A Reuters investigation reveals that AI-enhanced medical devices, including Acclarent's TruDi navigation system, have seen malfunction rates skyrocket from 8 to 100 incidents after AI integration, with cases of skull punctures, strokes, and arterial damage raising serious safety concerns.
The integration of artificial intelligence into medical devices promises enhanced precision and outcomes, but a recent Reuters investigation reveals a troubling pattern of increased malfunctions and patient harm following AI implementation. The report examines three AI-enhanced medical devices, with the most concerning case involving Acclarent's TruDi navigation system used for sinus surgery.
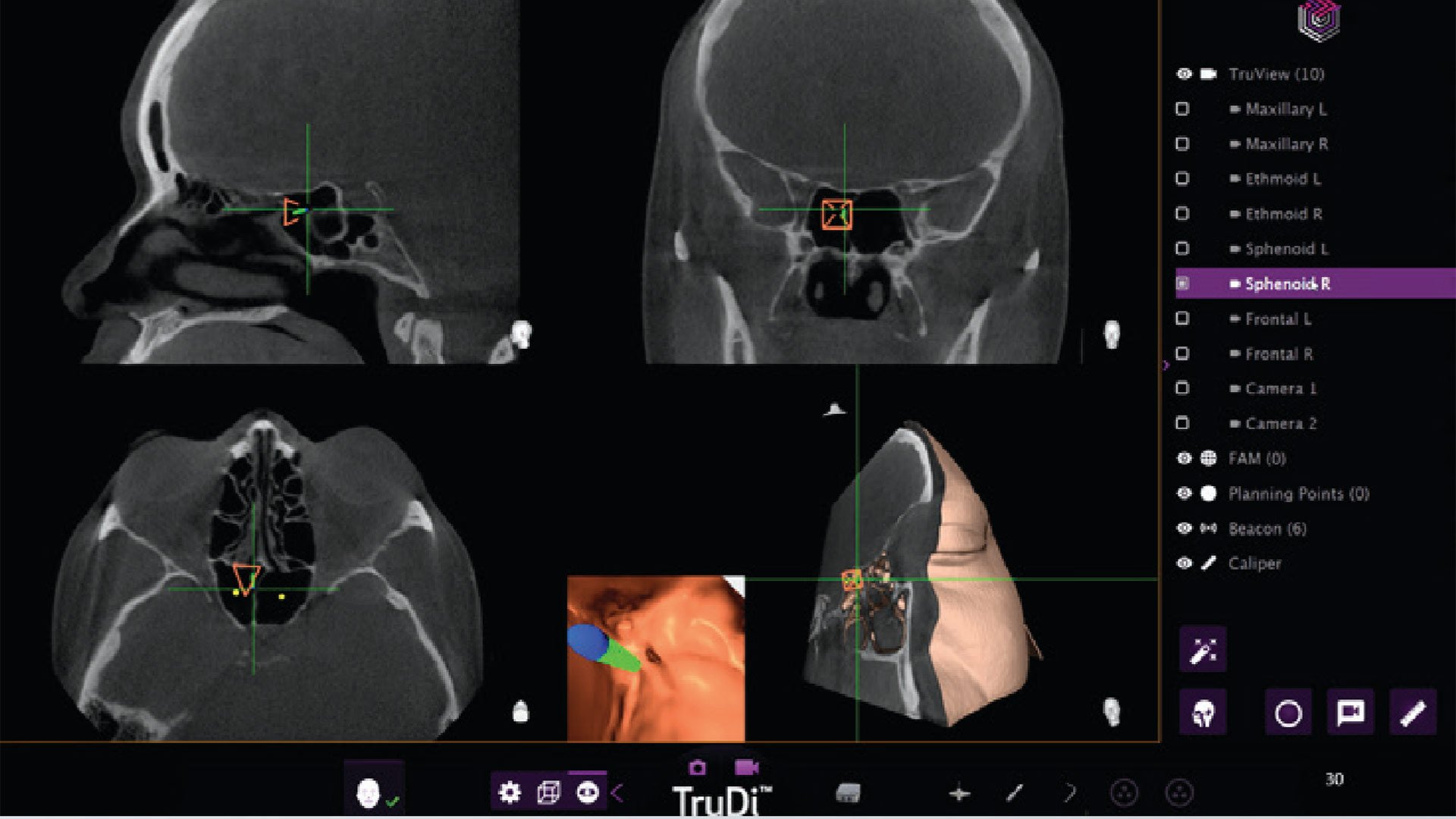
TruDi Navigation System: From 8 to 100 Malfunctions
The TruDi system, designed to simplify surgical planning and provide real-time feedback during delicate sinus procedures, experienced a dramatic increase in reported malfunctions after AI algorithms were integrated. Before the AI enhancement, the device had documented eight malfunctions over three years on the market. Following the AI integration, that number jumped to at least 100 malfunctions and adverse events, according to the Reuters report.
The complications attributed to the AI-enhanced TruDi system are severe and life-altering. Patients have experienced cerebrospinal fluid leaks, puncture of the skull base, major arterial damage, and strokes. Two specific cases highlight the gravity of these incidents.
Erin Ralph's case illustrates the potential dangers. Her lawsuit alleges that the TruDi system misdirected her surgeon to place instruments near the carotid artery, resulting in a blood clot and stroke. The aftermath required five days in intensive care, brain swelling treatment, and surgical removal of part of her skull. One year later, Ralph continues physical therapy for ongoing physical issues.
Donna Fernihough's experience was equally traumatic. During her procedure, her carotid artery reportedly "blew," causing blood to spray throughout the operating theater. Like Ralph, Fernihough suffered a stroke. Her lawyers claim the AI-enhanced system is "inconsistent, inaccurate, and unreliable," and that Acclarent "lowered its safety standards to rush the new technology to market."
FDA Oversight Challenges
The FDA's ability to effectively monitor and regulate AI-enhanced medical devices faces significant challenges. The agency reports that FDA-authorized medical AI devices have experienced twice the recall rate compared to the baseline for medical devices. This elevated risk is compounded by staffing constraints, as the FDA has lost 15 of its 40 AI scientists in the Division of Imaging, Diagnostics and Software Reliability (DIDSR) due to layoffs and departures under the DOGE initiative.
Beyond staffing issues, the FDA's approval process for AI-enhanced devices may be inadequate for ensuring patient safety. Currently, the agency appears to rely heavily on a device's prior reputation, effectively positioning new AI-enhanced versions as updates to existing devices. This approach may expedite market entry for manufacturers but potentially compromises thorough safety evaluation when human health is at stake.
Other AI-Enhanced Devices Under Scrutiny
The investigation also examined two additional AI-enhanced medical devices with concerning issues. The Sonio Detect fetal image analyzer, designed to identify fetal structures and body parts, is accused of using a faulty algorithm that misidentifies these critical elements. While no patient harm has been reported from this device, the algorithmic errors raise questions about reliability.
Medtronic's LINQ implantable cardiac monitors, which use AI to detect abnormal heart rhythms and pauses, have also faced allegations of failure to recognize these critical cardiac events. Again, no patient harm has been documented, but the potential for missed diagnoses presents serious safety concerns.
Industry Response and Legal Implications
The legal cases emerging from these incidents highlight the tension between technological innovation and patient safety. Plaintiffs in the TruDi cases argue that Acclarent prioritized speed to market over safety, allegedly setting a goal of only 80% accuracy for some new technology before integrating it into the navigation system.
These cases raise fundamental questions about the appropriate standards for AI-enhanced medical devices. Unlike traditional medical devices, AI systems can evolve and change their behavior over time, potentially introducing new risks that weren't present during initial approval. The current regulatory framework may not adequately address these dynamic characteristics.
The Path Forward
The incidents documented in the Reuters investigation underscore the need for more robust oversight of AI-enhanced medical devices. As these technologies become increasingly prevalent in healthcare settings, ensuring their safety and efficacy becomes paramount. This may require updated regulatory frameworks that specifically address the unique characteristics of AI systems, including their potential for continuous learning and adaptation.
The medical device industry faces a critical juncture. While AI offers the potential for improved surgical outcomes and diagnostic accuracy, the current evidence suggests that the rush to implement these technologies may be outpacing appropriate safety validation. As more AI-enhanced devices enter the market, the healthcare system must balance innovation with patient protection, ensuring that technological advancement doesn't come at the cost of human lives.
The experiences of patients like Erin Ralph and Donna Fernihough serve as sobering reminders that when AI systems fail in medical contexts, the consequences can be catastrophic. Moving forward, both manufacturers and regulators must prioritize comprehensive safety testing and ongoing monitoring to prevent similar incidents and maintain public trust in these potentially life-saving technologies.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion