Nvidia's explosive growth in AI hardware has propelled it past Apple to become TSMC's largest client, a shift that could reshape the semiconductor foundry's priorities and pricing structure.
The semiconductor industry's power dynamics have shifted dramatically in 2025. Nvidia, fueled by unprecedented demand for AI infrastructure, has reportedly overtaken Apple as Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company's (TSMC) largest customer. This marks the first time in years that Apple has been displaced from its position as the foundry's top revenue source.

The Numbers Behind the Shift
Nvidia's ascent is quantifiable. In 2024, Apple accounted for approximately 25% of TSMC's total revenue, while Nvidia contributed less than half that amount at 11%. By 2025, this equation reversed. Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang confirmed the change in a recent podcast, stating that Nvidia had become TSMC's biggest client. This assertion is backed by Nvidia's record-breaking Q3 fiscal 2026 results, which showed a staggering 62% year-over-year revenue increase.
The primary driver is Nvidia's Data Center business. Products like the H200 GPU, designed for AI training and inference, have seen insatiable demand from cloud providers and AI startups alike. According to figures from investment research firm I/O Fund, shared via analyst Beth Kindig on X, Nvidia's Data Center revenue for Q3 2025 surpassed Apple's iPhone revenue for the first time in history. This crossover highlights the sheer scale of the AI hardware boom.
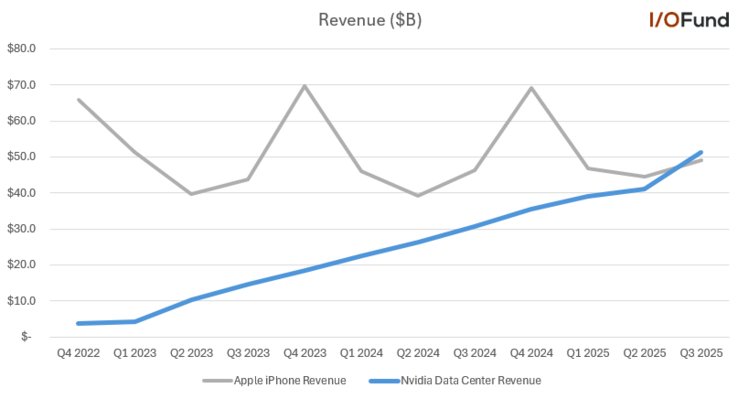
Implications for TSMC's Business Model
For years, Apple has enjoyed special privileges from TSMC, including discounts, priority access to the latest process nodes (like the 3nm and upcoming 2nm nodes), and guaranteed production capacity. This arrangement made strategic sense for TSMC, as Apple's orders provided a stable, high-volume revenue base.
With Nvidia now taking the top spot, TSMC's priorities are likely to shift. Industry rumors suggest TSMC is already pressuring Apple to accept a significant price hike, a move that would have been unthinkable when Apple was the undisputed revenue leader. While the validity of these specific rumors is unconfirmed, the broader trend is clear: TSMC will increasingly align its resources with its largest customer's needs.
This could mean Nvidia gains even more favorable terms for its advanced process nodes, which are critical for maintaining its performance lead in AI chips. The foundry's roadmap, including the transition to 2nm and beyond, will be heavily influenced by Nvidia's requirements for its next-generation Blackwell and Rubin architectures.
Market Context and Future Outlook
This shift doesn't indicate weakness on Apple's part. The iPhone 17 series remains immensely popular, and Apple's silicon division continues to produce industry-leading chips for its devices. However, the growth trajectory is fundamentally different. Apple's chip demand is tied to the relatively stable smartphone market, while Nvidia's demand is scaling exponentially with the global build-out of AI data centers.
The AI hardware market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 30% for the next several years. Nvidia's Data Center segment, which includes GPUs, networking, and software, is at the epicenter of this expansion. As long as this growth continues, Nvidia's position at TSMC will remain secure, if not strengthened further.
For TSMC, this transition presents both opportunity and risk. Diversifying its customer base away from over-reliance on Apple is generally seen as positive for long-term stability. However, it also means the foundry becomes more exposed to the cyclical nature of the AI market. A slowdown in AI investment could have a more pronounced impact on TSMC's revenue than a downturn in smartphone sales.
What This Means for the Industry
The semiconductor industry is witnessing a historic realignment. The era dominated by consumer electronics is giving way to one driven by AI infrastructure. Nvidia's rise to the top of TSMC's customer list is a tangible manifestation of this shift.
For competitors like AMD and Intel, who also rely on TSMC's advanced nodes, this could create a more challenging environment. As TSMC allocates more capacity and engineering resources to meet Nvidia's demands, other customers may face longer lead times or higher costs.
For consumers, the immediate impact may be minimal. However, the long-term effects could include faster innovation in AI hardware, as Nvidia's close collaboration with TSMC accelerates the development of next-generation chips. Conversely, if TSMC's pricing power increases due to concentrated demand, it could eventually filter down to higher costs for all chip buyers, including those in the consumer electronics space.
In summary, Nvidia's ascent to become TSMC's biggest customer is more than a financial footnote. It signals a fundamental shift in the technology landscape, where the demands of AI are now the primary driver of semiconductor manufacturing priorities. The relationship between chip designer and foundry has never been more critical, and the industry will be watching closely to see how this new dynamic unfolds.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion