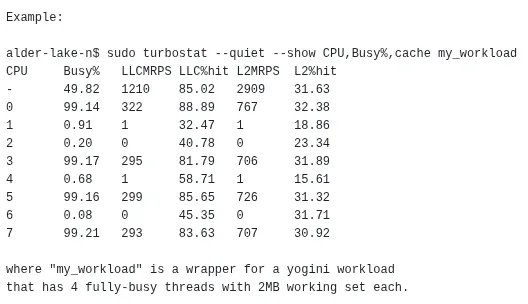
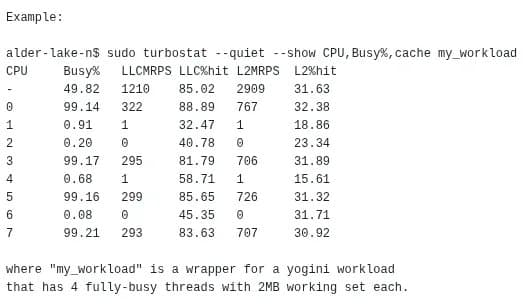
The Turbostat utility in Linux 7.0 now reports L2 cache statistics including M-References Per Second and hit rate percentage for recent Intel processors.
The Linux 7.0 kernel merge window has introduced a significant enhancement to the Turbostat utility, adding new L2 cache statistics reporting capabilities for recent Intel processors. This update brings valuable performance metrics that were previously unavailable through this popular command-line tool.
New L2 Cache Metrics
The updated Turbostat now reports two key L2 cache statistics:
- L2MRPS: L2 Cache M-References Per Second
- L2%hit: L2 cache hit rate percentage
These metrics provide deeper insight into cache behavior and memory access patterns, allowing system administrators and performance engineers to better understand how effectively the processor's L2 cache is being utilized.
Supported Processors
The new L2 cache reporting functionality is available for recent Intel processor generations that support the necessary performance counters. Specifically, this includes:
- Intel Xeon Sapphire Rapids and newer
- Intel Atom Gracemont and newer
- Intel Alder Lake and newer hybrid CPUs
This coverage spans both high-performance server/workstation CPUs and more recent consumer processor architectures, making the new metrics relevant to a wide range of use cases.
Implementation Details
The changes are implemented within the kernel source tree, where Turbostat resides. The new functionality leverages Intel's L2 performance counters, which explains the hardware generation limitations. The merge commit contains all technical details for those interested in the implementation specifics.
Practical Applications
These new metrics can be particularly valuable for:
- Performance tuning: Understanding cache hit rates helps optimize memory access patterns
- System monitoring: Tracking L2MRPS provides insight into memory subsystem load
- Bottleneck identification: Low hit rates may indicate memory access issues requiring attention
- Comparative analysis: Evaluating different processor generations or configurations
Usage
The new statistics are automatically included when running Turbostat on supported hardware with Linux 7.0 or later. Users can continue to use Turbostat as before, with the additional L2 metrics appearing alongside the existing frequency and idle statistics.
This enhancement demonstrates the ongoing evolution of Linux's performance monitoring tools, providing users with increasingly granular visibility into processor behavior. For those working with Intel systems in performance-critical environments, these new metrics offer another valuable data point for system optimization and troubleshooting.

Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion