Motorola's new Moto G Power (2026) receives a mediocre repairability rating due to its stubborn battery design that complicates repairs.
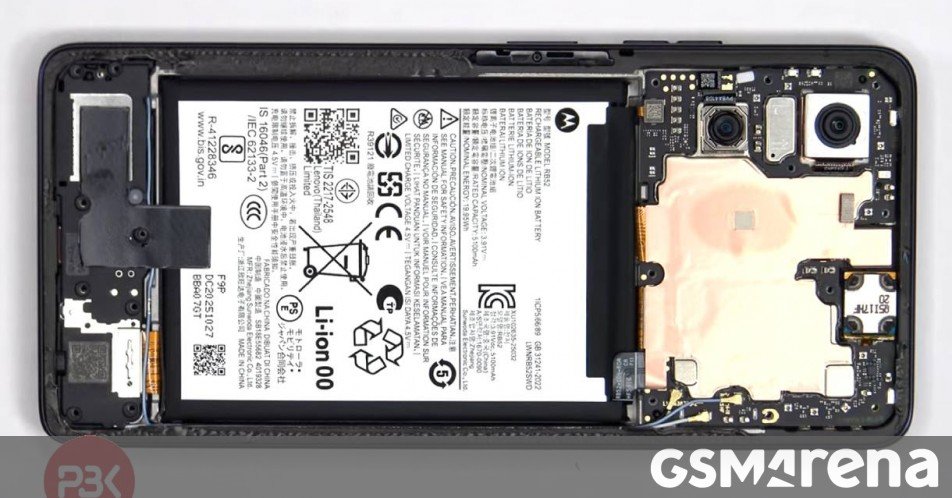
The recently launched Motorola Moto G Power (2026) faces criticism for its repairability limitations despite featuring solid mid-range specifications. According to a detailed teardown analysis by PBKreviews, the $300 smartphone earned a repairability score of just 5/10 primarily due to its difficult-to-access battery design.
This budget-friendly device features a 6.8-inch LCD display, MediaTek Dimensity 6300 chipset, expandable storage, and IP69 water/dust resistance with MIL-STD-810H durability certification. Its standout feature remains the 5,200mAh battery supporting 30W wired and 15W wireless charging, rated to maintain 80% capacity after 1,000 charge cycles.
However, disassembly reveals significant repair challenges:
- Excessive Battery Adhesion: The battery lacks pull tabs and uses substantial adhesive, requiring careful prying to remove
- Component Interference: Key connectors including the display cable run beneath the battery
- Button Repair Complexity: Accessing the power and volume button ribbons necessitates complete screen removal
These design choices create cascading repair difficulties. As PBKreviews demonstrates in their teardown video, replacing the battery risks damaging both the screen and battery itself. More concerningly, even simple button repairs become high-risk procedures that threaten multiple components.
While Motorola's battery longevity reduces immediate replacement needs, the design conflicts with growing right-to-repair priorities. The dual-camera system (50MP main with OIS + 8MP ultra-wide) and flicker sensor remain accessible, but critical components like the motherboard become collateral damage risks during battery procedures.
This repairability assessment highlights how physical design decisions impact long-term device sustainability, especially in budget devices where repair costs could approach replacement value. Motorola's rugged exterior protections unfortunately didn't extend to serviceable internal design, presenting a significant hurdle for both DIY repairs and professional technicians.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion