A comprehensive PwC survey of 4,454 CEOs reveals that while a third of enterprises see some value from AI deployment, only 12% achieve the ideal outcome of both increased revenue and reduced costs. The findings highlight a significant gap between AI hype and tangible business results, with data readiness and workforce adoption emerging as critical factors for success.
A recent survey by PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC) of 4,454 chief executives worldwide has delivered a sobering assessment of enterprise AI deployment, revealing that only 12% of business leaders have achieved the dual benefits of increased revenue and decreased costs from their artificial intelligence investments. The findings, published in PwC's latest Global AI Study, underscore the complex reality facing organizations as they navigate the transition from AI experimentation to measurable business value.
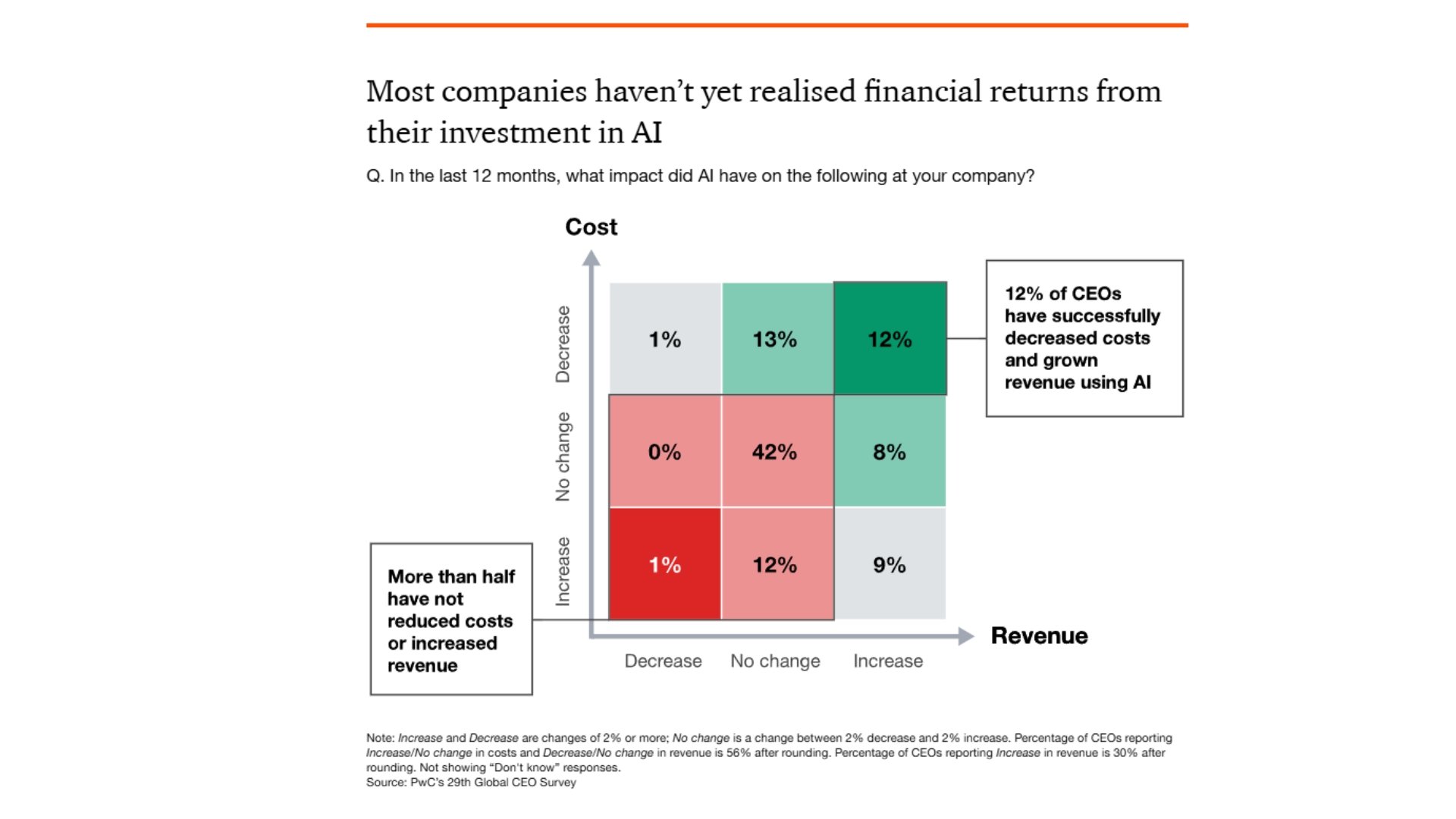
The Distribution of AI Outcomes
The survey data paints a nuanced picture of AI's impact on corporate bottom lines. While 55% of CEOs reported seeing no benefit from AI tools whatsoever, the remaining 45% experienced varying degrees of success:
- 12% achieved the ideal outcome: Higher revenues paired with lower costs
- 13% saw cost reductions without revenue changes
- 8% experienced revenue increases without cost changes
- 12% reported mixed or neutral outcomes: Either lower costs with lower revenues, or higher revenues matched by higher expenditures
- 12% saw negative outcomes: Increased costs without revenue changes (11%) or the worst-case scenario of increased expenses and decreased returns (1%)
This distribution reveals that while a third of enterprises gained some value from AI deployment, the majority have yet to see meaningful financial impact. The 55% seeing no benefit represents a significant portion of the market where AI investments have not yet translated into tangible business results.
The Readiness Gap: Why Most Deployments Underperform
PwC's analysis suggests that the inconsistent results stem from fundamental gaps in organizational preparedness. Mohamed Kande, PwC's Global Chairman, noted that "Companies that invest in data readiness, clear AI roadmaps, responsible guardrails, and a culture that enables adoption see better outcomes."
This insight points to several critical prerequisites that many organizations have overlooked:
Data Infrastructure: AI systems require clean, structured, and accessible data. Many enterprises are attempting to deploy AI on fragmented, siloed, or poor-quality data, leading to unreliable outputs and limited business value.
Strategic Roadmaps: Successful AI adoption requires clear objectives aligned with business goals, rather than technology-first approaches. The 12% achieving full benefits likely have well-defined use cases tied to specific revenue or cost metrics.
Governance Frameworks: Responsible AI implementation demands guardrails for ethics, compliance, and risk management. Organizations lacking these frameworks may face regulatory challenges or reputational risks that offset potential gains.
Cultural Adoption: AI tools are only as effective as the people using them. PwC's finding that only 14% of the workforce uses generative AI daily in their workflows suggests significant adoption barriers, including lack of training, resistance to change, or poorly designed user interfaces.
The Workforce Adoption Challenge
The statistic that only 14% of employees use generative AI daily reveals a critical bottleneck in enterprise AI value creation. This low adoption rate means that:
- Most workers lack firsthand experience with AI's capabilities and limitations
- Organizations may be underestimating the training and change management required
- The potential productivity gains from AI remain largely untapped
- There's limited feedback to improve AI systems based on real-world usage
The report suggests that this low adoption rate creates both a challenge and an opportunity. Organizations that can successfully scale AI usage across their workforce stand to gain significant competitive advantages, while those that cannot may fall behind.
Pathways to Success: What the 12% Do Differently
PwC's analysis indicates that companies achieving the full benefits of AI deployment share common characteristics:
- Extensive Integration: They apply AI across products, services, and customer experiences rather than in isolated use cases
- Revenue-Focused Implementation: They prioritize AI applications that directly drive top-line growth
- Cost Optimization: They identify specific operational areas where AI can reduce expenses without sacrificing quality
- Continuous Measurement: They establish clear metrics to track AI's impact on both revenue and costs
The report emphasizes that achieving both revenue growth and cost reduction requires AI to be embedded deeply into business operations rather than treated as a standalone technology initiative.
The Investment Pressure and Market Reality
The survey findings arrive amid significant investment in AI technologies. J.P. Morgan's recent projection that the AI industry needs to deliver $650 billion in revenue to achieve a 10% return on current investments highlights the financial pressure on AI providers and adopters alike.
To put this in perspective, achieving this revenue target would require:
- $34.72 from every current iPhone user, or
- $180 from every Netflix subscriber
This financial reality check suggests that the AI market must demonstrate substantial value creation to justify continued investment levels. The gap between current results and required returns creates pressure for both AI vendors and enterprise customers to accelerate value realization.
Implications for Enterprise Strategy
The PwC survey results suggest several strategic considerations for business leaders:
Investment Prioritization: Rather than broad, unfocused AI investments, organizations should prioritize use cases with clear ROI potential and measurable outcomes.
Capability Building: Investment in data infrastructure, talent development, and change management may be more critical than technology acquisition.
Phased Deployment: Organizations should consider starting with focused pilots that demonstrate value before scaling across the enterprise.
Partnership Strategy: Given the complexity of successful AI deployment, partnerships with experienced providers may accelerate value realization.
Looking Ahead: Bridging the Hype-Reality Gap
The survey reveals what PwC characterizes as a "precarious state" for AI services, where industry leaders continue to invest heavily despite inconsistent results. This dynamic creates both risks and opportunities:
Risks: Continued investment without clear returns may lead to budget reallocation or reduced confidence in AI technologies.
Opportunities: Organizations that solve the deployment challenge first may establish significant competitive advantages.
The report suggests that bridging the gap between AI hype and business results requires a more disciplined, strategic approach to deployment. Success appears to depend less on the sophistication of the AI technology and more on organizational readiness, clear objectives, and effective change management.
As enterprises continue their AI journeys, the 12% achieving full benefits provide a roadmap for others to follow, while the 55% seeing no benefit serve as a cautionary reminder that technology alone does not guarantee business success.
The path forward likely involves more measured, strategic approaches to AI deployment, with greater emphasis on data quality, workforce adoption, and clear alignment with business objectives. For organizations still in the early stages of AI adoption, the survey suggests that patience and preparation may be more valuable than rapid deployment.
Source: PricewaterhouseCoopers Global AI Study, 2024
For organizations seeking to improve their AI deployment outcomes, PwC's research suggests starting with data readiness assessments and clear business case development before proceeding with technology implementation.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion