A critical examination of recent research exploring consciousness theories, nonlinear dynamics in ecology, AI's impact on biology, and neural network training's fractal properties.
Max Hodak's Binding Problem: Consciousness as Feedback Control
Claimed: Entrepreneur Max Hodak proposes consciousness solves neuroscience's "binding problem" through brainwave-mediated feedback control. Gamma waves (40Hz) bind sensory features into unified percepts, while alpha waves (10Hz) create temporal coherence across neural activity. Hodak suggests consciousness might require discovering new fundamental physics.
What's New: The novel connection between specific neural oscillations and distinct binding mechanisms, with alpha waves acting as a "forward pass" synchronizing perception. Hodak's hypothesis that consciousness impacts physical reality implies undiscovered physics at the level of fundamental forces.
Limitations: As noted in critiques, equating feedback control with consciousness raises questions: Why wouldn't memory refresh qualify? The physics argument appears shaky—many emergent phenomena (e.g., buoyancy) affect reality without new physics. Evolution stumbling upon undiscovered physical fields remains biologically implausible without evidence. Full theory requires stronger empirical grounding.
Strogatz's Nonlinear Dynamics: Visualizing System Behavior
Practical Application: Steven Strogatz's Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos demonstrates how phase-space diagrams reveal system behavior more effectively than time-series observations. Case studies include predicting insect outbreak regimes by plotting dimensionless parameters (R vs K), identifying bifurcation points where population dynamics shift fundamentally.
Novel Insight: The text shows how mathematical transformations create interpretable visualizations—e.g., graphing predator-prey interactions to expose three distinct ecological states: suppressed populations, predator-controlled equilibrium, and catastrophic outbreaks.
AI Limitations: While LLMs assist in learning concepts, they can't replicate the human insight needed for dimensionality reduction. Choosing which parameters to make dimensionless (e.g., prioritizing resource constraints over predator counts) requires domain-specific intuition. As one practitioner noted, automating such judgment remains beyond current AI capabilities, preserving the role of mathematicians developing novel frameworks.

Amodei on AI-Accelerated Biology: A Century in Five Years?
Thesis: Anthropic CEO Dario Amodei contends AI could compress a century of biological progress into 5–10 years (Machines of Loving Grace). By overcoming data bottlenecks through intelligent tool design (e.g., multiplexed experiments), AI could derisk drug development and accelerate clinical trials.
Critical Response: Evidence contradicts this optimism. Despite exponential cost reductions in gene sequencing (1M-fold) and editing (CRISPR), drug approval rates have declined since the 1990s. Alzheimer's research exemplifies the challenge: amyloid-beta targeting failed repeatedly despite mechanistic understanding. Clinical trials can't be bypassed without full physiological simulation—a possibly insurmountable hurdle. As researcher Jacob Trefethen argues, biological complexity often necessitates human trials regardless of predictive models.
Structural Flaws: Amodei's economic model underestimates how labor scarcity constraints capital, paralleling AI's inability to magically overcome physical bottlenecks. Historically, capital abundance hasn't eliminated labor scarcity—why would intelligence differ?
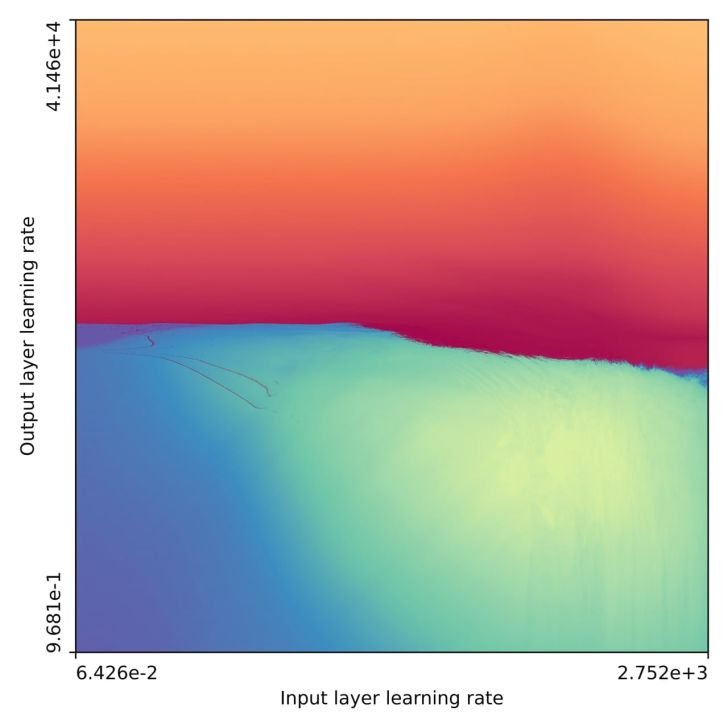
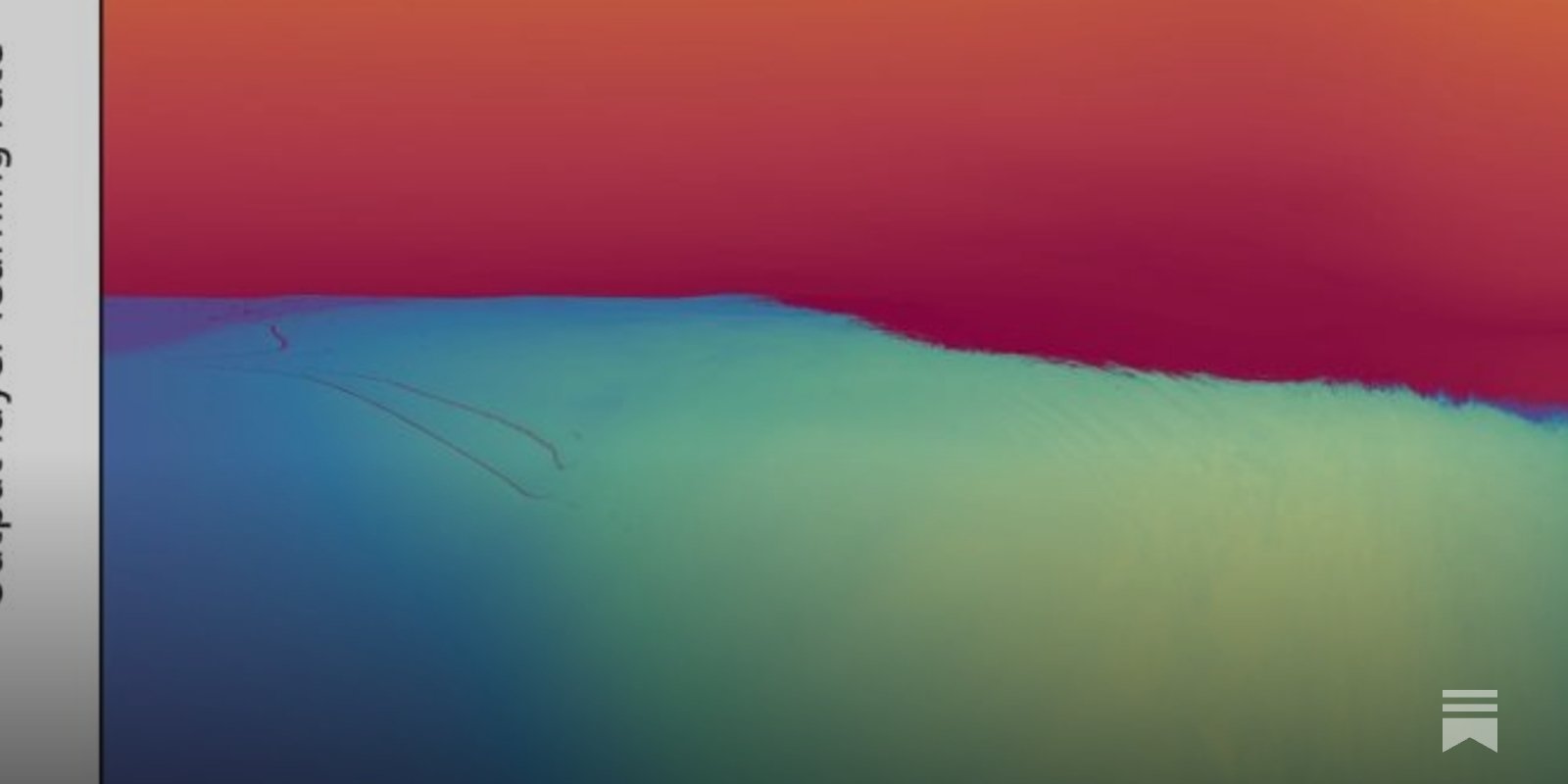
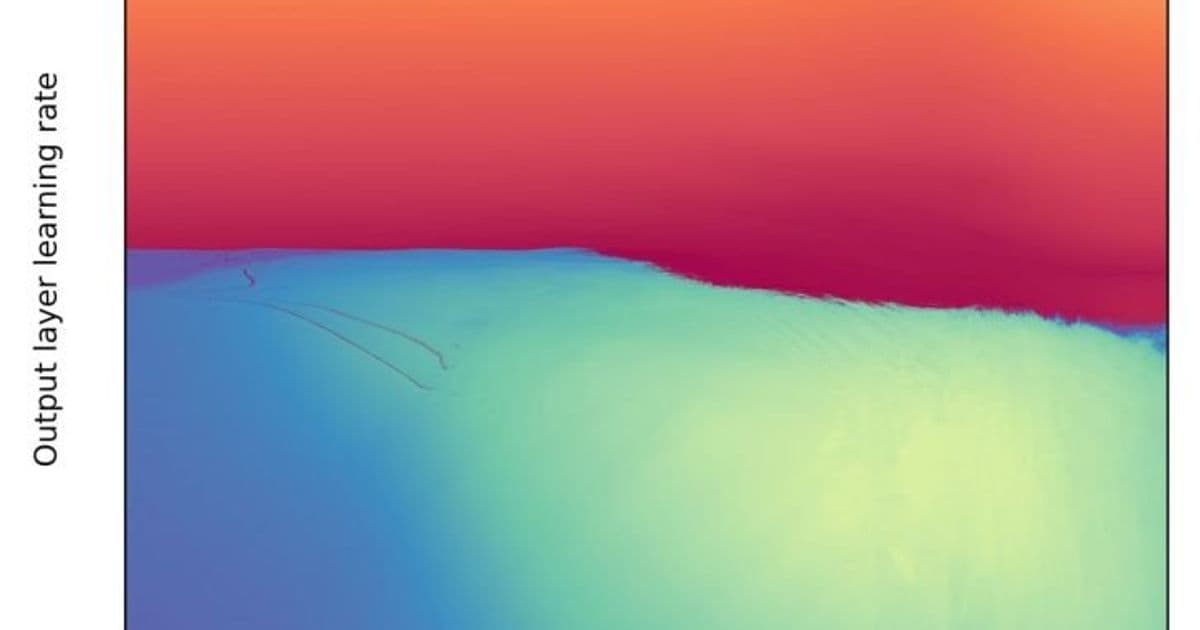
Neural Network Fractals: The Optimization Challenge
Discovery: Jascha Sohl-Dickstein's research reveals neural network training landscapes become fractal at convergence-divergence boundaries. High-learning-rate regions form intricate patterns (visualized here), making hyperparameter optimization difficult for gradient-based methods.
Implication: Evolution likely used gradient-free optimization to navigate these fractal landscapes when "training" biological neural networks. This explains why techniques like evolutionary algorithms outperform gradient descent for architecture search.
Unanswered Questions: While fractals emerge from iterative functions (like gradient steps), their prevalence across ML paradigms needs verification. Early evidence suggests chain-of-thought reasoning and RNNs exhibit similar variance issues, potentially linking to fractal dynamics. Key unknowns include why certain iterative processes generate fractals and how broadly this applies beyond weight optimization.
The Learning Revolution: LLMs as Cognitive Partners
A meta-observation emerges across these readings: LLMs fundamentally alter learning. One researcher noted struggling with complex material like Strogatz's text pre-LLMs, despite university training. The ability to pause, query, and cross-reference with chatbots enables deeper engagement with technical content—suggesting AI's most immediate impact may be accelerating human comprehension rather than replacing domain experts.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion