A new open-source project, Clawdbot, offers a locally-run personal AI agent that integrates with multiple LLMs and messaging services, aiming to give users more control over their data and workflows without relying on cloud-based assistants.
The push for personal AI assistants has largely been defined by cloud-based services from major tech companies, each with its own ecosystem and data policies. A new project called Clawdbot takes a different approach, offering an open-source, locally-run personal agent designed to run directly on a user's computer. This model prioritizes privacy and user control, allowing individuals to integrate various large language models (LLMs) and messaging services into a single, self-hosted assistant.
What's Claimed
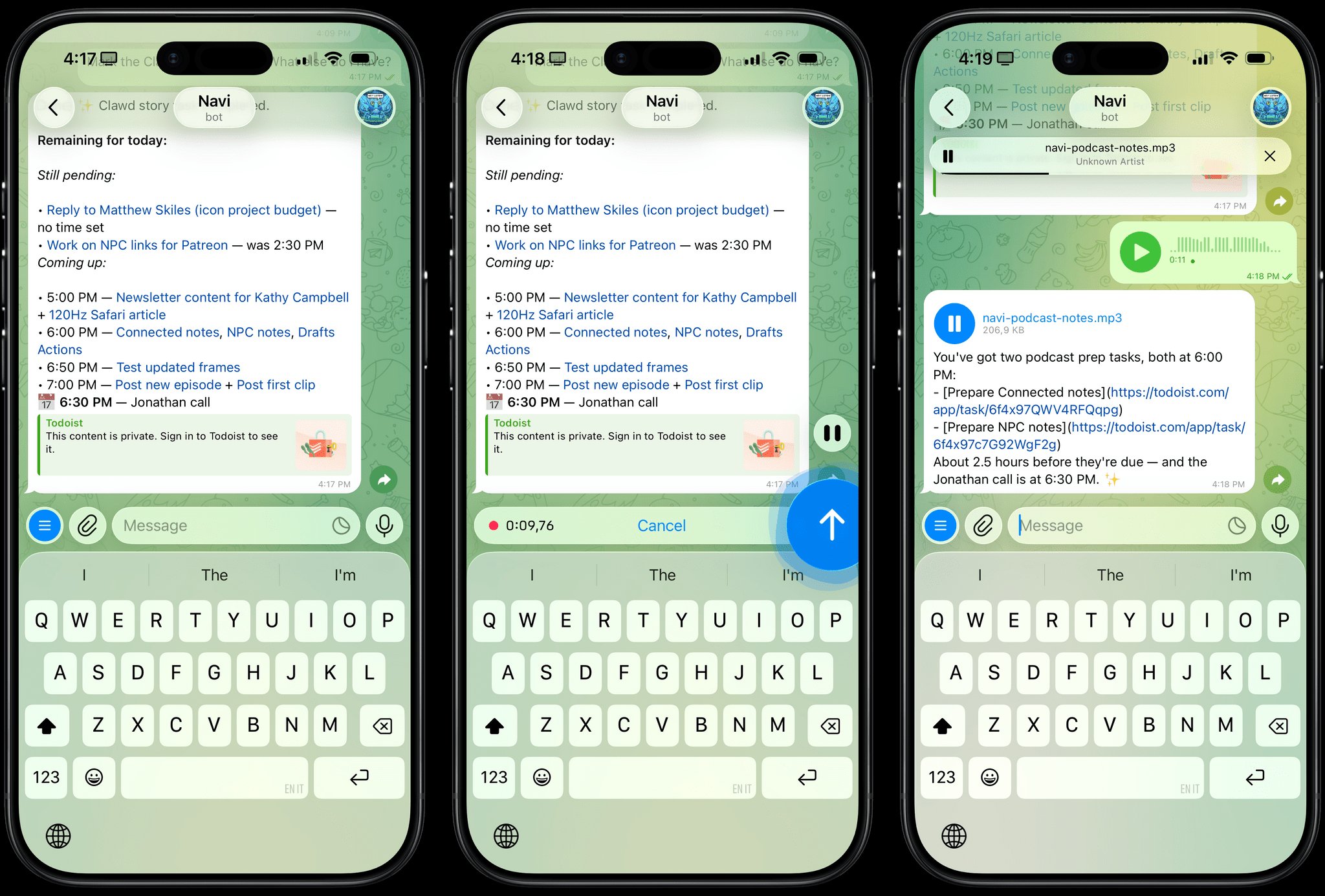
Clawdbot is presented as a personal digital assistant that can manage daily routines, answer questions, and interact with other services. According to its developer, the agent can be configured to know a user's name, preferences, and schedule. The core promise is a unified interface that connects to different LLMs—like those from OpenAI, Anthropic, or open-source models—and messaging platforms, all while keeping the data and processing on the user's own machine.
What's Actually New
While personal AI agents and local LLMs are not new concepts, Clawdbot's value lies in its specific integration model. Most local LLM tools focus on chat or specific tasks, but Clawdbot aims to be a persistent, context-aware agent that can act as a bridge between different services. Its open-source nature means users can inspect the code, modify its behavior, and avoid vendor lock-in. The ability to switch between different LLM providers without changing the core agent is a practical feature for users who want to experiment with different models or maintain flexibility.
Limitations and Practical Considerations
Running a personal AI agent locally requires significant computational resources. Users will need a capable machine, likely with a dedicated GPU, to run LLMs efficiently. While Clawdbot can leverage smaller, quantized models, the performance and capability will be directly tied to the hardware available. This is not a solution for low-power devices like smartphones or older laptops.
Integration with messaging services typically requires API access and authentication, which can be complex to set up for non-technical users. The project's success will depend on the community's ability to develop and maintain connectors for various platforms. Furthermore, the agent's effectiveness is limited by the quality of the underlying LLMs and the user's ability to configure them properly. It is a tool for those willing to invest time in setup and maintenance, not a plug-and-play consumer product.
Broader Context
Clawdbot fits into a growing trend of "local-first" software, which emphasizes data ownership and offline functionality. This approach is a direct response to the data collection practices of large cloud-based AI services. For developers, researchers, and privacy-conscious individuals, projects like this offer a way to explore AI capabilities without ceding control of personal data to third parties. It also represents a practical application of the open-source AI ecosystem, where models, tools, and frameworks are combined to create custom solutions.
For those interested in exploring the project, the source code and setup instructions are available on its GitHub repository. The project is still in its early stages, and users should expect to encounter bugs and configuration challenges as the community develops it further.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion