MIT engineers have developed bioresorbable pills containing radio frequency antennas that confirm ingestion, revolutionizing medication monitoring for chronic conditions.
The Adherence Challenge in Modern Medicine
Medication non-adherence contributes to hundreds of thousands of preventable deaths annually. For patients requiring strict treatment regimens—such as organ transplant recipients or those managing HIV/TB—missing doses can have catastrophic consequences. Traditional solutions struggle to provide real-time verification of medication ingestion.
Ingenious Engineering: How the Smart Pill Works
At the heart of MIT's breakthrough is a biodegradable capsule engineered with layered functionality:
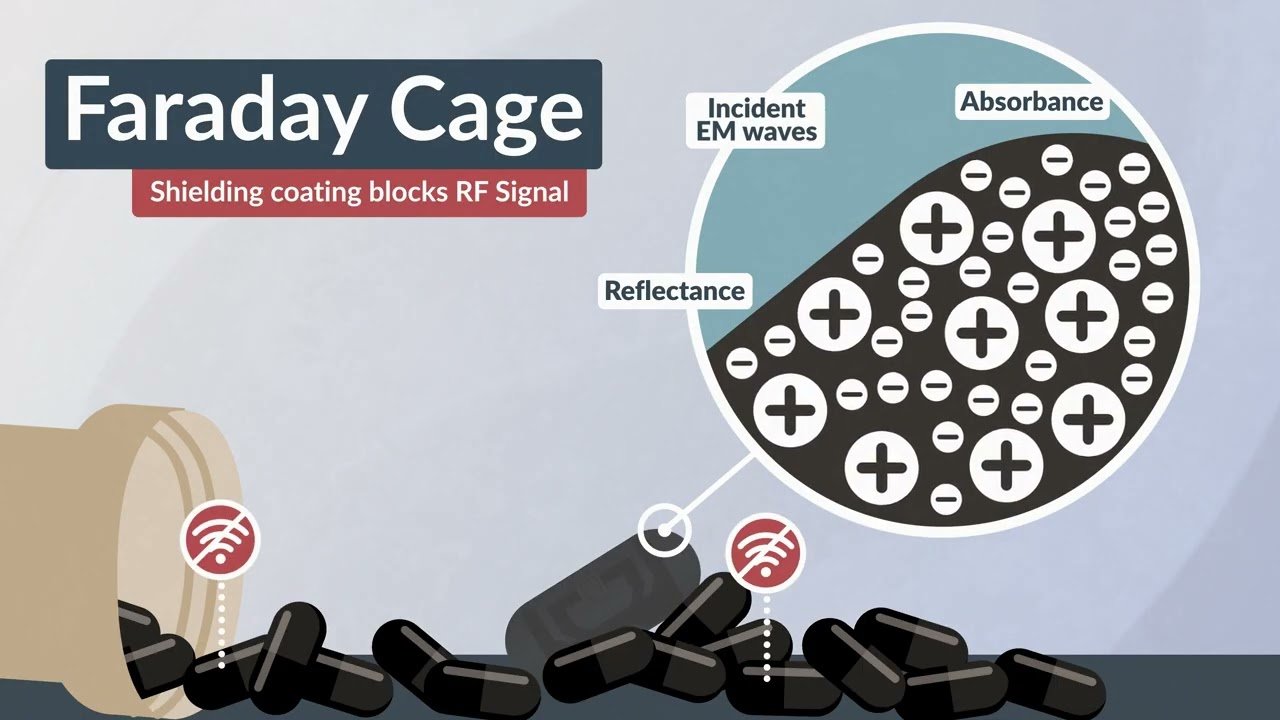
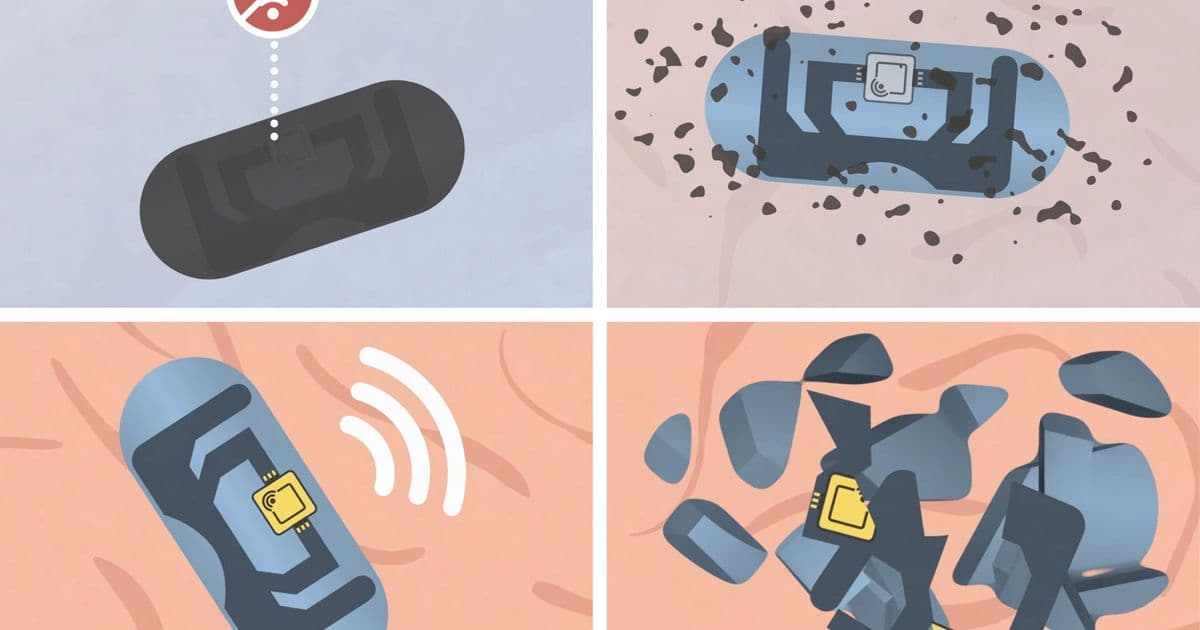
- Signal-Blocking Shell: A gelatin capsule coated with tungsten/molybdenum prevents RF transmission until ingestion
- Biodegradable Antenna: Zinc-cellulose antenna unrolls when stomach acid dissolves the coating
- RF Chip: Non-digestible microchip (400μm) transmits confirmation signal
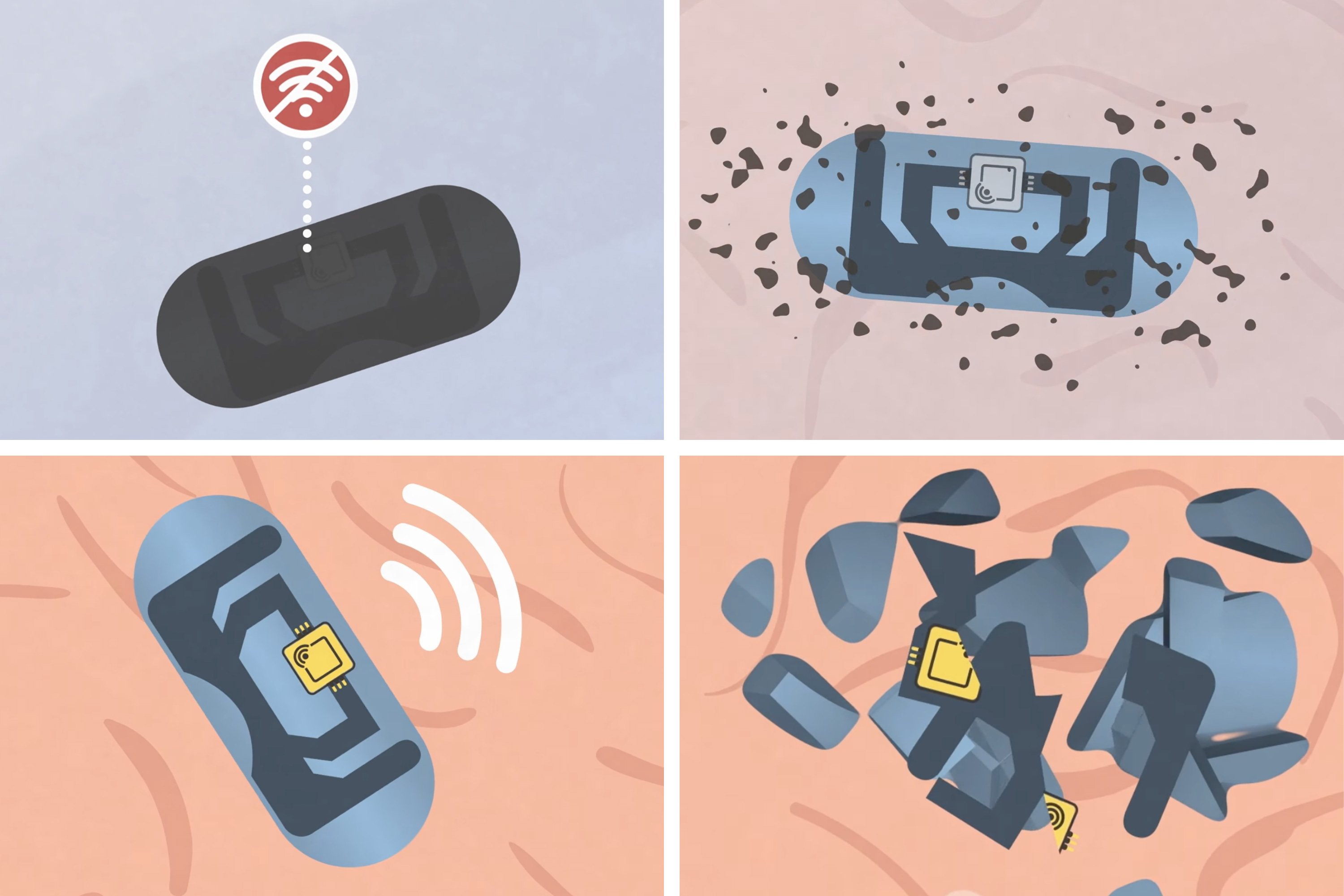
 Four-stage activation: Coating breakdown → Antenna deployment → RF transmission → Bioresorption
Four-stage activation: Coating breakdown → Antenna deployment → RF transmission → Bioresorption
Within 10 minutes of swallowing, the antenna responds to external RF signals (detectable within 2 feet), confirming ingestion. All components except the microchip dissolve within days using FDA-approved materials.
Technical Innovation Highlights
- Frequency Selection: Optimized RF band balances penetration depth and safety
- Material Science: Zinc-cellulose composite enables both conductivity and bioresorption
- Power Efficiency: Passive design requires no internal battery
- Safety Engineering: Minimal non-digestible components reduce GI obstruction risks
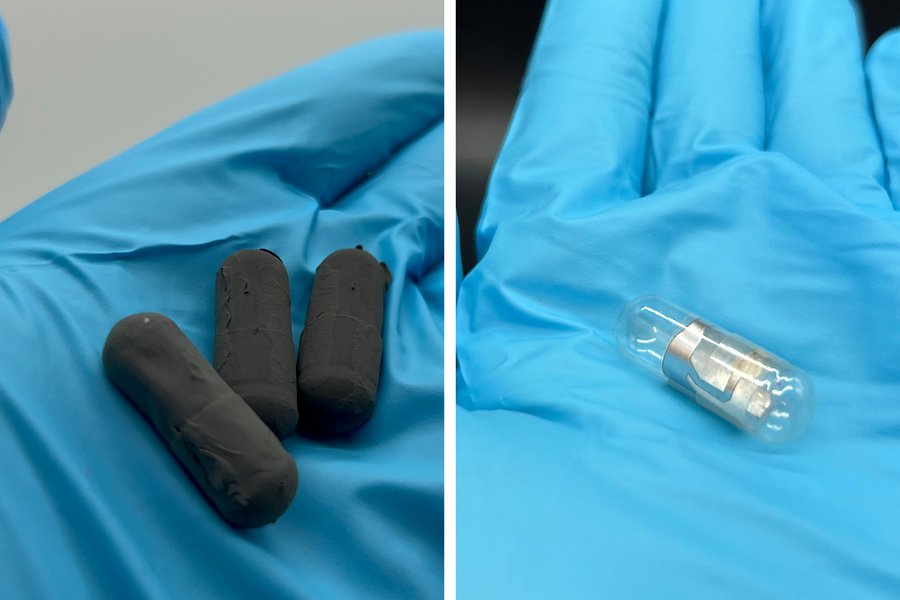 Prototype capsules showing coated (left) and activated (right) states
Prototype capsules showing coated (left) and activated (right) states
Clinical Applications and Future Development
This technology promises transformative impact for:
- Transplant patients requiring immunosuppressants
- TB/HIV antimicrobial therapy regimens
- Psychiatric medication management
- Post-stent anticoagulant treatment
Next steps involve human trials and integration with wearable receivers that automatically notify healthcare providers. "Our goal is to create a seamless feedback loop between patients and care teams," says Prof. Traverso.
 Video demonstration of the pill's activation sequence
Video demonstration of the pill's activation sequence
Robotic Integration Potential
While currently focused on adherence monitoring, this RF platform could evolve into an active drug-delivery system. Future iterations might incorporate:
- AI-powered dosage adjustment based on biometric feedback
- Swarm robotics for staggered drug release
- Biocompatible sensors for physiological monitoring
This innovation exemplifies how mechatronic engineering and biomedical AI converge to solve critical healthcare challenges, demonstrating MIT's leadership in translational bioengineering.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion