Microsoft's integration of LangChain with Azure SQL introduces native vector search capabilities, enabling developers to build sophisticated AI applications directly within SQL databases. The new langchain-sqlserver package simplifies implementation, with practical examples showing how to create Q&A systems and creative content generators.
Microsoft has expanded the AI capabilities of Azure SQL and SQL database in Microsoft Fabric with native vector search support, accompanied by the release of the langchain-sqlserver package. This integration allows developers to manage SQL Server as a Vectorstore within LangChain, significantly lowering the barrier to implementing advanced AI features in traditional database environments.
The announcement represents a strategic move to bridge the gap between relational databases and modern AI applications. By embedding vector search capabilities directly into SQL Server, Microsoft enables developers to leverage existing database infrastructure while incorporating sophisticated AI functionality without requiring specialized vector databases or complex data pipelines.
Vector search has become increasingly important for AI applications, particularly those involving natural language processing, recommendation systems, and semantic search. Traditional databases struggle with these use cases because they're optimized for structured data and exact matches rather than the fuzzy, similarity-based comparisons that power modern AI features.
The new langchain-sqlserver package addresses this limitation by providing a seamless interface between LangChain's powerful AI framework and SQL Server's robust data management capabilities. Developers can now implement vector similarity searches, retrieve relevant context for large language models, and build sophisticated retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems using familiar SQL tools.

To demonstrate the practical applications of this integration, Microsoft's tutorial uses the Harry Potter book series as a dataset. This choice serves multiple purposes: it's a well-known corpus that provides rich content for both Q&A and creative generation tasks, and it allows for relatable examples that showcase the technology's capabilities without requiring specialized domain knowledge.
The tutorial walks through a five-step implementation process:
First, developers need to install the langchain-sqlserver package, which is available through Python's package manager with a simple pip install command. This package contains the necessary code to integrate SQL Server with LangChain's vector store functionality.
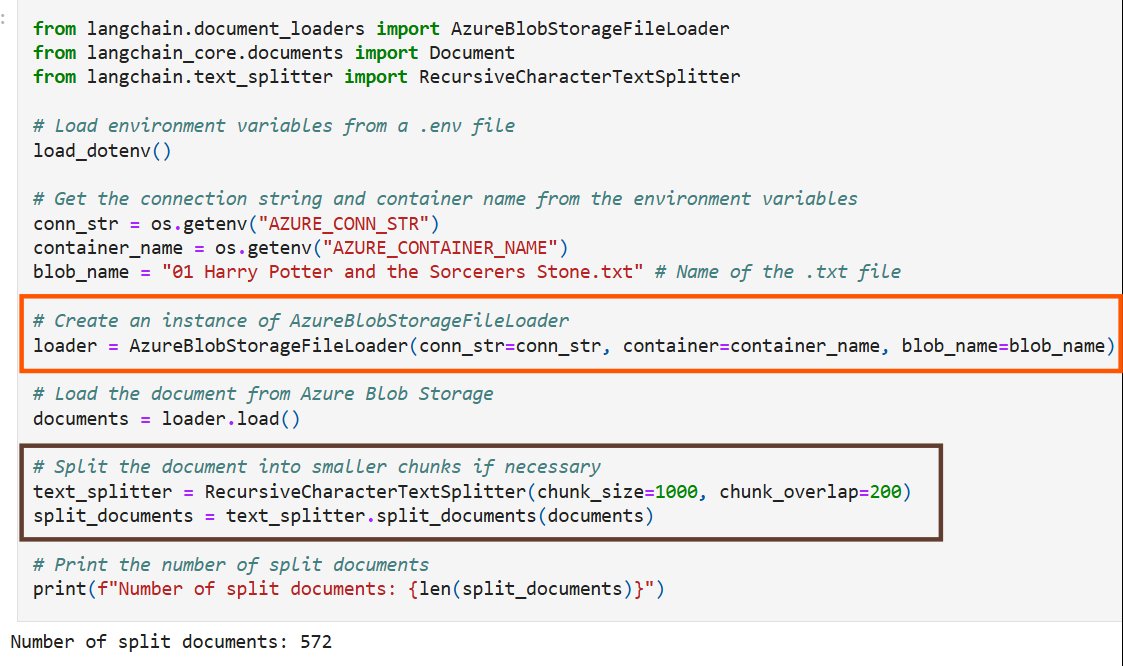
Next, the tutorial demonstrates how to load text data from Azure Blob Storage and split it into manageable chunks. LangChain's integration with Azure Blob Storage makes this process straightforward, while the text splitter ensures that content fits within the input token limits of embedding models like those from Azure OpenAI.
The third step involves defining functions for embedding generation and chat completion. While the tutorial specifically uses Azure OpenAI for embeddings, the architecture supports alternative embedding providers available through LangChain, giving developers flexibility in their implementation choices.
The fourth step initializes the vector store and inserts documents into Azure SQL with their corresponding embeddings. This is where the integration truly shines, as developers can accomplish sophisticated vector operations with just a few lines of code. The add_documents function handles both the storage of text content and its vector representation.
Finally, the tutorial covers querying data through similarity search, with support for filtering based on document metadata. This capability allows for more precise searches by narrowing results to specific subsets of data based on attributes like document type, creation date, or other custom metadata.
The tutorial presents two compelling use cases that demonstrate the technology's potential. The first is a Q&A system that can answer questions about the Harry Potter books with context-rich responses. By leveraging the vector store's similarity search capabilities, the system retrieves relevant passages and uses them to generate accurate answers through a large language model.
The second use case is more creative: a fan fiction generator that can produce new Harry Potter stories based on user prompts. This application retrieves relevant passages from the books that match the user's creative direction, then uses those passages as inspiration for the language model to generate original content while maintaining consistency with the established Harry Potter universe.
Both use cases showcase how the integration of vector search with LLMs can create more sophisticated and contextually aware applications. The Q&A system demonstrates practical information retrieval, while the fan fiction generator illustrates the creative potential of combining structured knowledge with generative AI.
For developers interested in implementing these solutions, Microsoft has made the complete code samples available through a GitHub repository. The repository contains the Jupyter notebooks used in the tutorial along with additional examples that explore different aspects of the technology.
The integration of vector search into SQL Server represents a significant advancement for developers working with AI applications. By eliminating the need for specialized vector databases and complex data synchronization, Microsoft has lowered the barrier to entry for implementing sophisticated AI features while maintaining the data management capabilities that make SQL Server a trusted choice for enterprise applications.
As AI continues to evolve, the ability to seamlessly integrate these capabilities with existing data infrastructure will become increasingly important. Microsoft's approach of extending familiar tools rather than requiring entirely new platforms aligns with this reality, potentially accelerating adoption across organizations of all sizes.
The vector support in SQL is currently in public preview, indicating that Microsoft is actively seeking feedback from the developer community. This collaborative approach suggests that future iterations of the technology will continue to evolve based on real-world usage patterns and emerging requirements.
For organizations considering AI implementations, this integration offers a practical pathway to explore these technologies without requiring significant architectural changes. The combination of familiar SQL interfaces with powerful AI capabilities creates an accessible on-ramp for developers looking to incorporate vector search and large language models into their applications.
The Harry Potter examples, while seemingly whimsical, demonstrate fundamental patterns that can be applied to numerous domains. From customer support systems that retrieve relevant product information to creative tools that generate marketing copy based on brand guidelines, the underlying technology has broad applicability across industries.
As the technology matures, we can expect to see more sophisticated implementations that push the boundaries of what's possible with integrated vector search and generative AI. The foundation laid by this integration provides a solid starting point for exploring these possibilities while maintaining the data management and security features that enterprise applications require.
For developers interested in exploring this technology further, the GitHub repository provides practical examples and the opportunity to contribute feedback that will shape future development. As with any emerging technology, community input will play a crucial role in identifying the most valuable features and addressing implementation challenges.
The integration of LangChain with Azure SQL represents not just a technical advancement, but also a strategic direction for Microsoft in the AI space. By making powerful AI capabilities accessible through familiar tools and interfaces, the company is helping to democratize these technologies while maintaining the enterprise-grade features that organizations have come to expect.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion