New Census Bureau data reveals U.S. population growth slowed to 0.5% in 2023, the lowest rate in over a century, primarily due to reduced immigration and sustained low birth rates.
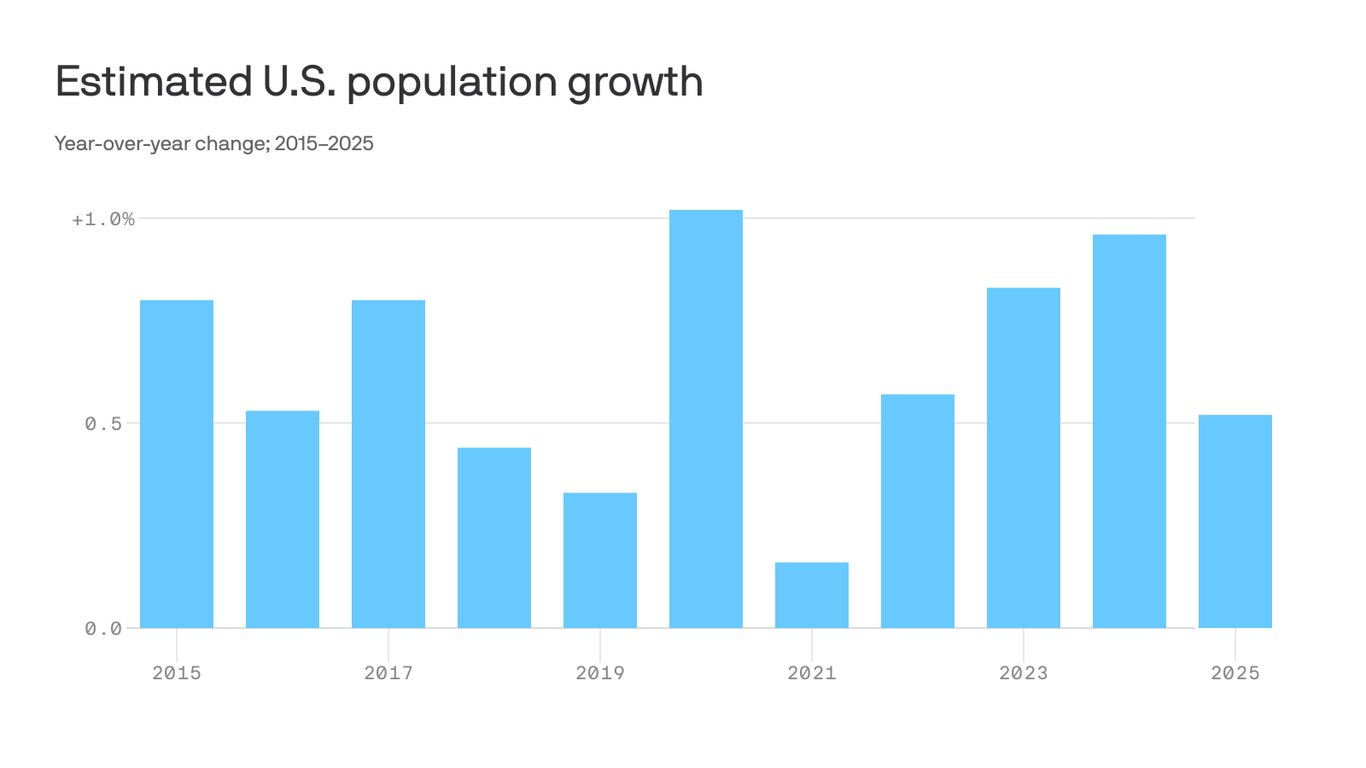
U.S. population growth reached its slowest pace in over a century during 2023, expanding by just 0.5% according to Census Bureau estimates. This marks the eighth consecutive year of sub-1% growth, a pattern unseen since the Great Depression era. The primary driver is a significant reduction in net international migration, which added approximately 500,000 people last year—down 40% from pre-pandemic levels and 65% below 2016 peaks.
Three structural factors are driving the trend:
- Immigration Policy Shifts: Stricter visa processing and refugee caps reduced net migration gains, with work-based visas like H-1Bs falling 15% year-over-year
- Birth Rate Deficit: The fertility rate remained at 1.64 births per woman, well below the 2.1 replacement level
- Aging Demographics: 17% of Americans are now over 65, the highest percentage ever recorded
Economic consequences are already materializing across key sectors:
- Labor Markets: Workforce growth slowed to 0.3% annually, exacerbating shortages in healthcare, construction, and technology
- Consumer Economies: States with population declines like Illinois (-0.26%) and Louisiana (-0.31%) show weakening retail sales and housing demand
- Fiscal Pressure: Social Security trustees project trust fund depletion by 2033 due to fewer workers per retiree
Corporate strategies are adapting accordingly. Walmart and Amazon have accelerated warehouse automation investments, while manufacturing firms increasingly locate new facilities in high-growth states like Texas and Florida. Demographic analysts project immigration would need to increase by 35% annually through 2030 to maintain historical GDP growth patterns.
This demographic shift creates bifurcated regional economies, with implications for real estate valuations, municipal bond markets, and long-term infrastructure planning. Without policy adjustments, the U.S. could face sustained sub-2% GDP growth within this decade.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion