European scientists leverage DeepMind's AlphaFold to unlock the 3D structure of a critical honeybee immunity protein, Vitellogenin, accelerating conservation efforts for endangered pollinators and enabling AI-assisted breeding programs for resilient bee colonies.
The global decline of honeybee populations, driven by pesticides, habitat loss, and climate change, has spurred urgent scientific intervention. Now, researchers in Europe are turning to artificial intelligence to decode one of nature's most complex biological puzzles: the honeybee's immune system. By applying DeepMind's AlphaFold, the revolutionary AI system that predicts protein structures with atomic-level accuracy, scientists have successfully modeled the three-dimensional structure of Vitellogenin (Vg), a key protein central to bee immunity, longevity, and stress resistance.
"Understanding Vitellogenin's structure is like finding the master key to bee health," explains Dr. Elena Rossi, a computational biologist leading the initiative. "AlphaFold allowed us to visualize how this protein functions at a level previously impossible, revealing new targets for interventions."
Vitellogenin serves as a multifunctional powerhouse in honeybees, regulating immune responses, detoxifying environmental toxins, and extending lifespan. Its structural insights—achieved through AlphaFold's ability to predict protein folding from amino acid sequences—provide a blueprint for enhancing bee resilience. These findings are now directly informing conservation strategies for endangered bee species, such as the Rusty Patched Bumblebee, and guiding the development of AI-driven breeding programs to cultivate colonies with superior immunity and stress tolerance.

The breakthrough underscores AlphaFold's transformative impact beyond medicine. While initially celebrated for solving the 50-year-old grand challenge of protein folding, the system is now catalyzing breakthroughs in agriculture and ecology. By predicting how mutations in the Vg protein affect its function, researchers can identify genetic markers for desirable traits, enabling precision breeding of bees better equipped to survive modern environmental challenges.
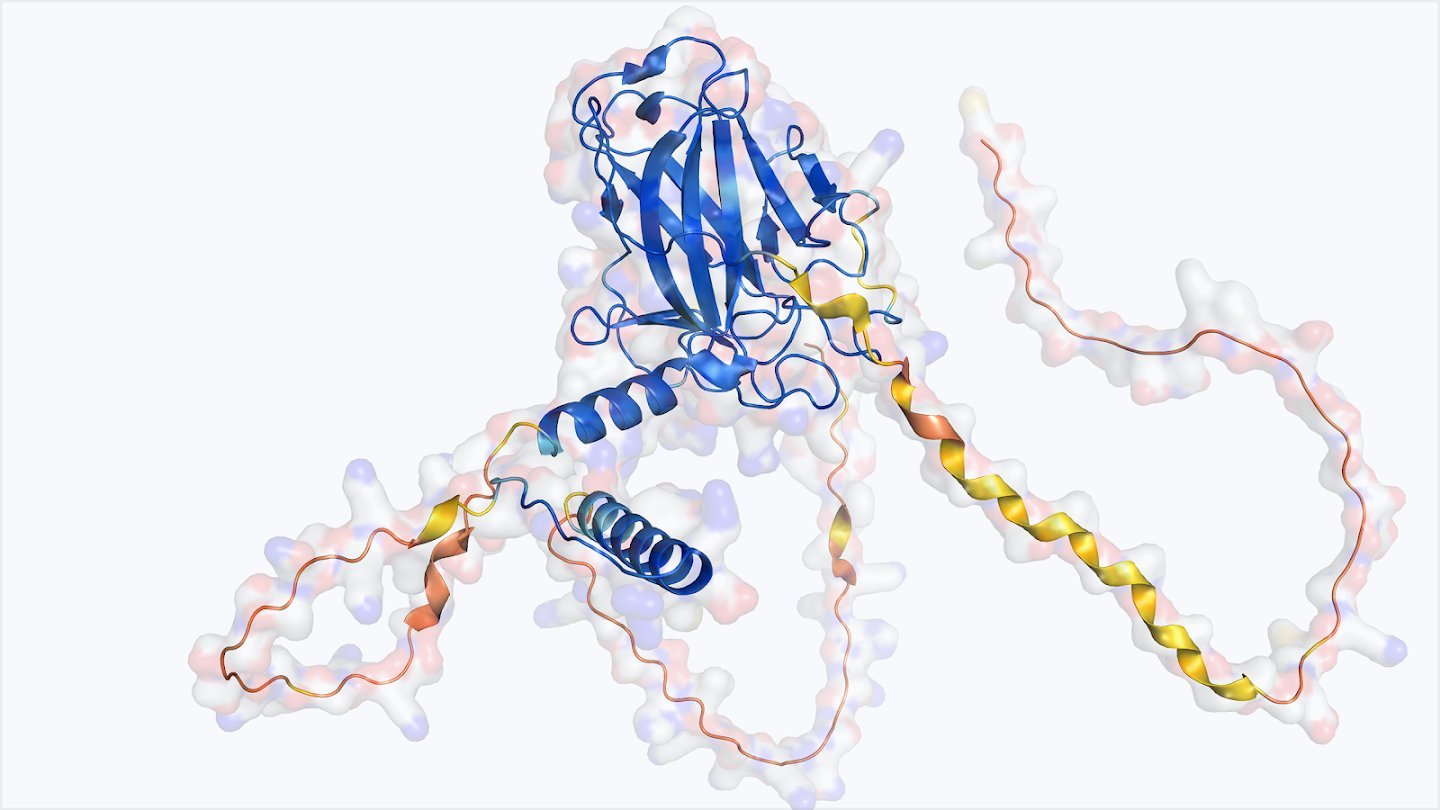
This research exemplifies the convergence of AI and environmental science. AlphaFold's predictions are being validated through wet-lab experiments, creating a feedback loop that refines both biological understanding and AI algorithms. The resulting data is integrated into global biodiversity databases, empowering conservationists and apiarists with actionable insights. As climate change intensifies threats to pollinators, such AI-augmented approaches offer a scalable path to safeguarding ecosystems that rely on bees for 75% of global food crops.
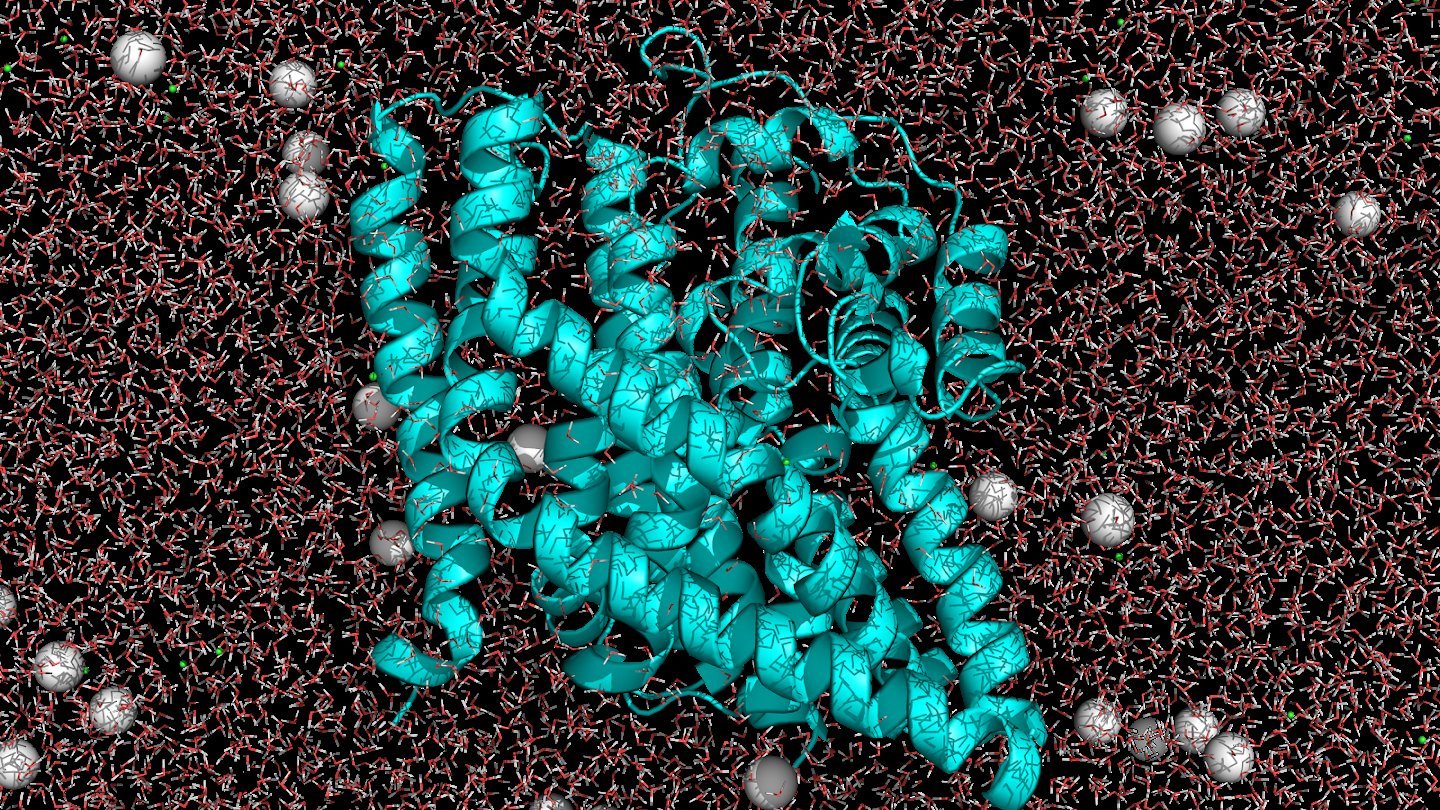
The implications extend to broader AI applications in conservation. By modeling complex biological systems, tools like AlphaFold can accelerate research into endangered species' genetic vulnerabilities, potentially unlocking similar breakthroughs for other at-risk organisms. As Dr. Rossi notes, "We're not just saving bees—we're building a new paradigm for AI-powered ecological stewardship where technology and nature collaborate for planetary health."
The marriage of deep learning and structural biology is rewriting the playbook for conservation, proving that AI's greatest potential may lie not just in digital realms, but in restoring the delicate balance of the natural world.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion