Raspberry Pi's $130 AI accelerator HAT+ 2 offloads LLM processing from the Pi 5 CPU using Hailo-10H silicon and 8GB RAM, but inconsistent results and pricing challenges limit its value proposition against software alternatives.
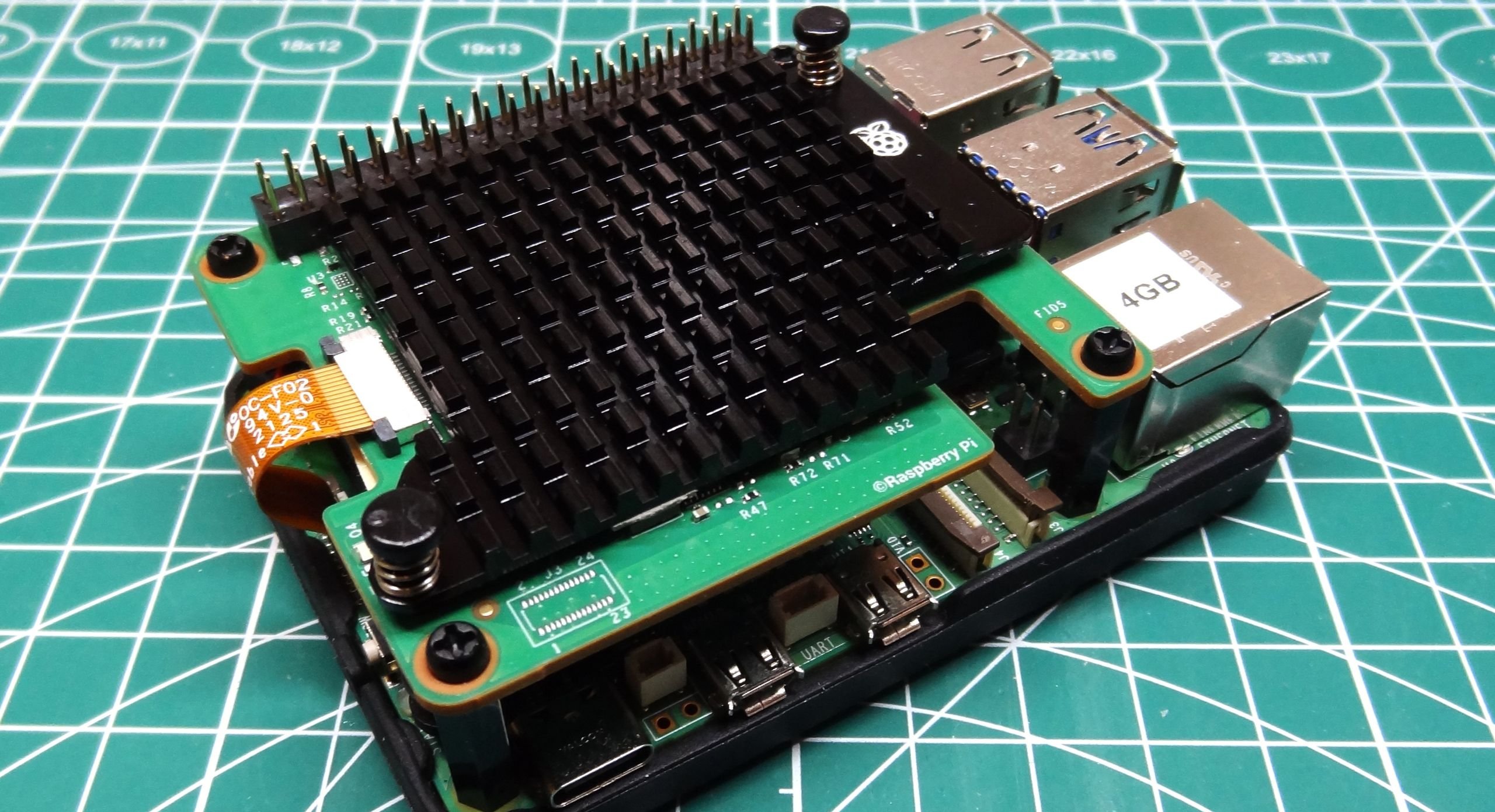

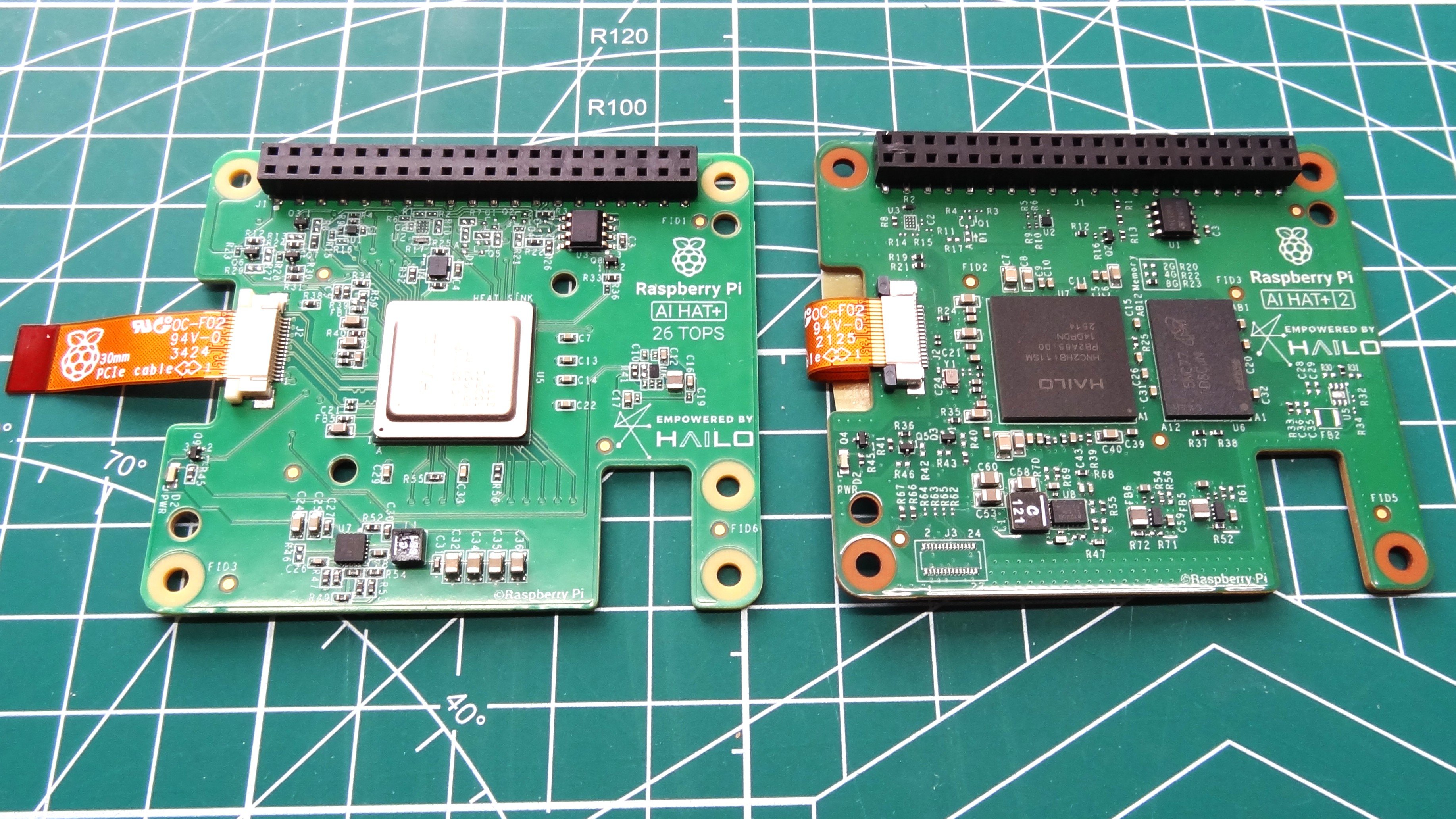
The Raspberry Pi Foundation's AI HAT+ 2 represents a strategic push into edge AI acceleration, pairing Hailo's 40-TOPS (INT4) 10H processor with 8GB DDR4X RAM. This hardware configuration enables offloading of large language model (LLM) workloads from Raspberry Pi 5's Cortex-A76 CPU, theoretically freeing system resources for real-time applications. However, our technical evaluation reveals significant implementation challenges.
Architectural Specifications
| Component | AI HAT+ 2 | Previous AI HAT+ |
|---|---|---|
| Accelerator | Hailo-10H | Hailo-8L |
| TOPS (INT4) | 40 | 13-26 |
| Onboard RAM | 8GB DDR4X | N/A |
| PCIe Interface | Gen 3 x1 | Same |
| Power Draw | 12W peak | 7W peak |
| Price | $130 | $70-$110 |
The Hailo-10H represents a process node improvement over previous-generation chips, enabling higher compute density. Its memory subsystem—8GB dedicated DDR4X—allows operation even on entry-level Pi 5 configurations (1GB/4GB models), potentially saving $50-$80 versus requiring an 8GB Pi 5. This memory isolation prevents CPU resource contention but introduces thermal constraints necessitating the included heatsink.

Inference Performance Benchmarks
Testing qwen2:1.5b LLM revealed mixed results:
- Speed Advantage: 13.58s response vs 22.93s on Pi 5 CPU
- CPU Utilization: Near-zero vs 100% core utilization
- Accuracy Issues: Both implementations failed basic knowledge tests
Coding tasks exposed deeper flaws. When instructed to "Write a Python script to display an image", the HAT+ 2 generated non-functional code missing critical libraries. The Pi 5 CPU produced longer but equally flawed output. Neither implementation delivered production-ready solutions.
Supply Chain Considerations
The $130 price positions this accessory at 2.6x the cost of Raspberry Pi's 4GB model. With Hailo chips fabricated on specialized processes not shared with mainstream CPUs, production scalability remains constrained. Compared to the previous-gen AI HAT+ ($70 for 13 TOPS), customers pay 85% more for primarily LLM-focused capabilities with equivalent vision processing throughput.
Practical Applications
- Edge Robotics: Offloading frees CPU for sensor processing
- Vision Prototyping: Comparable to previous HAT at higher cost
- LLM Experiments: Knowledge cutoff limitations require verification
For computer vision projects, the Raspberry Pi AI Camera ($25) delivers better value. Enterprises exploring edge LLMs face accuracy tradeoffs versus cloud APIs. The dedicated RAM enables smaller Pi configurations, but total system cost still approaches $200.
Market Implications
This release highlights the challenge of balancing performance, accuracy and cost in edge AI. While the architectural approach shows promise, current implementation doesn't justify the premium over software-based alternatives. As semiconductor partners like Hailo mature their SDKs, future iterations could improve value—but at launch, the HAT+ 2 serves a narrow niche requiring hardware-accelerated LLMs in portable form factors. For most developers, CPU-based AI or previous-gen accelerators offer more practical solutions.

The AI HAT+ 2 demonstrates Raspberry Pi's commitment to edge computing but underscores the industry-wide challenge of deploying performant, accurate AI at constrained price points. Its success hinges on software maturation and clearer differentiation from both software alternatives and the previous-generation hardware.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion