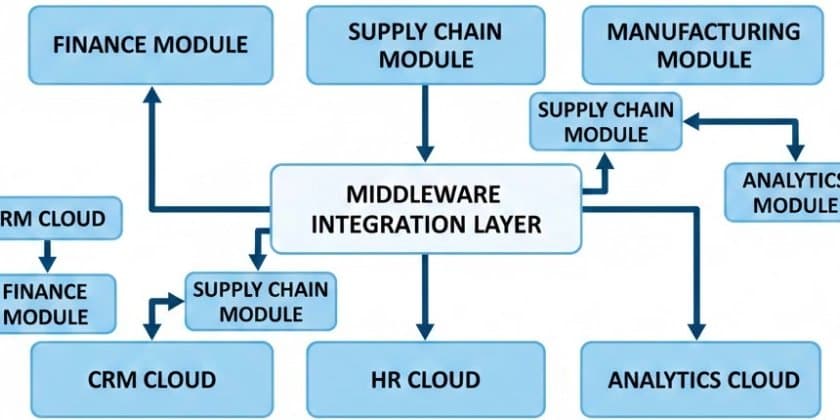
Why Integrate SAP S/4HANA with Cloud Applications?
Organizations today use cloud applications for CRM, HR, analytics, e-commerce, and automation. Without integration, data becomes siloed and business processes slow down. Key benefits include:
- Real-time data synchronization across systems - Eliminates manual data entry and reduces errors
- Faster decision-making with unified data - Provides a single source of truth for analytics
- Automation of end-to-end business processes - Streamlines workflows across departments
- Scalability and flexibility for future growth - Adapts to changing business needs
Common Integration Scenarios
SAP S/4HANA is commonly integrated with:
- CRM systems for customer and sales data synchronization
- HR platforms for employee and payroll information
- E-commerce platforms for orders, pricing, and inventory management
- Analytics and reporting tools for real-time insights
Each scenario requires a reliable and secure integration approach. The choice of pattern depends on factors like data volume, latency requirements, and business criticality.
Enterprise Integration Patterns
Several integration patterns are widely used when connecting SAP S/4HANA with cloud applications:
API-Based Integration
REST and OData APIs enable real-time, synchronous communication. This pattern is ideal for scenarios where immediate responses are required, such as order creation or customer updates. The advantage is low latency and direct data access, but it requires both systems to be available simultaneously.
Event-Driven Integration
Business events generated in SAP S/4HANA trigger actions in cloud systems. This approach improves scalability and reduces tight coupling between systems. When an order is created in S/4HANA, an event can trigger inventory updates in a warehouse management system. This pattern handles high volumes well and provides better fault tolerance.
Batch Integration
Data is transferred in scheduled intervals. This pattern works well for reporting, data warehousing, and non-time-critical processes. While it introduces latency, batch integration handles large data volumes efficiently and reduces the load on both source and target systems.
Middleware-Centric Integration
An integration platform acts as a central hub to manage transformations, routing, security, and monitoring. This is the most common approach in large enterprises because it provides:
- Centralized error handling and retry logic
- Data transformation capabilities
- Security policy enforcement
- Comprehensive monitoring and logging
Key Challenges in SAP Cloud Integration
While integration brings value, it also introduces challenges:
Complex data models and mappings - SAP S/4HANA has intricate data structures that don't always map cleanly to cloud applications. Custom fields, different data types, and business logic variations require careful mapping design.
Security and compliance requirements - Enterprise integrations must meet strict security standards. This includes data encryption in transit and at rest, proper authentication mechanisms, and audit trails for compliance.
Error handling and monitoring - Distributed systems fail in interesting ways. Network partitions, service outages, and data inconsistencies require robust error handling strategies and comprehensive monitoring.
Performance and scalability concerns - Integration solutions must handle peak loads without degradation. This includes managing connection pools, implementing caching strategies, and designing for horizontal scalability.
Addressing these challenges early in the design phase is critical for long-term success.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
To build reliable SAP S/4HANA integrations:
Use standard APIs instead of custom interfaces - SAP provides extensive standard APIs for common business objects. Using these reduces maintenance overhead and ensures compatibility with future S/4HANA releases.
Design loosely coupled integrations - Avoid tight dependencies between systems. Use asynchronous communication patterns where possible, implement circuit breakers, and design for partial failures.
Implement centralized monitoring and logging - Track message flows, monitor performance metrics, and log errors centrally. This enables quick troubleshooting and provides audit trails for compliance.
Plan for error handling and retries - Design idempotent operations that can be safely retried. Implement dead letter queues for messages that cannot be processed, and establish clear escalation procedures.
Secure data using authentication and encryption - Use OAuth 2.0 or SAML for authentication, encrypt sensitive data both in transit (TLS) and at rest, and implement proper access controls.
Conclusion
Integrating SAP S/4HANA with cloud applications is no longer optional—it's a necessity for digital transformation. By choosing the right integration patterns and following enterprise best practices, organizations can create agile, scalable, and future-ready architectures that support business growth.
The key is to start with a clear understanding of business requirements, choose appropriate integration patterns based on those requirements, and implement robust error handling and monitoring from the beginning. This approach ensures that your SAP S/4HANA integrations deliver value today while remaining maintainable and scalable for tomorrow's needs.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion