Microsoft's Agent Framework now allows developers to expose existing AI agents as MCP-compatible tools, enabling cross-platform consumption through the standardized Model Context Protocol.
Microsoft Streamlines AI Agent Integration with Model Context Protocol
Microsoft has enhanced its Agent Framework with new capabilities to expose AI agents as MCP (Model Context Protocol) tools, enabling consumption by any MCP-compatible client application. This development bridges standalone AI agents with the broader MCP ecosystem, addressing key multi-cloud and cross-platform integration challenges.

Technical Implementation Overview
The implementation process involves three key conversions:
- Agent → AIFunction: Using
.AsAIFunction()to encapsulate agent logic - AIFunction → McpServerTool: Via
McpServerTool.Create() - Hosting: Serving through ASP.NET Core with SSE transport
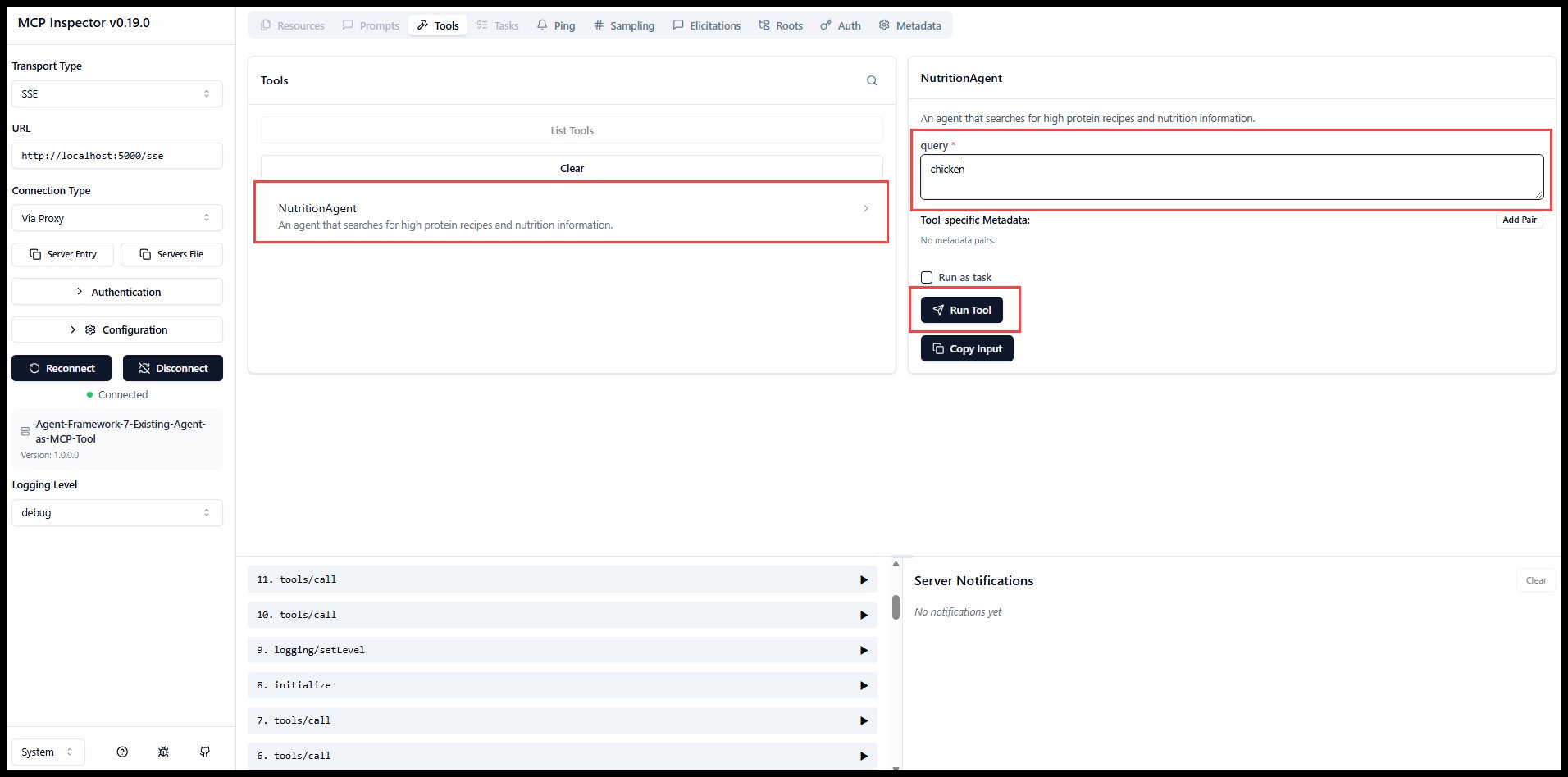
Developers can convert existing agents like the nutrition agent demonstrated in Microsoft's GitHub repository, which searches for high-protein recipes, into MCP-compatible endpoints. The agent's description metadata automatically populates MCP tool definitions visible to clients.
Strategic Advantages for Cloud Architectures
- Cross-Platform Reusability: Agents become discoverable by VS Code, Claude Desktop, and custom clients
- Protocol Standardization: Eliminates custom integration code through MCP's specification
- Cloud-Native Deployment: HTTP/SSE transport aligns with modern microservices patterns
- Agent Composability: Enables multi-cloud agent workflows through standardized tool invocation
Migration Considerations
Organizations with existing Microsoft Agent Framework implementations can:
- Wrap agents with minimal code changes
- Maintain current tooling while gaining MCP compatibility
- Gradually expose agents through MCP without disrupting existing integrations
The MCP Inspector tool simplifies testing, allowing developers to validate agent exposure during migration.
Business Impact Analysis
| Approach | Pre-MCP Integration | MCP-Enabled Agents |
|---|---|---|
| Development Cost | High (per-client integration) | Low (single implementation) |
| Discovery Mechanism | Proprietary | Standardized MCP discovery |
| Deployment Flexibility | Environment-specific | Cloud-agnostic |
| Tool Composability | Limited | Cross-platform chaining |
Strategic Recommendations
- Hybrid Agent Ecosystems: Maintain core agent logic in Azure while exposing via MCP to AWS/GCP clients
- Progressive Exposure: Start with non-critical agents using the ModelContextProtocol.AspNetCore package
- Monitoring Strategy: Implement cross-provider observability for MCP tool calls
This advancement positions Microsoft's agent framework as a bridge between proprietary AI capabilities and open protocol ecosystems, potentially reshaping how organizations deploy conversational AI across multi-cloud environments. The technical documentation provides implementation guidance for existing Agent Framework users.
For organizations evaluating AI agent strategies, this development reduces lock-in concerns while maintaining Microsoft toolchain advantages—a balanced approach for hybrid cloud environments.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion