GitLab has patched multiple high-severity vulnerabilities affecting its self-managed platforms, including flaws enabling token theft and server crashes, requiring immediate upgrades for all affected installations.
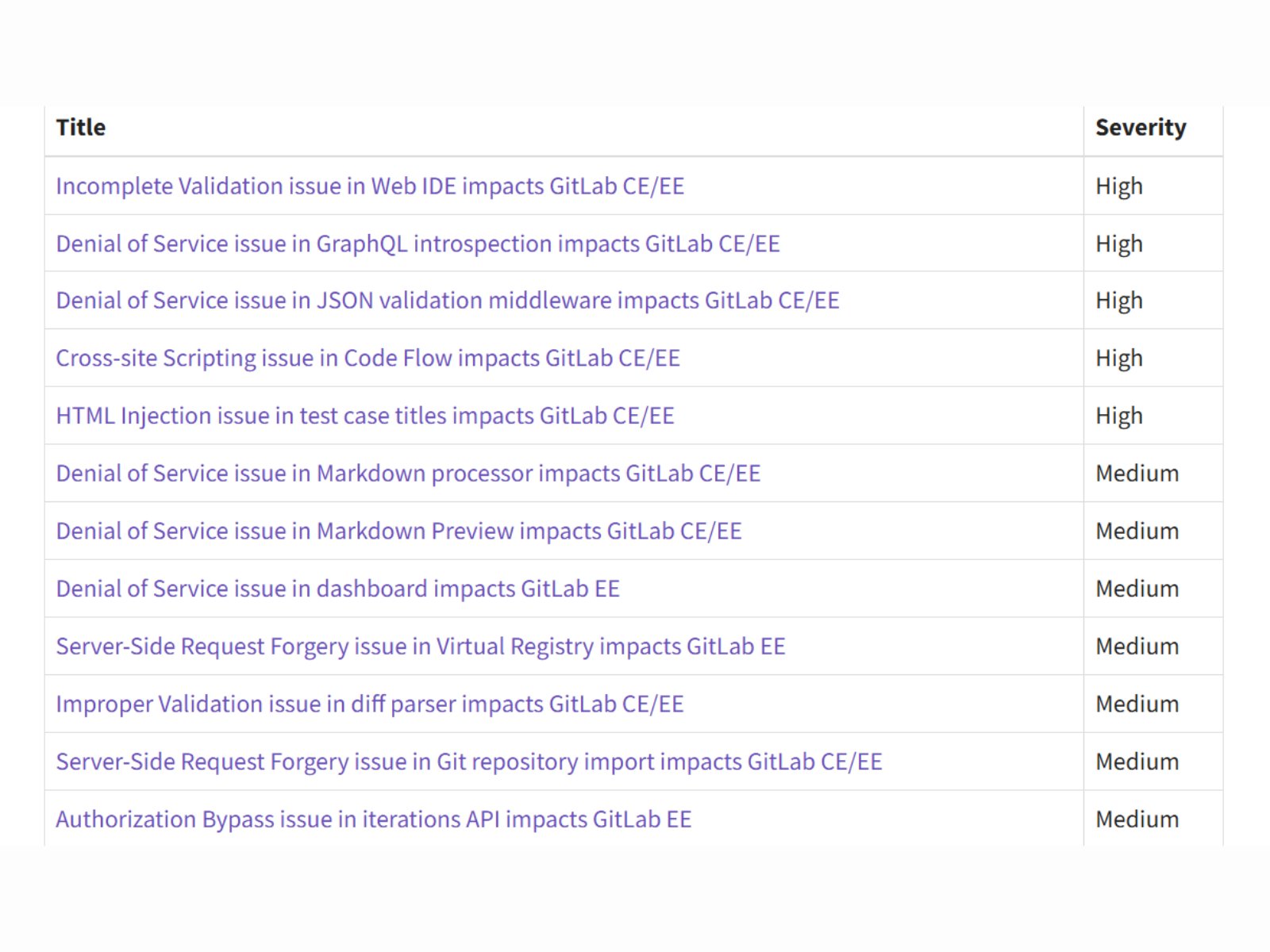
GitLab has issued emergency updates to address five high-severity vulnerabilities across its Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE) platforms, with the company emphasizing immediate action for self-managed instances. The patches, released as versions 18.8.4, 18.7.4, and 18.6.6, resolve critical security gaps that could expose repositories to unauthorized access or disrupt services through denial-of-service attacks.
The most severe flaw, tracked as CVE-2025-7659 (CVSS 8.0), involves inadequate validation in GitLab's Web IDE. This vulnerability permits unauthenticated attackers to steal access tokens, potentially compromising private repositories. Unlike authentication bypass issues in earlier GitLab versions, this exploit requires no user interaction, making it particularly dangerous for exposed instances.
Denial-of-service vulnerabilities also pose significant risks:
- CVE-2025-8099: Allows repeated GraphQL queries to crash servers
- CVE-2026-0958: Bypasses JSON validation middleware to exhaust system resources
Additional patched threats include:
- Cross-site scripting (CVE-2025-14560) enabling script injection
- Content manipulation vulnerability (CVE-2026-0595)
- Medium-severity flaws in Markdown processing and dashboard components
- Server-side request forgery (SSRF) risks
Who Must Act
Self-managed GitLab installations running any version prior to the patched releases are affected. GitLab.com users and GitLab Dedicated customers require no action, as these environments receive automatic updates. Administrators should prioritize upgrades based on these risk factors:
- Instances with public-facing Web IDE access
- Organizations storing sensitive intellectual property in repositories
- High-traffic deployments vulnerable to DoS attacks
Upgrade Requirements
- Single-node deployments: Expect downtime during database migrations
- Multi-node clusters: Can upgrade without downtime using GitLab's recommended procedures
- Mandatory post-upgrade steps: Review release notes and verify repository integrity
GitLab maintains a twice-monthly patch schedule but accelerates updates for critical vulnerabilities like these. Vulnerability details will become public 30 days post-patch, creating a limited window for attackers to reverse-engineer exploits. The company advises testing in staging environments before production deployment.
For organizations evaluating GitLab against alternatives like GitHub Enterprise, these security events highlight the importance of self-managed instance maintenance. While cloud-hosted options reduce administrative burden, self-managed deployments offer greater control at the cost of prompt vulnerability management.
Administrators should monitor the GitLab security advisory page for emerging threats and establish a patch deployment protocol requiring critical updates within 24 hours of release.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion