Xiaomi has released Xiaomi-Robotics-0, a 4.7B-parameter Vision-Language-Action model that achieves 30Hz real-time control on RTX 4090 GPUs, outperforming 30+ state-of-the-art models in simulation and demonstrating practical capabilities in real-world dual-arm robot tasks.
Xiaomi has open-sourced Xiaomi-Robotics-0, a 4.7-billion-parameter embodied Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model that achieves remarkably low inference latency while maintaining high performance across both simulation and real-world robotics tasks. The model, announced by founder Lei Jun on February 12, 2026, is now available on GitHub and Hugging Face with complete code, model weights, and technical documentation.
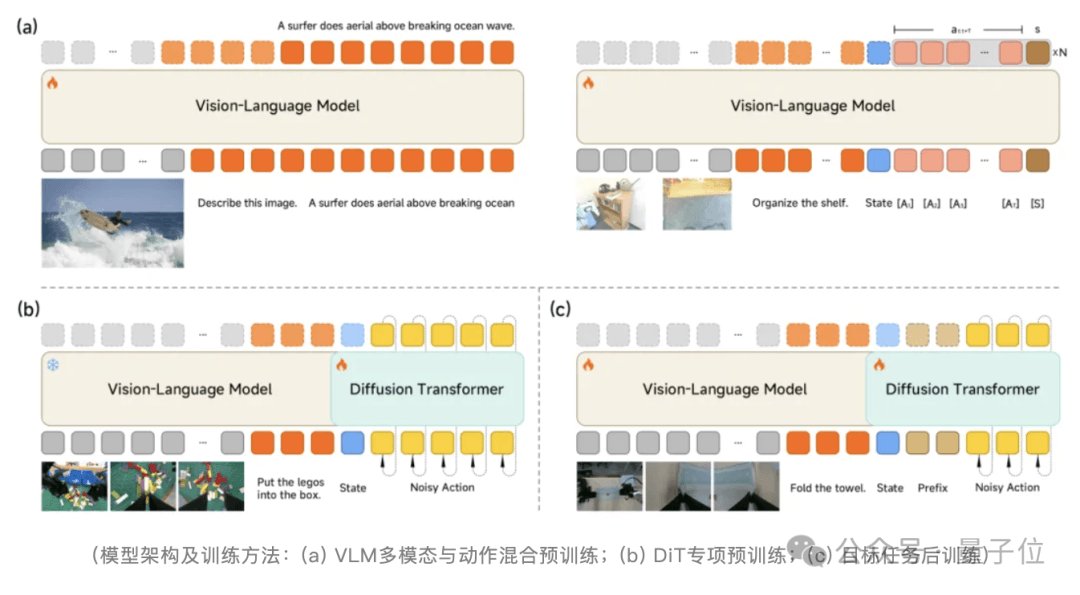
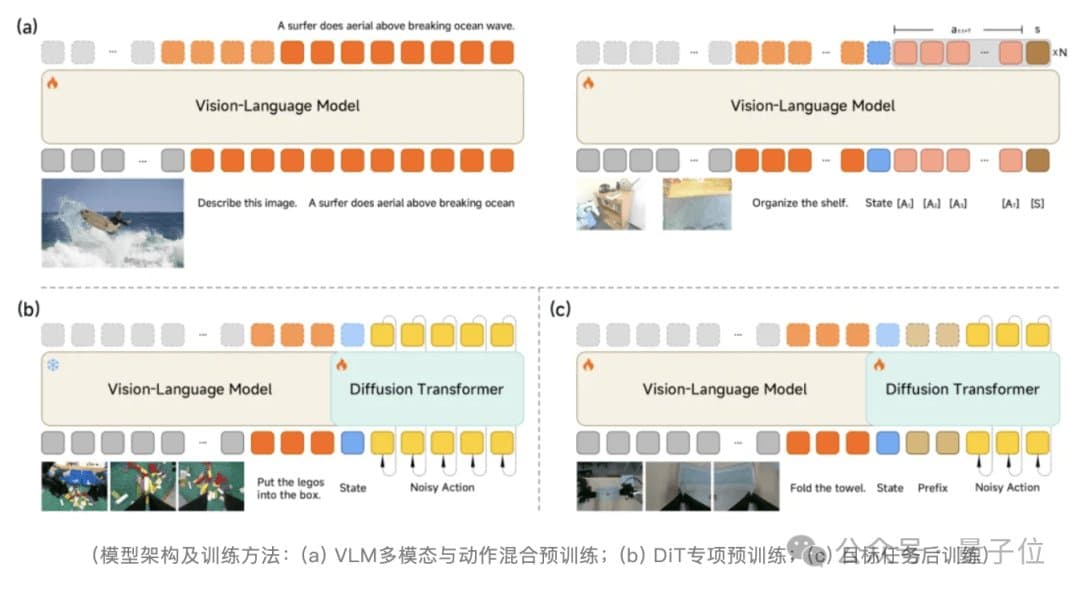
Architecture: Decoupling Perception from Action
The model's architecture centers on a Mixture-of-Transformers approach that separates the Vision-Language Model (VLM) from a 16-layer Diffusion Transformer (DiT). This architectural choice is significant because it allows the system to handle different computational requirements for perception versus action generation.
The VLM component focuses on instruction comprehension and spatial reasoning—essentially the "brain" that understands what needs to be done. Meanwhile, the DiT serves as the "motor cortex," generating high-frequency continuous motion sequences through flow matching techniques. This separation enables the system to optimize each component for its specific task rather than forcing a single architecture to handle both perception and action generation.
Performance Breakthroughs
Xiaomi-Robotics-0 achieves 80 milliseconds inference latency with 30Hz real-time control capability, running on consumer-grade hardware—specifically an NVIDIA RTX 4090 GPU. This performance level is particularly noteworthy because it demonstrates that sophisticated embodied AI can operate within the timing constraints required for real-world robotics without requiring specialized or expensive hardware.
The model's training follows a two-stage pre-training approach. First, an Action Proposal mechanism forces the VLM to jointly predict multimodal action distributions during visual understanding, aligning feature and action spaces. Then, while the VLM is frozen, the DiT is trained to generate precise motion sequences. Post-training introduces asynchronous inference and a Λ-shaped attention masking strategy, which decouples inference from execution timing while prioritizing current visual feedback.
Benchmark Dominance
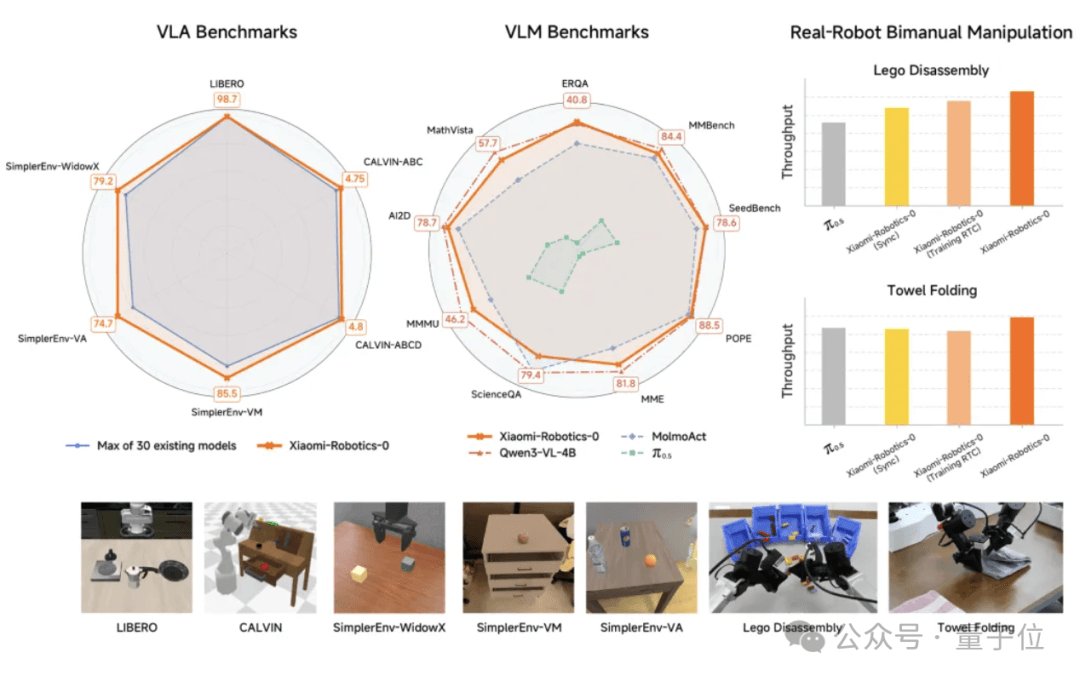
In simulation testing, Xiaomi-Robotics-0 outperformed more than 30 benchmark models—including established approaches like π0, OpenVLA, RT-1, and RT-2—across multiple datasets including LIBERO, CALVIN, and SimplerEnv. The model achieved multiple new state-of-the-art results, with particularly impressive performance on the Libero-Object task where it reached a perfect 100% success rate.
Real-World Capabilities
Beyond simulation, the model has demonstrated practical capabilities in real-world deployment. A dual-arm robot powered by Xiaomi-Robotics-0 showed stable hand-eye coordination in long-horizon, high-degrees-of-freedom tasks such as block disassembly and towel folding. Crucially, the system retained object detection and visual question-answering capabilities while performing these complex manipulation tasks, demonstrating that the model can handle both high-level reasoning and low-level control simultaneously.
Technical Significance
The open-sourcing of Xiaomi-Robotics-0 represents a meaningful contribution to the embodied AI community. By releasing not just the model weights but complete code and documentation, Xiaomi enables researchers and developers worldwide to build upon this work. The model's ability to run on consumer hardware while achieving state-of-the-art performance addresses one of the key challenges in robotics: making advanced AI capabilities accessible without requiring specialized infrastructure.
The 4.7B parameter size strikes a balance between capability and efficiency, being large enough to capture complex behaviors while remaining practical for deployment. The 80ms latency is particularly important because it falls within the timing constraints that make robots feel responsive and safe to interact with in human environments.
Implications for Robotics Development
This release could accelerate progress in several areas of robotics. The model's demonstrated ability to handle both high-level instruction following and precise low-level control suggests it could serve as a foundation for more general-purpose robots. The open-source nature means the research community can iterate on and improve the architecture, potentially leading to even better performance and efficiency.
The success on tasks like block disassembly and towel folding—which require both planning and fine motor control—indicates the model could be applicable to a wide range of household and industrial robotics applications. The retention of visual question-answering capabilities while performing manipulation tasks also suggests potential for more interactive and adaptable robotic systems.
Xiaomi's approach of combining architectural innovation with practical performance targets represents a model for how embodied AI research can progress: focusing not just on achieving the best possible results in controlled environments, but on creating systems that can actually operate in the real world with reasonable computational resources.
Comments
Please log in or register to join the discussion