Search Results: "Hallucination"
Found 57 articles

Cloud
How to Get Accurate Azure Answers in ChatGPT Using MCP
3/3/2026
AI
Mind the gap: Closing the AI trust gap for developers
2/18/2026

AI
Haizhi Technology's HKEX Debut: 250% Surge and the Promise of Graph-Model Fusion for LLM Hallucination
2/13/2026

AI
LLMs Need Companion Bots to Check Work, Keep Them Honest
2/7/2026
AI
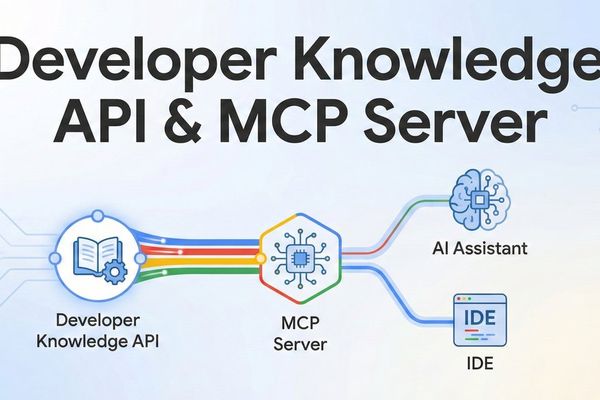
Google Tackles AI Hallucinations with Developer Knowledge API and Context Protocol
2/7/2026

AI
West Midlands Police Suspends Microsoft Copilot After AI Hallucination Scandal
1/28/2026

AI
AI Agents Achieve Fourfold Improvement in LED Steering at Sandia National Labs
1/26/2026

Regulation
NeurIPS Papers Contaminated with AI Hallucinations: 100 Fabricated Citations Found in Accepted Research
1/22/2026