Microsoft's Zero Trust approach extends to AI agents, requiring explicit verification of every access request to protect critical resources from emerging threats.
As AI agents, semantic search, and automation accelerate how work gets done, organizations face new security challenges that traditional perimeter-based defenses cannot address. Microsoft's Zero Trust security framework provides a comprehensive approach to protect your environment by verifying every access request—whether from humans, machines, or AI—before it reaches critical resources.
The Evolution of Zero Trust in an AI-Driven World
Zero Trust security operates on a simple but powerful principle: never assume trust, always verify. This approach has become increasingly critical as AI reshapes both productivity and the threat landscape. When data isn't properly classified and protected, AI's powerful semantic search capabilities can surface information that was once difficult to find and potentially share it with unauthorized users.
Ungoverned AI agents present another significant risk. These agents often possess extensive permissions across systems, enabling them to move through organizations at unprecedented speed to complete tasks. However, if compromised, they can cause substantial damage before detection.
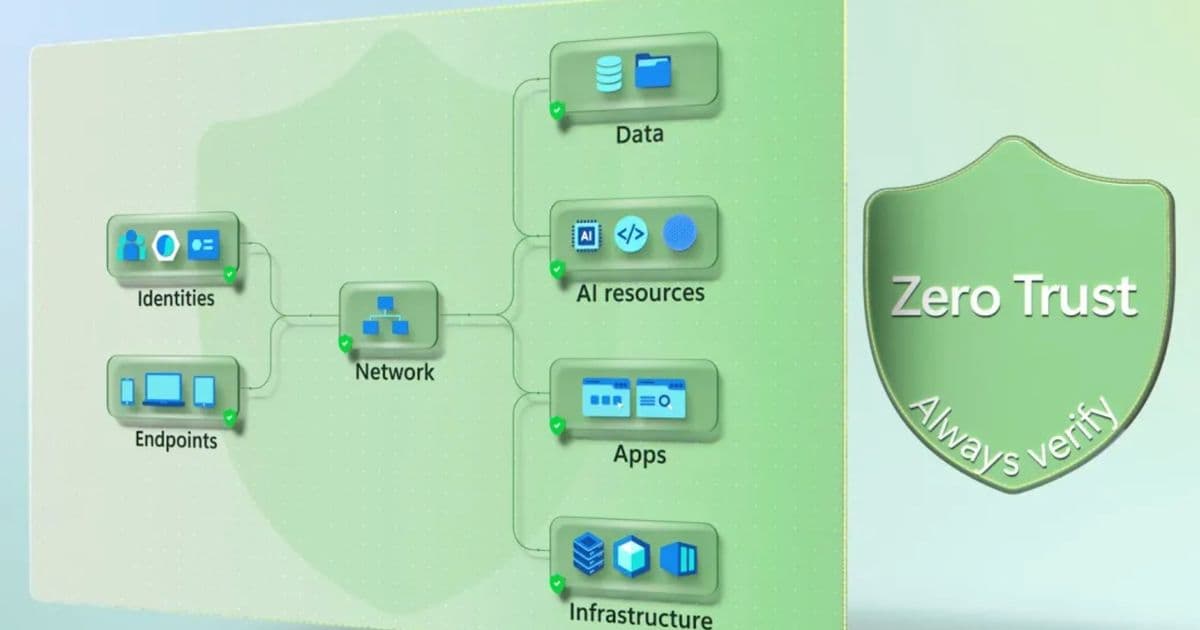
The Zero Trust Architecture: A Layered Defense
Think of your IT environment as a flow from identities and endpoints trying to gain access, across your network, to the sensitive data, AI resources, applications, and infrastructure they need to reach. Every step introduces risk, and attackers only need to exploit one weak link.
Protection must be layered across:
- Identities (human users, agents, and workloads)
- Endpoints (devices and virtual machines)
- Network (the bridge between actors and resources)
- Data (the ultimate target of breaches)
- AI resources (models, agents, APIs, and compute)
- Applications (where AI meets data)
- Infrastructure (cloud environments, servers, containers)
Protecting Identities: Human and Non-Human
Human identities remain prime targets for phishing, impersonation, and credential theft. The solution starts with limiting access to what each person needs, then adding phishing-resistant authentication to confirm users are who they claim to be.
Microsoft Entra's Conditional Access verifies every request using passkeys and other strong methods. Microsoft Purview's Data Security Posture Management tracks how users interact with data and AI, helping spot risks early. Integration with Defender for Cloud Apps allows blocking risky applications, while Global Secure Access enforces identity-integrated network controls.
Non-human identities like AI agents require different protections. The new Entra Agent ID gives each AI agent its own unique, manageable identity, applying the same visibility, governance, and Zero Trust controls used for human users. Conditional Access can evaluate agent risk in real-time for each authorization request, while ID governance with human agent sponsor approval scopes agents for just enough access to authorized tasks.
Securing Endpoints in the AI Era
Device endpoints, whether corporate or personally owned, pose serious risks if compromised or non-compliant. AI extends endpoint considerations to computer-using agents that can interact with endpoints like full virtual machines to temporarily access resources within networks or from cloud service providers.
As access requests move inward, they pass through control layers that evaluate context and behavior. Microsoft Intune ensures connecting devices or VMs pass compliance checks before accessing resources. Defender for Endpoint provides continuous assessment using threat intelligence and forensics to expose patterns, automatically respond, and raise defenses against trending attacks.
Protecting Network and Data
The network serves as a bridge between malicious actors and valuable resources. The first defense layer uses network and device-based firewalls to filter traffic and prevent unwanted connections. Network segmentation then limits lateral movement if a breach occurs. These defenses are stronger when tied directly with identity controls using Global Secure Access.
Data remains the ultimate target of security breaches, vulnerable to theft, manipulation, or leakage. Microsoft Purview delivers unified Zero Trust controls across unstructured data in Microsoft 365 and beyond, applying sensitivity labels that drive consistent enforcement such as encryption, access controls, and DLP across collaboration and AI experiences.
For structured data across Fabric and other clouds, the same sensitivity labels extend protection intent to data stores, enabling consistent access controls and policy enforcement so sensitive data remains protected wherever it's used, including AI workloads.
Securing AI Resources and Applications
AI resources—models, agents, APIs, data pipelines, and compute—are critical components of your Zero Trust architecture. If compromised, they can leak sensitive data, generate malicious outputs, or enable lateral movement across systems.
Protection means securing the resources themselves, not just access. Microsoft Foundry's Prompt Shields assess prompts and outputs, while runtime protections secure compute environments like GPU-enabled virtual machines used for AI. Defender for Cloud provides isolation and compliance controls, and continuous monitoring of agent behavior with risk scoring through Agent Analytics enables centralized governance.
The application layer is where AI meets data, increasingly powered by AI and semantic search to enable users to retrieve information more efficiently. While these capabilities enhance productivity, they also amplify attacker capabilities if access is compromised.
Defender for Cloud Apps provides visibility into all apps in use, risk-based controls to govern app behavior, and data protection policies to prevent misuse and data exfiltration.
Infrastructure: The Foundation of Zero Trust
Infrastructure spans cloud environments, servers, containers, and orchestration systems. Compromised infrastructure can lead to severe consequences including service outages, ransomware, and instability.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud delivers comprehensive workload protection across Azure, AWS, and GCP, including vulnerability scanning and advanced threat detection. Azure Confidential Computing encrypts data while in use in memory using hardware-based trusted execution environments, processing data only after requests are explicitly verified.
Continuous Validation and Adaptive Security
Security configurations should not be set and forgotten. Continuous validation with constant monitoring and adaptive policies is critical to maintaining Zero Trust. Across all layers, SecOps needs continuous assessment, monitoring, and optimization with controls to minimize and detect risks.
Microsoft Defender with Sentinel as its integrated SIEM extends detection and response across endpoints, identities, SaaS apps, email and collaboration tools, and more.
Getting Started with Zero Trust for AI
Microsoft provides comprehensive resources to help organizations implement Zero Trust for AI:
- Visit aka.ms/GoZeroTrust for free workshops and additional resources
- Watch the full series at aka.ms/ZTMechanics for hands-on guidance
- Subscribe to Microsoft Mechanics for ongoing insights into implementing Zero Trust across identities, endpoints, data, AI resources, applications, networks, and infrastructure
The Zero Trust approach ensures that as AI reshapes how work gets done, your organization can maintain security without impacting productivity. By continuously assessing risk, securing resources at runtime, and adapting policies as conditions change, you can protect productivity and keep pace with an evolving threat landscape.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion