Microsoft Copilot offers practical guidance for winter planning, from budget-friendly ski trips to local seasonal activities and home-based entertainment, demonstrating its utility as a personal planning assistant beyond enterprise use cases.
Winter often brings a paradox: the desire for seasonal activities conflicts with the practical challenges of cold weather, travel costs, and planning. Microsoft Copilot has been positioning itself as a versatile assistant, and recent examples show its application in personal planning scenarios that mirror enterprise decision-making processes. The same principles of cost-benefit analysis, resource optimization, and scenario planning that apply to cloud migrations can be directed toward planning a ski trip or a family snow day.
What Changed: Copilot's Personal Planning Capabilities
Microsoft has been expanding Copilot's use cases beyond productivity and coding assistance into lifestyle planning. The examples provided show Copilot functioning as a travel agent, local guide, and activity coordinator. This represents a shift in how AI assistants are being marketed—not just as tools for work, but as comprehensive planning partners.
The key development is the application of structured prompting to personal scenarios. Users can specify constraints (budget, time, location) and receive tailored recommendations. This mirrors how businesses use AI for vendor selection or migration planning, where multiple variables must be balanced.
Provider Comparison: Copilot vs. Traditional Planning Methods
When planning a winter activity, traditional methods involve multiple steps: researching destinations, comparing prices, reading reviews, and coordinating with others. Copilot attempts to consolidate this into a single interaction.
Traditional Planning:
- Time-intensive: Hours of research across multiple sites
- Fragmented information: Reviews, prices, and logistics scattered
- Static recommendations: Based on outdated or incomplete data
Copilot-Assisted Planning:
- Consolidated output: Recommendations with integrated details
- Dynamic constraints: Adjusts to budget and time limitations
- Contextual awareness: Considers location and user preferences
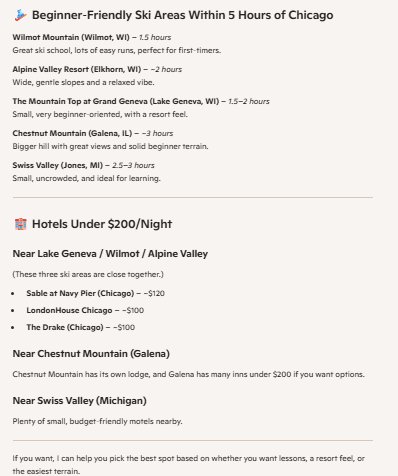
For a ski trip example: "I live outside Chicago and want to try skiing for the first time. What are the best mountains to visit for beginners that are within a five-hour drive. Also, list 3-5 hotels I can stay in for less than $200 a night."
This prompt structure mirrors a business requirement document: location constraints, user profile (beginner), budget limits, and specific deliverables (hotel list). The AI's response synthesizes data that would otherwise require checking multiple travel sites, ski resort reviews, and hotel booking platforms.
Business Impact: The Pattern of AI-Assisted Decision Making
The underlying pattern here applies directly to cloud strategy and migration planning. Consider these parallels:
1. Constraint-Based Optimization Just as Copilot balances budget, time, and location for a ski trip, businesses must balance cost, performance, and compliance when selecting cloud providers. The AI's ability to filter options based on multiple constraints demonstrates the same logic used in cloud vendor selection.
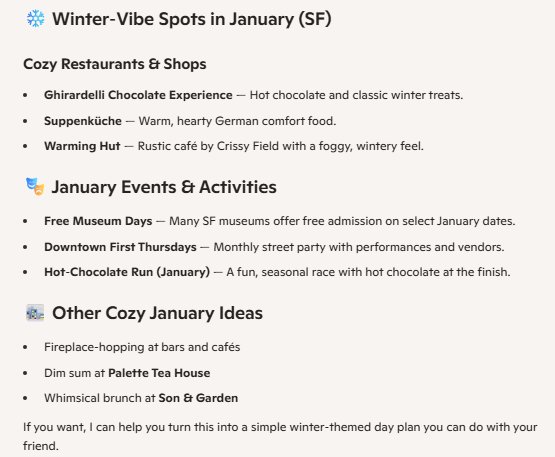
2. Local vs. Remote Solutions The example of finding winter activities in San Francisco—where traditional seasonal activities are limited—parallels the decision between cloud and on-premises solutions. Sometimes the optimal solution isn't the obvious one; it requires creative thinking about available resources.
3. Resource Maximization The snow day itinerary example shows how to maximize existing resources (household items) for multiple outcomes (entertainment and education). This directly applies to cloud optimization: getting more value from existing infrastructure before migrating, or designing systems that serve multiple purposes.

Technical Implementation: How the Prompt Engineering Works
The effectiveness of Copilot's responses depends on prompt structure. Each example follows a clear pattern:
- Context Setting: "I live outside Chicago..." establishes location and experience level
- Specific Requirements: "within a five-hour drive" and "less than $200 a night" define boundaries
- Clear Deliverables: "best mountains for beginners" and "3-5 hotels" specify output format
This mirrors how technical teams should structure requests for AI assistance in cloud planning:
- Current state assessment (where we are)
- Requirements (what we need)
- Constraints (budget, timeline, compliance)
- Desired outcome (specific deliverables)
The AI's ability to parse these constraints and generate coherent recommendations demonstrates natural language processing applied to structured problem-solving. For businesses, this means AI can assist in initial vendor research, cost estimation, and scenario planning before human experts validate the recommendations.

Practical Application: From Personal to Professional
The transition from personal planning to business strategy involves scaling the same principles:
Personal Planning (Copilot Example):
- Goal: Plan a ski trip
- Constraints: Budget, time, location
- Output: Destination recommendations, hotel options
Business Planning (Cloud Migration):
- Goal: Migrate to cloud
- Constraints: Budget, timeline, compliance requirements
- Output: Provider recommendations, cost estimates, migration paths
The key insight is that AI assistance follows the same logical framework regardless of domain. The difference lies in data sources and validation requirements. For personal activities, Copilot can synthesize public information. For business decisions, it would need access to internal data and compliance parameters.
Strategic Considerations for AI Planning Tools
When evaluating AI assistants for planning tasks—whether personal or professional—consider these factors:
Data Freshness: Recommendations are only as current as the underlying data. For rapidly changing markets (cloud pricing, travel costs), verify AI suggestions against official sources.
Constraint Handling: The AI's ability to manage multiple constraints simultaneously is valuable, but complex requirements may need iterative refinement.
Validation Requirements: Personal plans might accept AI recommendations with minimal verification. Business decisions require human validation, especially for compliance, security, and cost commitments.
Integration Potential: The most powerful applications connect AI planning with execution tools. For example, Copilot's recommendations could integrate with booking systems or project management tools.
The Broader Pattern: AI as Planning Partner
Microsoft's positioning of Copilot for winter activities reflects a broader trend: AI assistants are becoming planning partners across domains. This evolution follows a pattern similar to cloud adoption:
- Initial Skepticism: "AI can't plan as well as humans"
- Limited Adoption: "AI helps with specific, narrow tasks"
- Integrated Use: "AI is part of our planning workflow"
- Strategic Dependence: "AI informs our decision-making process"
For cloud professionals, this pattern should be familiar. The same evolution is happening with AI planning tools. The key is understanding where AI adds value (data synthesis, constraint management, initial research) and where human expertise remains critical (validation, complex negotiations, strategic decisions).
Conclusion: Planning as a Transferable Skill
The examples of Copilot assisting with winter planning demonstrate that effective planning follows consistent principles regardless of domain. The AI's ability to parse constraints, synthesize information, and generate structured recommendations shows promise for more complex business scenarios.
For cloud strategists, the lesson is twofold: First, AI tools like Copilot can assist with preliminary research and scenario planning for migrations, vendor selection, and cost optimization. Second, the prompt engineering techniques shown in these personal examples—clear context, specific constraints, defined deliverables—directly apply to business AI interactions.
The winter activities examples are essentially micro-versions of cloud migration planning: define requirements, set constraints, evaluate options, and select a path. As AI capabilities expand, the gap between personal planning and business strategy will continue to narrow, making these tools increasingly valuable for complex decision-making processes.


Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion