Modal reveals their comprehensive framework for managing GPU reliability across 20,000+ concurrent units, detailing provider selection, machine image optimization, and layered health monitoring strategies.
The Unseen Infrastructure Behind GPU Reliability
At the frontier of cloud computing, Modal operates a globally distributed GPU fleet exceeding 20,000 concurrent units, launching over four million cloud instances across AWS, GCP, Azure, and OCI. This scale exposes fundamental truths about GPU reliability that challenge conventional wisdom about cloud infrastructure. Rather than treating GPUs as commoditized resources, Modal's approach reveals how systematic testing, continuous monitoring, and provider-specific adaptations form an essential reliability stack for AI workloads.

Decoding Hyperscaler Differentiation
Provider selection transcends simple pricing comparisons. Modal's benchmarking uncovers significant reliability variations obscured by marketing claims:
- Cloud A demonstrates superior launch reliability (99.6% success rate) but suffers 50% slower H100 performance on Stable Diffusion workloads
- Cloud C experienced months of thermal issues with GPUs hitting 94°C, crippling FLOP/s performance by half
- Cloud D offers best price/performance but exhibits frequent hardware clock slowdowns and memory limitations
These findings necessitate provider-specific pricing adjustments based on Modal's modal-host-bench system, which quantifies performance deltas like the 67.5% torch_matmul speed advantage of SXM H100s over PCIe variants.
Machine Images as Reliability Foundation
Machine image consistency forms Modal's operational bedrock. Their globally standardized images feature:
- Uniform kernel and NVIDIA driver versions (580.95.05)
- Automated testing pipelines validating both host and container compatibility
- Continuous integration replacing error-prone manual updates
This approach reveals stark provider differentiation: Cloud C boots images in under 2 minutes while certain neoclouds require 5+ minutes. Crucially, Cloud D's 3-hour regional replication latency presents operational challenges absent in competitors.
Layered Health Monitoring Architecture
Modal employs a tiered checking strategy balancing thoroughness against operational overhead:
- Boot Checks: Lightweight validation avoiding deep diagnostics that delay failover
- Passive Monitoring: Continuous dmesg and
dcgmi healthtracking catching:- ECC errors
- Thermal violations (>88°C)
- Hardware slowdowns
- Active Diagnostics: Weekly exclusive-GPU tests including:
- DCGM diag level 2
- GPUBurn stress testing
- NCCL all-reduce for NVLink validation
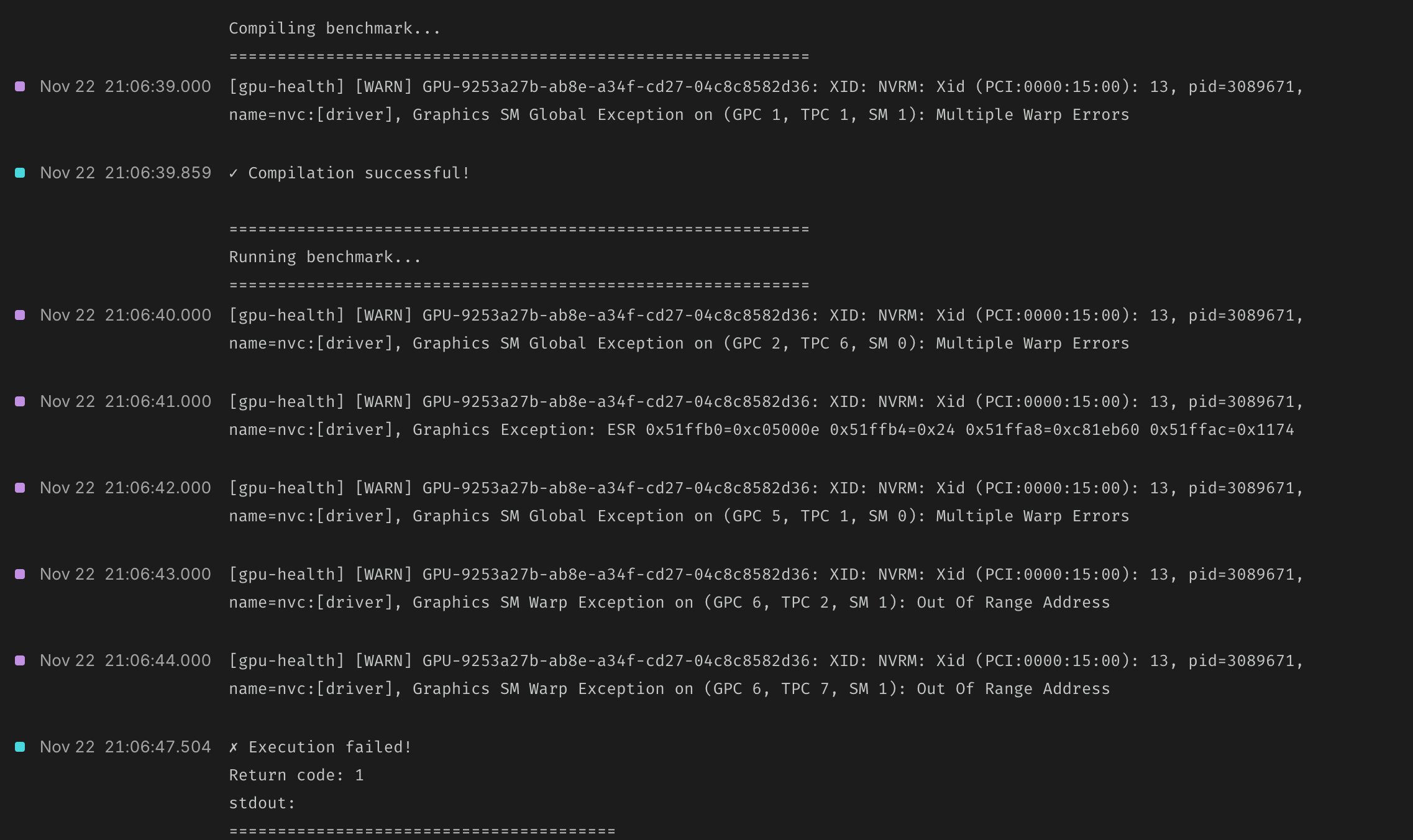
The system automatically quarantines failing nodes rather than attempting GPU-level recovery—a pragmatic choice given cloud instance ephemerality.
Observability and Support Realities
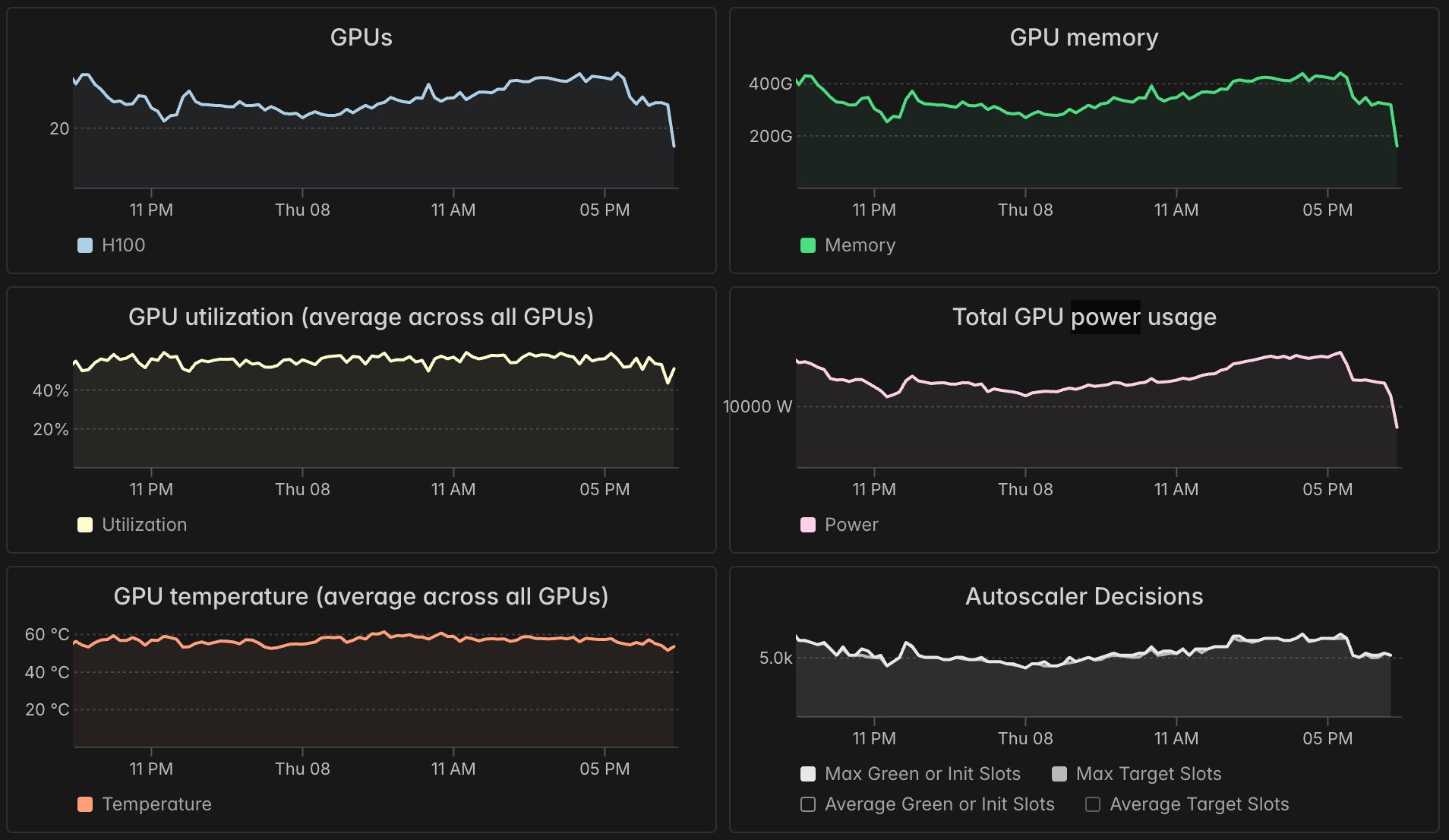
Modal surfaces GPU health through container-level metrics (memory, utilization, temperature, power) supplemented by detailed error logging. Their Xid/sXid error dictionary provides unprecedented diagnostic transparency. Yet limitations persist: aggregated metrics struggle to pinpoint single faulty GPUs in multi-GPU hosts.
Support infrastructure handles inevitable edge cases:
- Enterprise customers receive Slack-integrated support with Pylon tracking
- Automatic GPU replacement leverages Modal's autoscaling architecture
- Credits compensate for undetected failures
The Reliability Gap in AI Infrastructure
Meta's LLaMA 3 training revelation puts GPU reliability in stark perspective: 58.7% of unexpected issues stemmed from GPUs, compared to just 0.5% from CPUs. This orders-of-magnitude reliability gap explains why Modal's investment in GPU-specific systems isn't optimization—it's fundamental to production AI. As hardware evolves toward CPU-like stability, these practices represent today's necessary bridge.
Modal's open sharing of their reliability stack offers more than technical insights; it underscores that hyperscale GPU operations require specialized infrastructure beyond what any single cloud provider delivers. The future of AI infrastructure belongs to those who treat GPU reliability not as a given, but as a continuous engineering discipline.
Image credits: Modal

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion